SCHEME OF WORK
WEEK TOPIC
1 Computer Appreciation (Practical session)
2 Technology of Different Information Ages:
(a) Different Information Ages and their tools:
(i) Stone Age (ii) Iron Age (Hoe and Cutlass) (iii) Middle Age (Feather, Pen and Ink)
3. (b) Different Information Ages and their tools:
(iv) Industrial Age (Machine) (v) Electronic Age (Computer and Internet age)
4 Data and Information:
(a) Meaning, Sources and Examples of
(i) Data – Types of Data; Classification of Data Information;
(ii) Information; Forms of Information, Advantages and Disadvantages of Oral Information; Advantages and Disadvantages of Written Information
5. Data and Information:
(b) Qualities of Good Information: (i) Accurate (ii) Meaningful
(iii) Comprehensive (iv) Relevant (v) Timely and (vi) Suitable
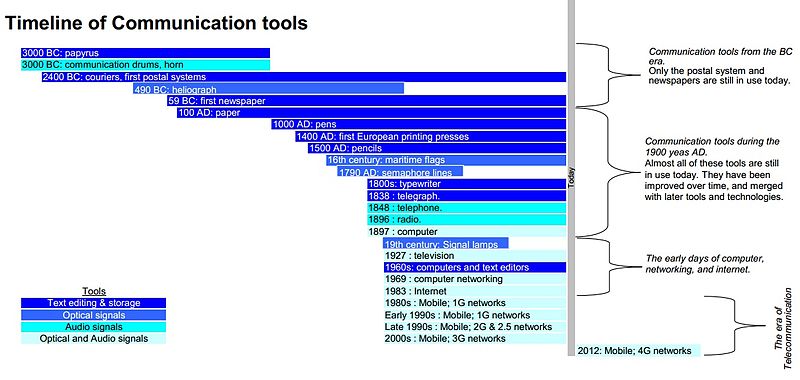
6. Information Transmission:
(a) Ancient methods of transmitting Information – Oral, beating of drums, fire lighting, town crying, whistling, drawing diagrams, making representation.
7. Information Transmission:
(b) Modern methods of transmitting Information – Prints, telephone, telex, radio, television, fax, satellite, Internet, GSM
8. Information Transmission:
(c) Classification of means of transmitting information – Electronic, Non-electronic (d) Modes of receiving information – audio, visual and audio-visual.
9. Revision
1ST TERM
WEEK 1
LESSON 1
Computer Appreciation (Practical session)
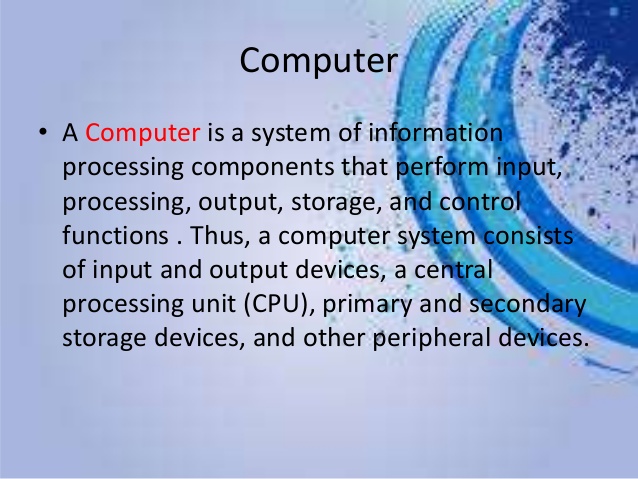

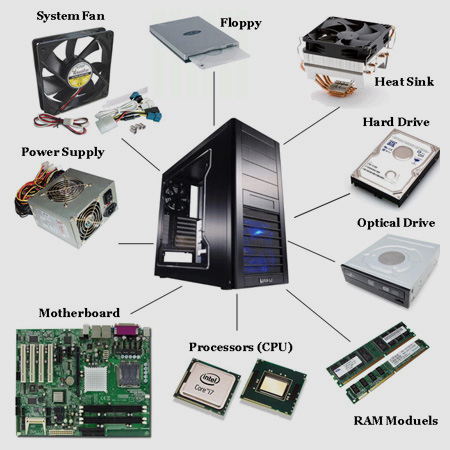
A computer has basic parts in common with other models.
1. Housing. A tower houses just the components that make the computer function. ...
2. Motherboard. The motherboard is also called the logic, system or base board. ...
3. Processor (CPU) THE CPU is the core of your computer. ...
4. Hard Drive. ...
5. Display Adapter. ...
6. RAM (Memory) ...
7. Optical Drive.

Evaluation
Computer Appreciation (Practical session)


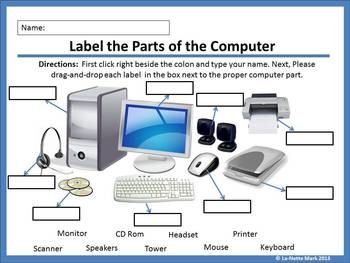
A computer has basic parts in common with other models.
1. Housing. A tower houses just the components that make the computer function. ...
2. Motherboard. The motherboard is also called the logic, system or base board. ...
3. Processor (CPU) THE CPU is the core of your computer. ...
4. Hard Drive. ...
5. Display Adapter. ...
6. RAM (Memory) ...
7. Optical Drive.


Evaluation

WEEK 2
LESSON 2
TOPIC: TECHNOLOGY OF DIFFERENT INFORMATION AGES
CONTENT
- Definition of Technology
- Definition of Information Age
- Technology of Different Information Ages and their tools
DEFINITION OF TERMS
Definition of Technology:
Technology can be defined as the specific methods, materials, materials, and devices used to solve practical problems.
Definition of Information Age:
The Information Age, also commonly known as the Computer Age or Information Era, refers to the present period in our society which will be characterized by the ability of individuals to transfer information freely, and to have instant access to knowledge that would have been difficult or impossible to find.
The age of Information Technology has indeed taken a lot of people by surprise. Our society has been divided even before the era of Information Technology (IT) even began. Society has always been divided into different groups based on different views.
The first group consist of those who have no access to IT. This group of people do not have the privilege of obtaining information in a quick and less troublesome manner. They would obtain their information through other means such as the media. The other group consist of those who grew up in the era of IT. The IT compliant generation have perfectly accustomed their lives to IT. Computers, mobile phones, Internet and various other electronic gadgets are part of our daily lives. It has become a necessity.
TECHNOLOGY OF DIFFERENT INFORMATION AGES AND THEIR TOOLS
CONTENT
1. Stone Age: This was a period when stone was used for making different kinds of tools. Technology was very primitive during this age. For example, clay was used for pottery while basalt and sandstone was used for making grinding stones.

