NEW SCHEME OF WORK:
WEEKS TOPICS
1. Revision of Last Term's Work.
2. Board Practice: basic board practice: (1) setting drawing paper on the board. (ii) Sharpening pencil to conical point and knife edge. (iii) using the tee and set squares for drawing boarder lines and horizontal and vertical lines (iv) positioning and drawing the title block. (v).writing(freehand) legible letters and numerals
3. Freehand Sketching : basic freehand techniques of drawing lines, curves, circles, and irregular shapes
4. Scales and Scale Drawing: (a) reading graduation on the metric rule. (b) measuring and comparing given sizes
5. Scales And Scale Drawing(cont’d) :(c) scale drawing: (i) types of scale; full size, 1:1 (ii) reduction scale e.g. 1:5, 1:10, 1:20, 1:100, etc. (iii) enlarged scale, e.g. 2:1, 3:1, etc.
6. Woodwork Hand Tools; (a) Measuring tools; metric rule, inside callipers, outside callipers, pair of dividers, etc. (b) Setting and Marking out tools: try-square, sliding bevel, meter square, pair of compasses, trammels, etc.
7. Woodwork Tools (cont’d) (c) Driving tools; hammer; mallet and screw driver, etc. (d) Boring tools; wood brace’ ratchet brace and bradawl, etc.
8. Uses of materials:
(a) Wood
(b) Metals
9. Woodwork Tools (cont’d) (e) Holding devices; Bench hook, Bench vice, ‘G’ cramp, sash clamp, etc. (f) cutting and pairing tools; rip saw, cross cut saw, tenon saw, bow saw, dovetail saw, jack plane, smoothing plane, spoke shaves, chisels, etc.
10. Use of woodwork tool and appliances (saw, planes, grinding and sharpening) sketches/labeling.
11. Metal work tools; Hand tools, marking out tools, uses and sketches.
9. Concept of Energy and Power; (a) Concept of Energy and power. (b) Definitions: (i) power (ii) energy (iii) units (c) relationship between energy and power
10. Revision
2ND TERM
WEEK 1
LESSON 1
TOPIC: Board Practice
SUB-TOPICS:
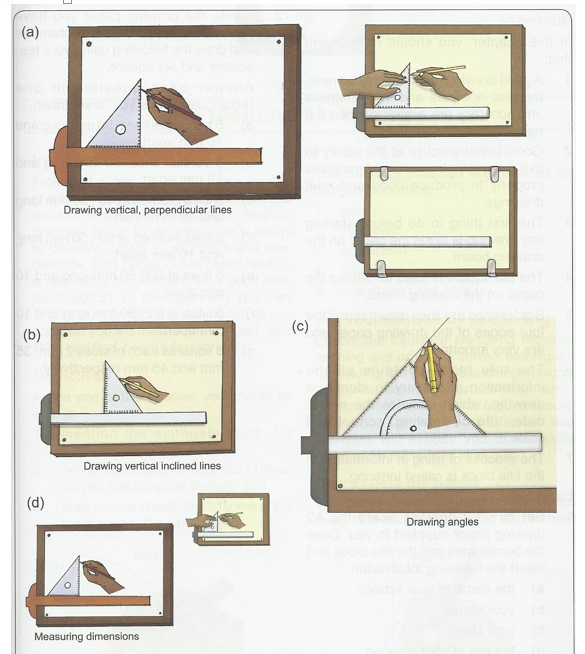
(i) The instrument required for a good board practice
(ii) Setting Drawing Paper on the Board
(iii) Sharpening pencil to conical point and knife edge
(iv) Using the tee and set squares for drawing boarder lines and other horizontal and vertical lines
(v) Positioning and drawing the title block.