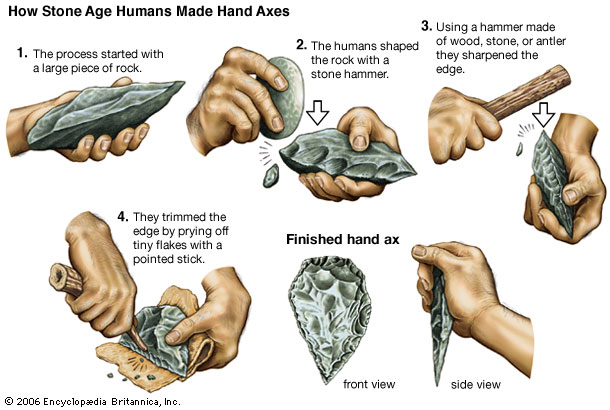
A variety of Stone Age tools

2. Iron Age: During the Iron Age, tools and weapons were made from iron. The earliest use of iron implements originated from Anatolia. The early man used iron to make farm tools such as cutlasses, hoes and axes for producing crops. Traps made from iron were used for hunting animals. Weapons for war were also made from iron.

3. Middle Age: The middle age lasted for about a millennium. The middle age is dated from the 5th century to the beginning of the 16th century. The middle age is also referred to as the Medieval Age. The Middle Age was a period when man started discovering better ways of improving his life. This period witnessed the development of writing and major progress in technology. During this period, the use of feathers and ink for writing was invented. The oldest evidence of writing by man was discovered in Mesopotamia at 3000 BC.

EVALUATION
1. Define the following terms:
(i) Technology (ii) Information Age
2. Mention the 5 information ages.
Reading Assignment
1. Many important inventions and achievements occurred during the Industrial Revolution. One example is given below. Can you think of others? Make your list below;
• The invention of Automobile (steam engine)
• .................................................................................
• .................................................................................
• .................................................................................
• .................................................................................
2. Read the following information ages:
i. Industrial Age ii. Electronic Age iii. The present age.
TOPIC: TECHNOLOGY OF DIFFERENT INFORMATION AGES
CONTENT
- Definition of Technology
- Definition of Information Age
- Technology of Different Information Ages and their tools
DEFINITION OF TERMS
Definition of Technology:
Technology can be defined as the specific methods, materials, materials, and devices used to solve practical problems.
Definition of Information Age:
The Information Age, also commonly known as the Computer Age or Information Era, refers to the present period in our society which will be characterized by the ability of individuals to transfer information freely, and to have instant access to knowledge that would have been difficult or impossible to find.
The age of Information Technology has indeed taken a lot of people by surprise. Our society has been divided even before the era of Information Technology (IT) even began. Society has always been divided into different groups based on different views.
The first group consist of those who have no access to IT. This group of people do not have the privilege of obtaining information in a quick and less troublesome manner. They would obtain their information through other means such as the media. The other group consist of those who grew up in the era of IT. The IT compliant generation have perfectly accustomed their lives to IT. Computers, mobile phones, Internet and various other electronic gadgets are part of our daily lives. It has become a necessity.

TECHNOLOGY OF DIFFERENT INFORMATION AGES AND THEIR TOOLS
CONTENT
1. Stone Age: This was a period when stone was used for making different kinds of tools. Technology was very primitive during this age. For example, clay was used for pottery while basalt and sandstone was used for making grinding stones.


A variety of Stone Age tools

2. Iron Age: During the Iron Age, tools and weapons were made from iron. The earliest use of iron implements originated from Anatolia. The early man used iron to make farm tools such as cutlasses, hoes and axes for producing crops. Traps made from iron were used for hunting animals. Weapons for war were also made from iron.

3. Middle Age: The middle age lasted for about a millennium. The middle age is dated from the 5th century to the beginning of the 16th century. The middle age is also referred to as the Medieval Age. The Middle Age was a period when man started discovering better ways of improving his life. This period witnessed the development of writing and major progress in technology. During this period, the use of feathers and ink for writing was invented. The oldest evidence of writing by man was discovered in Mesopotamia at 3000 BC.

EVALUATION
1. Define the following terms:
(i) Technology (ii) Information Age
2. Mention the 5 information ages.
Reading Assignment
1. Many important inventions and achievements occurred during the Industrial Revolution. One example is given below. Can you think of others? Make your list below;
• The invention of Automobile (steam engine)
• .................................................................................
• .................................................................................
• .................................................................................
• .................................................................................
2. Read the following information ages:
i. Industrial Age ii. Electronic Age iii. The present age.
WEEK 3
LESSON 3
TOPIC: TECHNOLOGY OF DIFFERENT INFORMATION AGES
CONTENT
- Industrial Age
- Electronic Age
Industrial Age:
This was the period of the Industrial revolution. It was a period between the late 18th century and early 19th century. During this period, there were changes in agriculture, transportation, production and manufacturing. The industrial revolution brought great effect in the socio-economic and cultural conditions of the world. The industrial revolution marked a major turning point in human society. The Industrial Age witnessed the invention of machines like Printing machines, Steam engine, Sewing machines, light bulb, Electronic telegraph and telephone to communicate.


Electronic Age:
This age brought about a great transformation in the mechanical way of processing data into information which is rapidly changing our world via the use of computer and other electronic devices. During the electronic age, electronic components and machines became very popular. Electronic calculator came into existence during this time. The major tools during this age are the Computer and Internet. The Electronic Age has increased our standard of living and also improves the quality of our lives.

EVALUATION
(i) State TWO advantages of the Electronic age over the Industrial Age
(i) Mention at least ONE tool produced during each information Age?
ASSIGNMENT
Choose from the alternatives lettered A – E the correct answer to fill the blanks.
1. How many stages in human development have we had so far?
(a) 3 (b) 4 (c) 5 (d) 6 (e) 7
2. In which one of the following was widespread use of rock tools?
(a) Industrial Age (b) Electronic Age (c) Iron Age (d) Stone Age (e) None of the above
3. Which of the following is not in this group?
(a) Iron Passenger Ships (b) Rail System (c) Iron Bridges (d) Factories (e) None of the above
4. What would you call the period in which violence, crime, war, etc increased across the world?
(a) Iron Age (b) Middle Age (c) Stone Age (d) Industrial Age (e) None of the above
5. Which of the following was invented during the Electronic Age?
(a) Factory (b) Computer (c) Writing (d) Electricity (e) All of the above
6. The greatest changes the world has witnessed occurred during the Electronic Age. True / False
7. The current age is known as the Electronic Age. True / False
8. Stone Age farming was done by the use of machines. True / False
9. The Iron Age refers to the period in which writing was discovered. True / False
10. The first factories ever built were built in France. True / False
Reading Assignment
(i) Data (ii) Information
TOPIC: TECHNOLOGY OF DIFFERENT INFORMATION AGES
CONTENT
- Industrial Age
- Electronic Age
Industrial Age:
This was the period of the Industrial revolution. It was a period between the late 18th century and early 19th century. During this period, there were changes in agriculture, transportation, production and manufacturing. The industrial revolution brought great effect in the socio-economic and cultural conditions of the world. The industrial revolution marked a major turning point in human society. The Industrial Age witnessed the invention of machines like Printing machines, Steam engine, Sewing machines, light bulb, Electronic telegraph and telephone to communicate.


Electronic Age:
This age brought about a great transformation in the mechanical way of processing data into information which is rapidly changing our world via the use of computer and other electronic devices. During the electronic age, electronic components and machines became very popular. Electronic calculator came into existence during this time. The major tools during this age are the Computer and Internet. The Electronic Age has increased our standard of living and also improves the quality of our lives.


EVALUATION
(i) State TWO advantages of the Electronic age over the Industrial Age
(i) Mention at least ONE tool produced during each information Age?
ASSIGNMENT
Choose from the alternatives lettered A – E the correct answer to fill the blanks.
1. How many stages in human development have we had so far?
(a) 3 (b) 4 (c) 5 (d) 6 (e) 7
2. In which one of the following was widespread use of rock tools?
(a) Industrial Age (b) Electronic Age (c) Iron Age (d) Stone Age (e) None of the above
3. Which of the following is not in this group?
(a) Iron Passenger Ships (b) Rail System (c) Iron Bridges (d) Factories (e) None of the above
4. What would you call the period in which violence, crime, war, etc increased across the world?
(a) Iron Age (b) Middle Age (c) Stone Age (d) Industrial Age (e) None of the above
5. Which of the following was invented during the Electronic Age?
(a) Factory (b) Computer (c) Writing (d) Electricity (e) All of the above
6. The greatest changes the world has witnessed occurred during the Electronic Age. True / False
7. The current age is known as the Electronic Age. True / False
8. Stone Age farming was done by the use of machines. True / False
9. The Iron Age refers to the period in which writing was discovered. True / False
10. The first factories ever built were built in France. True / False
Reading Assignment
(i) Data (ii) Information
WEEK 4
LESSON 4
TOPIC: DATA AND INFORMATION
CONTENT
- Meaning, Sources and Examples of Data
- Types of Data
- Classification of Data and Information
- Meaning of Information
- Forms of Information
- Advantages and disadvantages of Oral Information
- Advantages and disadvantages of Written information
Meaning, Sources and Examples of Data
Data are raw facts and figures about an event or activity, somebody, something or some place. Data can also be defined as unprocessed information. Data can exist in a variety of forms -- as numbers or text on pieces of paper, as bits and bytes stored in electronic memory, or as facts stored in a person's mind. Data is the plural of datum, a single piece of information.
Sources of Data:
There are two major sources / methods of data collection, these includes;
• Primary Data
• Secondary Data
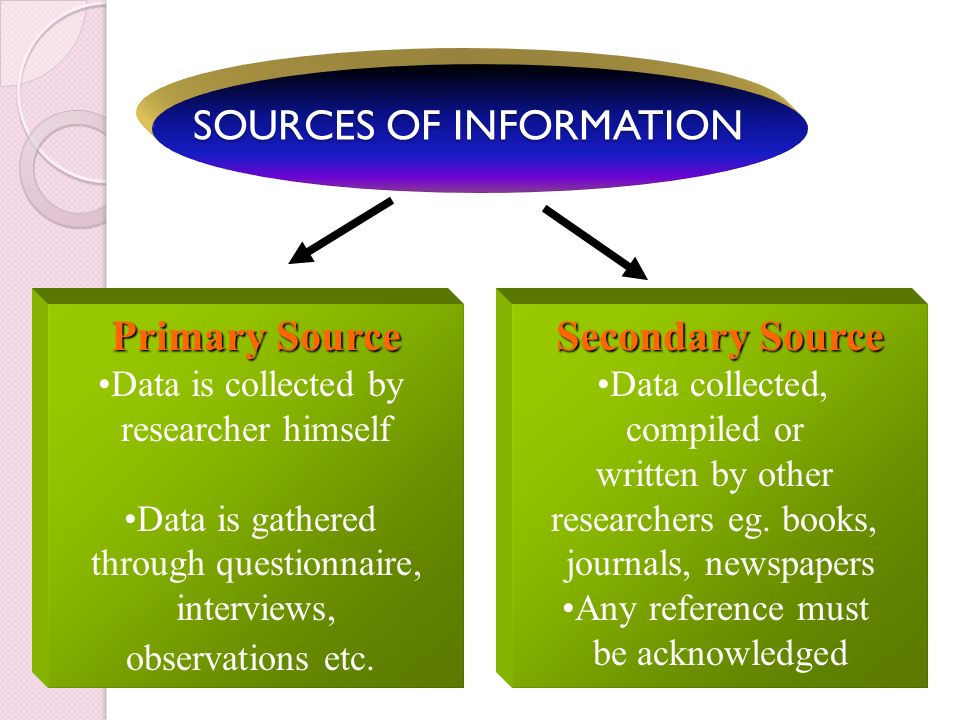
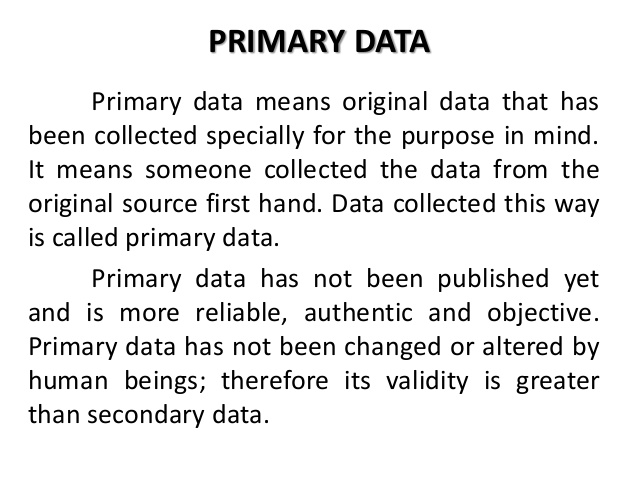