(vi) Writing (freehand) legible letters and numerals

The instruments required for good board practice
The instruments required for good board practice are:
(1) Drawing board and Tee-square
(2) Set-square (30o, 60o , 45o angles)
(3) Compass and Dividers
(4) Protractor and French curves
(5) Drawing pencils (HB and 2H)
(6) Eraser and Drawing paper
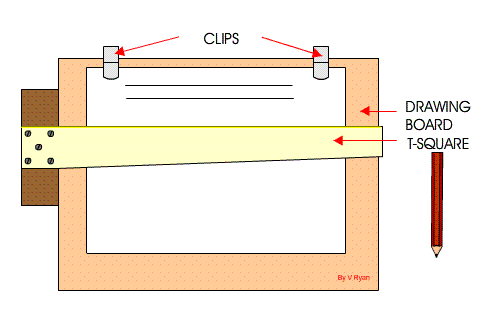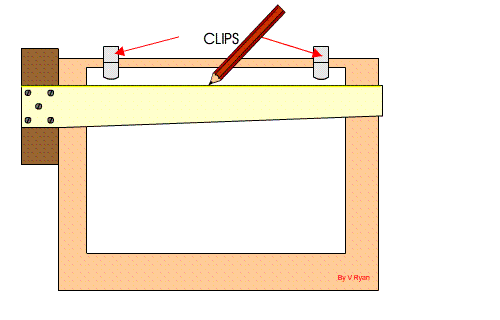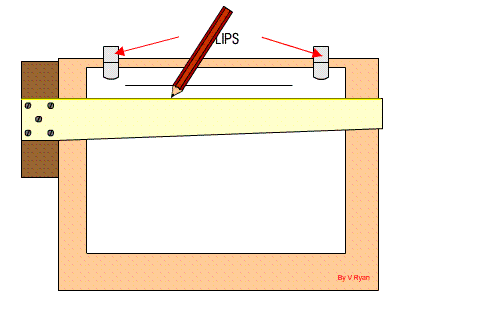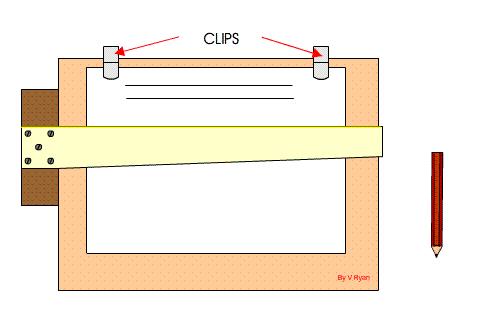
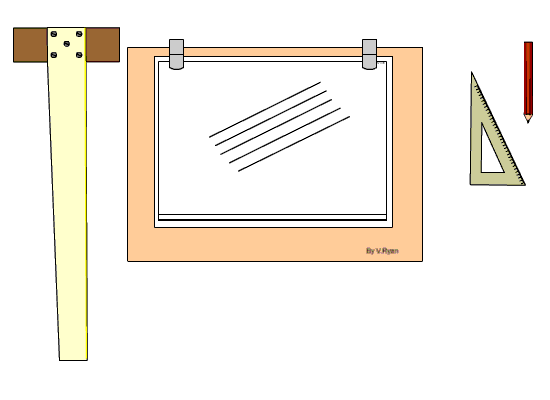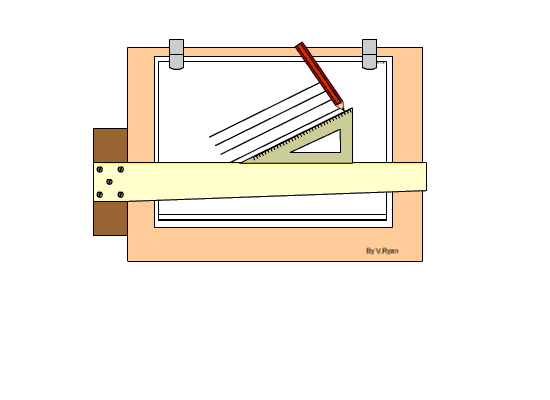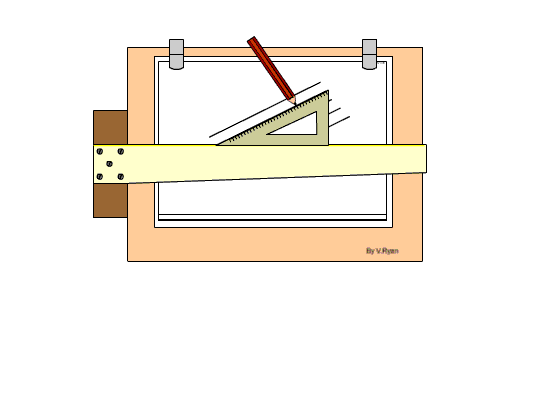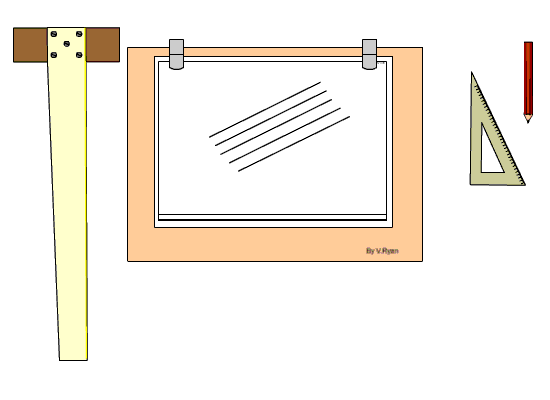
Setting Drawing Paper on the Board
Step 1: The drawing board is conveniently placed on the table with the paper on the board, leaving equal size all round, with the Tee-square edge to the left hand side.
Step 2: Place the tee-square on the paper and gently move or slide the tee-square to the top edge of the paper. Set the top edge of the paper parallel to the edge of the tee-square with the stock of the tee-square firmly against the edge of the drawing board on the left-hand side.
Step 3: Hold the paper with four pieces of adhesive tape or two metal cups to hold the paper in position at four corners.
Step 4: Gently slide the tee-square down without moving the paper.
https://youtu.be/YE0oZZO7vbk
Sharpening of Drawing Pencils to conical point and knife edge
A well sharpened pencil is very essential to technical drawing. Pencils for lettering and freehand sketching should be sharpened to a ‘conical point’ while those for geometrical or engineering drawing should be sharpened to a ‘chisel point’.
All horizontal lines are drawn with the aid of tee-square. The set-square is used sitting squarely on the tee-square to draw vertical lines.
EVALUATION
1. Briefly explain how set-square can be used to draw vertical lines.
2. Mention five drawing instruments.