Primary Data: This is the direct collection of facts and figures about someone or an event by the Investigator or Researcher. Some means of primary data includes direct observation, interview, experiment and the use of questionnaire.
This method enables the investigator to collect exact information in greater details.
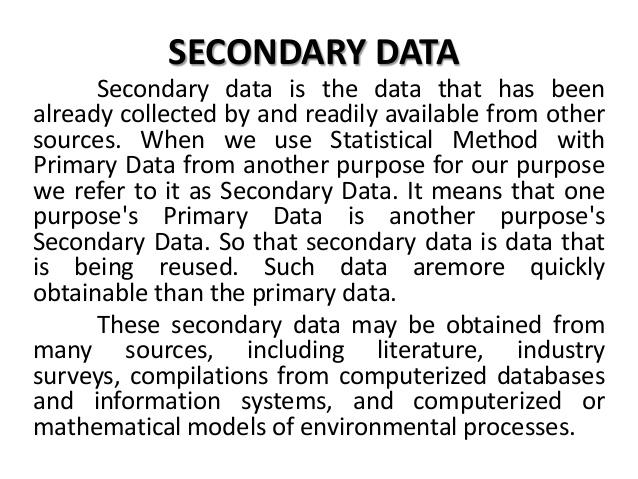
Secondary Data: This is data collected by someone other than the user. Common sources of secondary data include censuses, surveys, organizational records and data collected through qualitative methodologies or qualitative research.
Such data are cheaper and more quickly obtainable than the primary data and also may be available when primary data cannot be obtained at all.
For example when you fill out a form it is considered raw material or unprocessed facts (data) it is then used to maintain a record and create information.
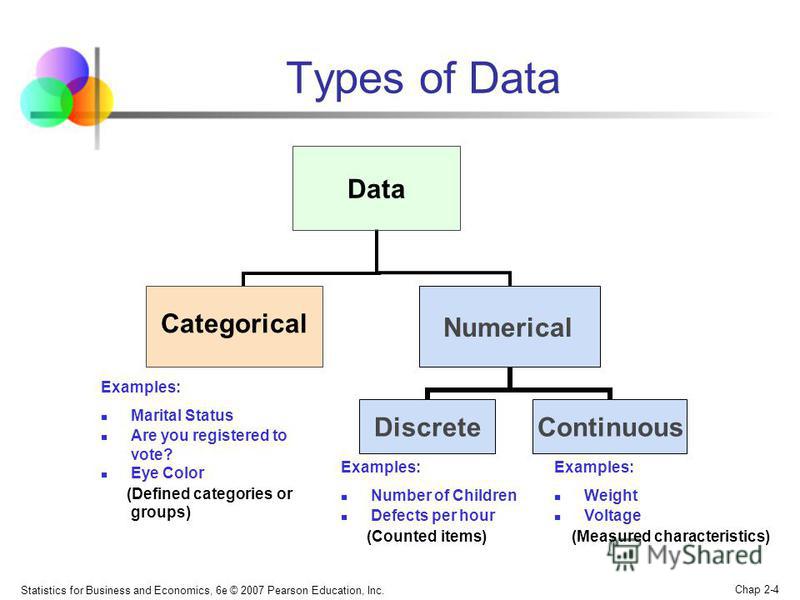
Types of Data
(i) Numeric data: These refer to figures or numbers. For example, students’ age
(ii) Alphabetic data: These types of data consist of letters, A-Z. Examples includes names (Kingsley, Deeper Life High School, Lagos,etc.)
(iii) Alpha-numeric data: These are combinations of numbers and alphabets (or labels). For example, schools’ address: Km 42, Abuja-Lokoja express way, car plate number: GK 324 ABJ
(iv) Audio data: These are voice data usually sent into the computer through the microphone.
(v) Graphic data: These are also referred to as visual data or video data which includes pictures, images, diagrams, etc
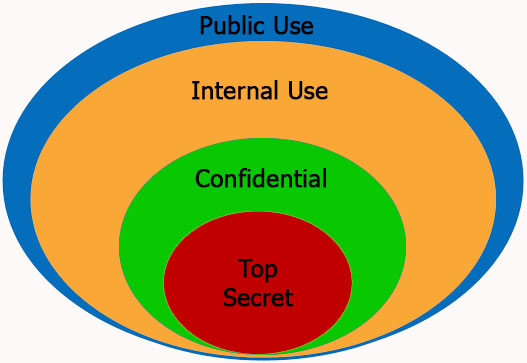
Classification of Data / Information
Data / Information classification is the categorization of data/information for its most effective and efficient use. Data can be classified according to its critical value or how often it needs to be accessed, with the most critical or often-used data stored on the fastest media while other data can be stored on slower (and less expensive) media.
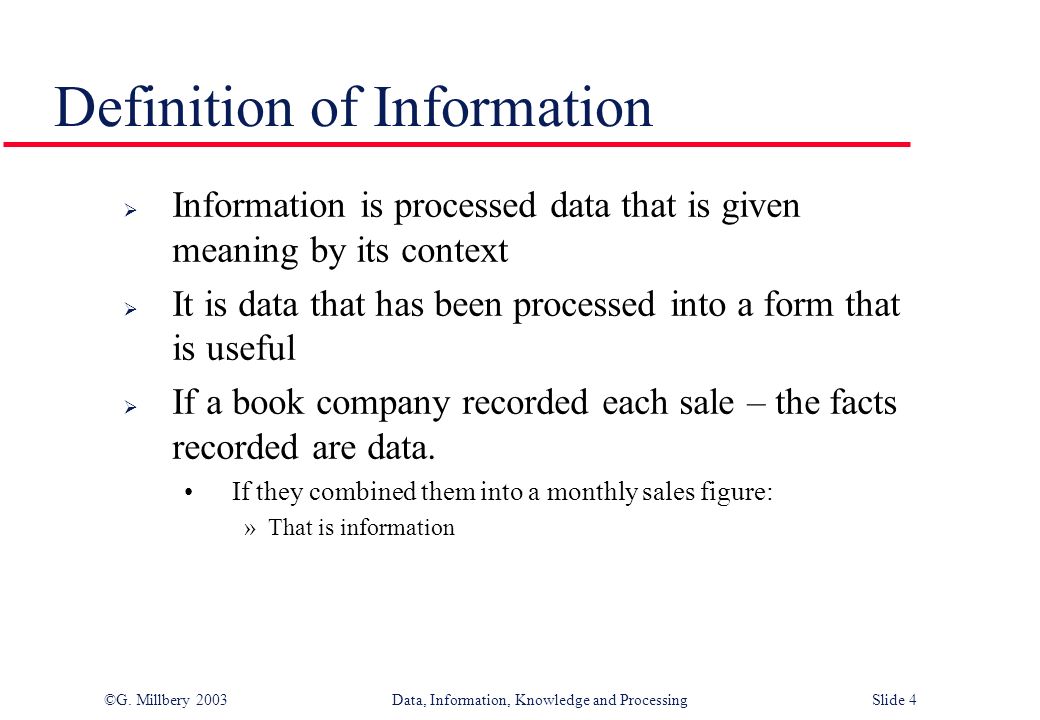
Meaning of Information
Information can defined as processed data, i.e. data that has been verified to be accurate and timely, it is also specific and organized for a purpose, presented within a context that gives it meaning and relevance, and can lead to an increase in understanding and decrease in uncertainty.
A piece of information is considered valueless if, after receiving it, things remain unchanged.
Forms of Information
Oral information: This type of information is passed or received verbally
Written Information: This is a form of information passed through words, pictures and illustrations
Visual information: Information presented in graphical or pictorial form
Sensory Information: Information sent through sense organs like facial expression, body language
Historic Information: These are facts known about a person, organization, city or country. It could be written or unwritten.


Advantages of Oral Information
(i) Effectiveness and Efficiency
(ii) They are fast
(iii) Cost
(iv) Flexibility
Disadvantages of Oral Information
(i) Denial
(ii) Volatile / Temporary in nature
(iii) Incoherence
(iv) less authentic
(v) requires maximum attention
Advantages of Written Information
(i) Permanent in nature
(ii) Dependable
(iii) High degree of Clarity
(iv) It can be used for reference purpose
Disadvantages of Written Information
(i) It could be misinterpreted
(ii) Problem of Illiteracy
(iii) It lacks immediate feedback
(iv) People may not always read them
EVALUATION
(i) State the difference between Data and Information
(ii) Mention and Explain FOUR types of data known to you
ASSIGNMENT
1. The disadvantages of oral information are the following except: (a) Denial
(b) Volatile in nature (c) Incoherence (d) Cost
2. _____ is defined as processed data. (a) Data (b) Information (c) People (d) Disk
3. ____ is Information presented in graphical or pictorial form. (a) Oral (b) written
(c) visual (d) sensory
4. Data collected by someone other than the user is called __ (a) Primary data
(b) secondary data (c) informal data (d) pictorial data
5. The data that consist of letters, A-Z is called. (b) Numeric data (b) Alphabetic data
(c) Audio data (d) graphic data
Reading Assignment
Read about the Qualities of good information.
TOPIC: DATA AND INFORMATION
CONTENT
- Meaning, Sources and Examples of Data
- Types of Data
- Classification of Data and Information
- Meaning of Information
- Forms of Information
- Advantages and disadvantages of Oral Information
- Advantages and disadvantages of Written information
Meaning, Sources and Examples of Data
Data are raw facts and figures about an event or activity, somebody, something or some place. Data can also be defined as unprocessed information. Data can exist in a variety of forms -- as numbers or text on pieces of paper, as bits and bytes stored in electronic memory, or as facts stored in a person's mind. Data is the plural of datum, a single piece of information.
Sources of Data:
There are two major sources / methods of data collection, these includes;
• Primary Data
• Secondary Data

Primary Data: This is the direct collection of facts and figures about someone or an event by the Investigator or Researcher. Some means of primary data includes direct observation, interview, experiment and the use of questionnaire.
This method enables the investigator to collect exact information in greater details.

Secondary Data: This is data collected by someone other than the user. Common sources of secondary data include censuses, surveys, organizational records and data collected through qualitative methodologies or qualitative research.
Such data are cheaper and more quickly obtainable than the primary data and also may be available when primary data cannot be obtained at all.
For example when you fill out a form it is considered raw material or unprocessed facts (data) it is then used to maintain a record and create information.

Types of Data
(i) Numeric data: These refer to figures or numbers. For example, students’ age
(ii) Alphabetic data: These types of data consist of letters, A-Z. Examples includes names (Kingsley, Deeper Life High School, Lagos,etc.)
(iii) Alpha-numeric data: These are combinations of numbers and alphabets (or labels). For example, schools’ address: Km 42, Abuja-Lokoja express way, car plate number: GK 324 ABJ
(iv) Audio data: These are voice data usually sent into the computer through the microphone.
(v) Graphic data: These are also referred to as visual data or video data which includes pictures, images, diagrams, etc

Classification of Data / Information
Data / Information classification is the categorization of data/information for its most effective and efficient use. Data can be classified according to its critical value or how often it needs to be accessed, with the most critical or often-used data stored on the fastest media while other data can be stored on slower (and less expensive) media.

Meaning of Information
Information can defined as processed data, i.e. data that has been verified to be accurate and timely, it is also specific and organized for a purpose, presented within a context that gives it meaning and relevance, and can lead to an increase in understanding and decrease in uncertainty.
A piece of information is considered valueless if, after receiving it, things remain unchanged.

Forms of Information
Oral information: This type of information is passed or received verbally
Written Information: This is a form of information passed through words, pictures and illustrations
Visual information: Information presented in graphical or pictorial form
Sensory Information: Information sent through sense organs like facial expression, body language
Historic Information: These are facts known about a person, organization, city or country. It could be written or unwritten.


Advantages of Oral Information
(i) Effectiveness and Efficiency
(ii) They are fast
(iii) Cost
(iv) Flexibility
Disadvantages of Oral Information
(i) Denial
(ii) Volatile / Temporary in nature
(iii) Incoherence
(iv) less authentic
(v) requires maximum attention
Advantages of Written Information
(i) Permanent in nature
(ii) Dependable
(iii) High degree of Clarity
(iv) It can be used for reference purpose
Disadvantages of Written Information
(i) It could be misinterpreted
(ii) Problem of Illiteracy
(iii) It lacks immediate feedback
(iv) People may not always read them
EVALUATION
(i) State the difference between Data and Information
(ii) Mention and Explain FOUR types of data known to you
ASSIGNMENT
1. The disadvantages of oral information are the following except: (a) Denial
(b) Volatile in nature (c) Incoherence (d) Cost
2. _____ is defined as processed data. (a) Data (b) Information (c) People (d) Disk
3. ____ is Information presented in graphical or pictorial form. (a) Oral (b) written
(c) visual (d) sensory
4. Data collected by someone other than the user is called __ (a) Primary data
(b) secondary data (c) informal data (d) pictorial data
5. The data that consist of letters, A-Z is called. (b) Numeric data (b) Alphabetic data
(c) Audio data (d) graphic data
Reading Assignment
Read about the Qualities of good information.
WEEK 5
LESSON 5
TOPIC: DATA AND INFORMATION
CONTENT: - Qualities of good Information
Qualities of good Information
(i) Relevance: it should be related to the issue under consideration
(ii) Reliability: It must be dependable, unfailing as the user of the information must have confidence in it
(iii) Accuracy: Information should be correct and free from every error
(iv) Availability: It must be available and communicated to the users as at when it is needed.
(v) Suitability: It should be right for the purpose or occasion in which it is being made
(vi) Meaningful: It should be expressed in a language and way that the receiver will understand
(vii) Comprehensive: Good information must be full, complete and easy to understand
(viii) Economical: It must not be too costly so that the user can afford it
(ix) Specific and concise

EVALUATION
List SEVEN qualities of good information
Choose from the alternatives lettered A – E the correct answer to fill the blanks.
1. Data can be any of the following EXCEPT
(a) Speed of runners in a race (b) Population figures of a school (c)Radio news
(d) Figures from calculations. (e) none of the above
2. Data which has been processed is referred to as
(a) Instructions (b) Facts (c) Information (d) Transaction (e) Details
3. Which one of the following is not information?
(a) A Biography (short story) of a person (b) Road Signs (c) Results from computer processing (d) Job Vacancy Advertisement (e) None of the above
READING ASSIGNMENT
(i) Define Information Transmission
(ii) Mention two methods of transmitting information
TOPIC: DATA AND INFORMATION
CONTENT: - Qualities of good Information
Qualities of good Information
(i) Relevance: it should be related to the issue under consideration
(ii) Reliability: It must be dependable, unfailing as the user of the information must have confidence in it
(iii) Accuracy: Information should be correct and free from every error
(iv) Availability: It must be available and communicated to the users as at when it is needed.
(v) Suitability: It should be right for the purpose or occasion in which it is being made
(vi) Meaningful: It should be expressed in a language and way that the receiver will understand
(vii) Comprehensive: Good information must be full, complete and easy to understand
(viii) Economical: It must not be too costly so that the user can afford it
(ix) Specific and concise

EVALUATION
List SEVEN qualities of good information
Choose from the alternatives lettered A – E the correct answer to fill the blanks.
1. Data can be any of the following EXCEPT
(a) Speed of runners in a race (b) Population figures of a school (c)Radio news
(d) Figures from calculations. (e) none of the above
2. Data which has been processed is referred to as
(a) Instructions (b) Facts (c) Information (d) Transaction (e) Details
3. Which one of the following is not information?
(a) A Biography (short story) of a person (b) Road Signs (c) Results from computer processing (d) Job Vacancy Advertisement (e) None of the above
READING ASSIGNMENT
(i) Define Information Transmission
(ii) Mention two methods of transmitting information
WEEK 6
LESSON 6
TOPIC: INFORMATION TRANSMISSION
CONTENT
- Definition of Information Transmission
- Methods of transmitting information
Definition of Information Transmission
INFORMATION TRANSMISSION
Information transmission is the passing on or publishing of information to someone or a group of people in order to get the right responses. Some information when passed on or given requires a feedback while some do not require feedback. For example, information that the principal wants to meet with all JSS 1 students by 12 noon will make the students to go to his office. However, information that reminds students to be in their classes after break period does not mean that the students should go to the principal’s office.
There are two methods of transmitting information. They are:
1. Ancient methods
2. Modern methods
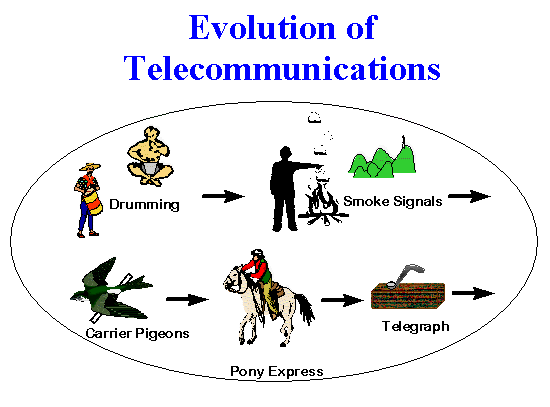
ANCIENT METHODS OF TRANSMITTING INFORMATION
Ancient methods include the following:
i. Oral method
ii. Drum beating
iii. Fire lighting
iv. Town crying
v. Whistling
vi. Drawing diagrams
vii. Making representation
Although these are ancient methods, some communities still use some of them to transmit information. The reason may be because there are no other means or because they are cheaper to use.
EVALUATION
1. What is information transmission?
2. List the two methods of information transmission
3. Mention five ancient methods of transmitting information
ASSIGNMENT
What is the difference between Ancient method and Modern method of transmitting information?
TOPIC: INFORMATION TRANSMISSION
CONTENT
- Definition of Information Transmission
- Methods of transmitting information
Definition of Information Transmission
INFORMATION TRANSMISSION
Information transmission is the passing on or publishing of information to someone or a group of people in order to get the right responses. Some information when passed on or given requires a feedback while some do not require feedback. For example, information that the principal wants to meet with all JSS 1 students by 12 noon will make the students to go to his office. However, information that reminds students to be in their classes after break period does not mean that the students should go to the principal’s office.
There are two methods of transmitting information. They are:
1. Ancient methods
2. Modern methods

ANCIENT METHODS OF TRANSMITTING INFORMATION
Ancient methods include the following:
i. Oral method
ii. Drum beating
iii. Fire lighting
iv. Town crying
v. Whistling
vi. Drawing diagrams
vii. Making representation
Although these are ancient methods, some communities still use some of them to transmit information. The reason may be because there are no other means or because they are cheaper to use.

EVALUATION
1. What is information transmission?
2. List the two methods of information transmission
3. Mention five ancient methods of transmitting information
ASSIGNMENT
What is the difference between Ancient method and Modern method of transmitting information?
WEEK 7
LESSON 7
TOPIC: INFORMATION TRANSMISSION
MODERN METHODS OF TRANSMITTING INFORMATION
With modern inventions in communication, many ancient methods have been replaced with more efficient modern ways of transmitting information. These include the following. Writing, Printing, Telephone, Telex, Facsimile (Fax), Radio, Television, Satellite, Internet and Global Systems for Mobile communication (GSM),
(i) Writing: Information can be transmitted by wiring; this is done either by hand or by using machines such as typewriters or computers.
(ii) Printing: Information transmission by printing involves the production of information on paper using typewriter or others printing device/machine.
(iii) Telephone: Telephones allow people voices to be transmitted over a short or long distance, either by cables or by waves.
(iv) Telex: A telex machine is sued to transmit information that are textual in natural from one person to another usually over a long distance
(v) Facsimile (Fax): This is a telecommunication device that transmits documents or pictures as electronic signals over the telephone system. The document can be on a piece of paper or on a computer.
It works like a photocopying machine because it makes a copy of the original document and sends it to the receiver.
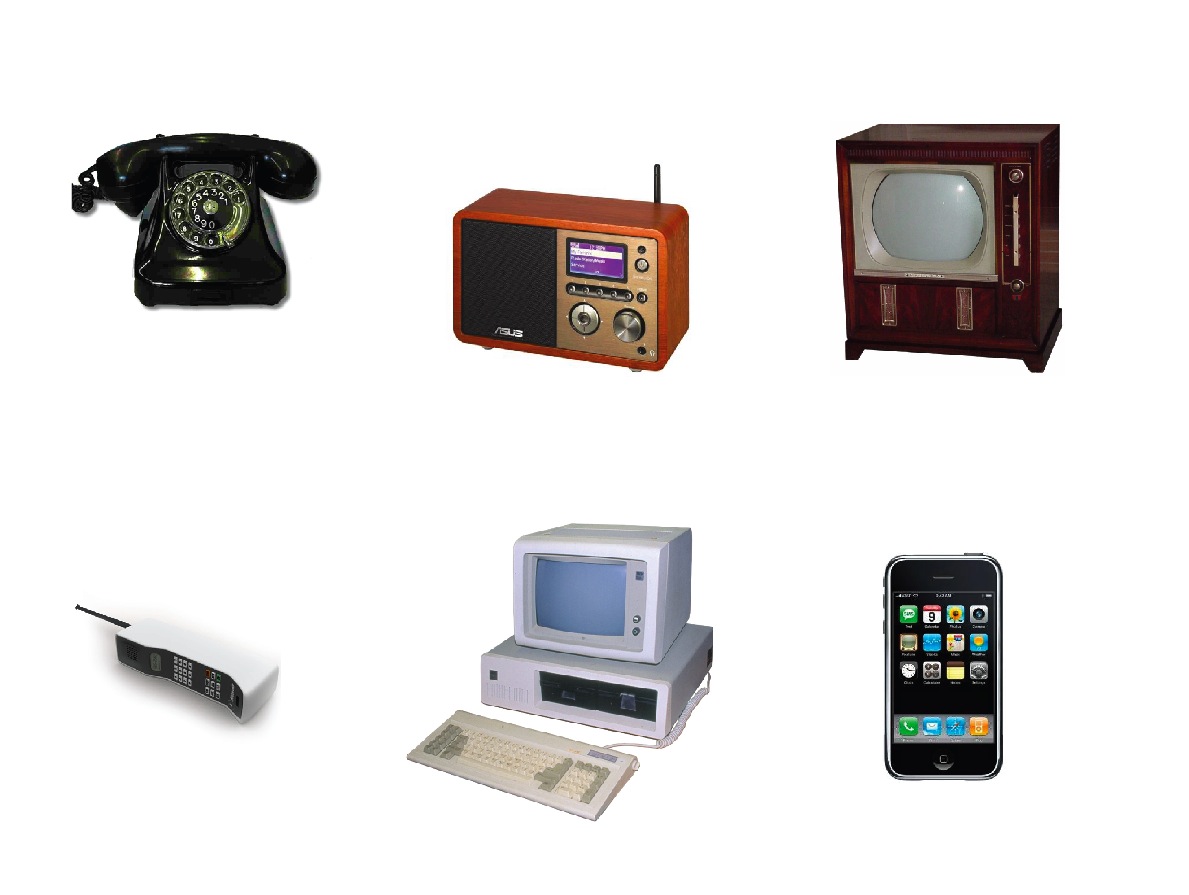

(vi) Radio: It is used to broadcast voice (i.e. audio) information to people who might be in different geographical locations. This is done from Radio Stations.
(vii) Television: This is used to transmit information both in voice (audio) and seeing (vision) from a television station to people in different geographical locations.
(viii) Satellites: Satellites are used for broadcasting radio and television signals, it allows pictures and sounds to be broadcast live. It is a type of space craft they are also used to transmit telephone signal and high volume data.
(ix) Internet: It is a collection of computers, all linked together via telephone lines, cables or satellites, to share information worldwide. It is the largest computer network in the world. People can search for information, listen to news, read newspapers, send and receive mails (e-mail) and do many other things on the internet (simply called NET).
(x) Global System for Mobile-Communications (GSM). GSM phones allow users to utilize one phone and a number or two in many different locations. This enables people to communicate using texts, pictures and voice, distance not being a barrier.

EVALUATION
State FIVE modern methods of transmitting information
ASSIGNMENT
Read means of transmitting information and mode of receiving information.
Objective Question
1. __________________ is an ancient method of transmitting information
(a) Internet (b) Town Crying (c) Telephone (d) Radio
2. One of the fastest modern means of transmitting information is not by
3. (a) Drum Beating (b) Internet (c) Radio (d) Television
4. The connection of large number of computer sets is called ___________
(a) GSM (b) Internet (c) Telephone (d) Satellite
5. ____________ is used for broadcasting radio and television signals.
(a) Internet (b) WWW (c) Satellite (d) GSM
6. ____________ is the passing on or publishing of information to an individual or group of people in order to get responses.
(a) Information Technology (b) Information Transmission
(c) Information Communication (d) Informal Transmission
7. Which of the following is not a modern way of passing information?
(a) Bush burning (b) Telephone (c) Telex (d) Internet
8. ......................... transfer text messages in coded or abridged forms.
(a) Satellite (b) Television (c) Fax (d) Telex
9. Which of the following is the largest computer network in the world?
(a) GSM (b) Television (c) satellites (d) Internet
10. In a tabular form, list five methods of ancient and modern means of transmitting information.
TOPIC: INFORMATION TRANSMISSION
MODERN METHODS OF TRANSMITTING INFORMATION
With modern inventions in communication, many ancient methods have been replaced with more efficient modern ways of transmitting information. These include the following. Writing, Printing, Telephone, Telex, Facsimile (Fax), Radio, Television, Satellite, Internet and Global Systems for Mobile communication (GSM),
(i) Writing: Information can be transmitted by wiring; this is done either by hand or by using machines such as typewriters or computers.
(ii) Printing: Information transmission by printing involves the production of information on paper using typewriter or others printing device/machine.
(iii) Telephone: Telephones allow people voices to be transmitted over a short or long distance, either by cables or by waves.
(iv) Telex: A telex machine is sued to transmit information that are textual in natural from one person to another usually over a long distance
(v) Facsimile (Fax): This is a telecommunication device that transmits documents or pictures as electronic signals over the telephone system. The document can be on a piece of paper or on a computer.
It works like a photocopying machine because it makes a copy of the original document and sends it to the receiver.

(vi) Radio: It is used to broadcast voice (i.e. audio) information to people who might be in different geographical locations. This is done from Radio Stations.
(vii) Television: This is used to transmit information both in voice (audio) and seeing (vision) from a television station to people in different geographical locations.
(viii) Satellites: Satellites are used for broadcasting radio and television signals, it allows pictures and sounds to be broadcast live. It is a type of space craft they are also used to transmit telephone signal and high volume data.
(ix) Internet: It is a collection of computers, all linked together via telephone lines, cables or satellites, to share information worldwide. It is the largest computer network in the world. People can search for information, listen to news, read newspapers, send and receive mails (e-mail) and do many other things on the internet (simply called NET).
(x) Global System for Mobile-Communications (GSM). GSM phones allow users to utilize one phone and a number or two in many different locations. This enables people to communicate using texts, pictures and voice, distance not being a barrier.

EVALUATION
State FIVE modern methods of transmitting information
ASSIGNMENT
Read means of transmitting information and mode of receiving information.
Objective Question
1. __________________ is an ancient method of transmitting information
(a) Internet (b) Town Crying (c) Telephone (d) Radio
2. One of the fastest modern means of transmitting information is not by
3. (a) Drum Beating (b) Internet (c) Radio (d) Television
4. The connection of large number of computer sets is called ___________
(a) GSM (b) Internet (c) Telephone (d) Satellite
5. ____________ is used for broadcasting radio and television signals.
(a) Internet (b) WWW (c) Satellite (d) GSM
6. ____________ is the passing on or publishing of information to an individual or group of people in order to get responses.
(a) Information Technology (b) Information Transmission
(c) Information Communication (d) Informal Transmission
7. Which of the following is not a modern way of passing information?
(a) Bush burning (b) Telephone (c) Telex (d) Internet
8. ......................... transfer text messages in coded or abridged forms.
(a) Satellite (b) Television (c) Fax (d) Telex
9. Which of the following is the largest computer network in the world?
(a) GSM (b) Television (c) satellites (d) Internet
10. In a tabular form, list five methods of ancient and modern means of transmitting information.
WEEK 8
LESSON 8
TOPIC: INFORMATION TRANSMISSION
CONTENT:
• Classification of means of transmitting information – electronic, non-electronic
• Modes of receiving information – audio, visual and audio-visual
Classification of means of transmitting information
The means of passing information in modern times can be majorly classified into two;
• Electronic means
• Non-electronic means
Electronic means:
The electronic means involve the use of electronic equipment that require electricity to power them. Examples include the following;
• Radio:
• Television
• Computer
• Telephone
• Telex
• Fax
• Satellite
• Internet
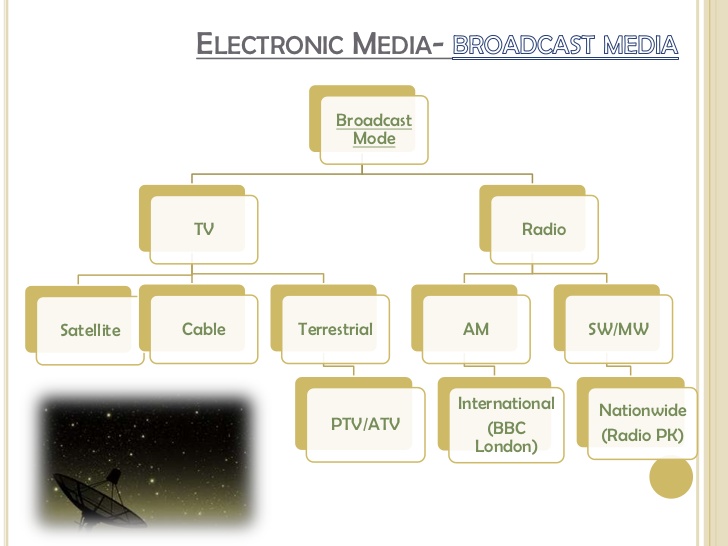
Non-Electronic means:
These are means of transmitting information that do not require electricity to power them. Examples includes
• Printed media like newspapers, textbooks, magazines, journals and handbills.
• Writing
• Drawing: representing information in an artistic way, e.g the logo of a company
• Signs: e.g. traffic signs

Modes of Receiving Information
This refers to the manner or form in which transmitted information can be gotten and properly used. There are THREE major ways of receiving information;
• Audio: This involves receiving information in form of sound. Examples are music on tape and lectures on CD-ROM.
• Visual: This involves receiving information in picture or graphic forms. Examples are slides on CD-ROM
• Audio-visual: This involves receiving information using the combination of both audio and visual forms. An example is a video recorded on tapes.
EVALUATION
1. List the two major means of transmitting information. Briefly explain the difference
2. State one example each of the following modes of receiving information;
• Audio
• Visual
• Audio-visual
ASSIGNMENT
1. .............. transfers text messages in coded or bridged forms.
(a) Satellite (b) Television (c) Fax (d) Telex
2. Which of these is not an electronic means of transmitting information?
(a) Satellite (b) Television (c) Newspaper (d) Telex
3. Which of these is not a non-electronic means of transmitting information?
(a) newspapers (b) textbooks, (c) Writing (d) Telex
4. Writing is one of the electronic methods of passing information. True/False
5. Electronic information means any information passed through an electronic device. True / False
TOPIC: INFORMATION TRANSMISSION
CONTENT:
• Classification of means of transmitting information – electronic, non-electronic
• Modes of receiving information – audio, visual and audio-visual
Classification of means of transmitting information
The means of passing information in modern times can be majorly classified into two;
• Electronic means
• Non-electronic means

Electronic means:
The electronic means involve the use of electronic equipment that require electricity to power them. Examples include the following;
• Radio:
• Television
• Computer
• Telephone
• Telex
• Fax
• Satellite
• Internet

Non-Electronic means:
These are means of transmitting information that do not require electricity to power them. Examples includes
• Printed media like newspapers, textbooks, magazines, journals and handbills.
• Writing
• Drawing: representing information in an artistic way, e.g the logo of a company
• Signs: e.g. traffic signs

Modes of Receiving Information
This refers to the manner or form in which transmitted information can be gotten and properly used. There are THREE major ways of receiving information;
• Audio: This involves receiving information in form of sound. Examples are music on tape and lectures on CD-ROM.
• Visual: This involves receiving information in picture or graphic forms. Examples are slides on CD-ROM
• Audio-visual: This involves receiving information using the combination of both audio and visual forms. An example is a video recorded on tapes.
EVALUATION
1. List the two major means of transmitting information. Briefly explain the difference
2. State one example each of the following modes of receiving information;
• Audio
• Visual
• Audio-visual
ASSIGNMENT
1. .............. transfers text messages in coded or bridged forms.
(a) Satellite (b) Television (c) Fax (d) Telex
2. Which of these is not an electronic means of transmitting information?
(a) Satellite (b) Television (c) Newspaper (d) Telex
3. Which of these is not a non-electronic means of transmitting information?
(a) newspapers (b) textbooks, (c) Writing (d) Telex
4. Writing is one of the electronic methods of passing information. True/False
5. Electronic information means any information passed through an electronic device. True / False