LESSON 2
Using the tee and set squares for drawing Lines
This is a practical topic. The teacher should DEMONSTRATE this as much as possible in class for the students
The various uses of setsquares are given below:
Types and Uses of Lines in Technical Drawing
TYPES OF LINES ...........................THEIR USES
Thick continuous line ..................For visible outlines and edges.
Thin continuous line ..................For dimension lines, projection lines and construction lines.
Thin long chain line ..................For cutting and viewing planes as centre lines and path lines for indicating movement
Thick continuous wavy line................. For short break lines and boundary lines.
Thin continuous wavy line ..................For limits of partial views.
Thin ruled line with short zig-zags ....................For long break lines.
Arrow heads ...................Used at the end of dimension lines
Dotted straight line ....................For hidden outlines and edges
Boarder lines are also called margins. A space of about 10-15mm is left all around the drawing paper and is demarcated with straight lines. These drawing paper are called border lines. They beautify the drawing paper and protect the drawing inside.
Positioning and drawing the title block
Title Block: It gives necessary information about the drawing such as name of designer, school, class, date, scale etc. The title block is usually at the bottom right-hand corner of the drawing paper.
Writing (freehand) legible letters and numerals
Lettering is the art of writing of letters (alphabets) and numbers (figures) in bold form or lower case form on drawing.
The most important point is that the characters of the lettering must be uniform, legible, equally spaced and well proportioned. Lettering can be done either by free hand or with an instrument. The two styles of lettering are vertical or inclined styles.
https://youtu.be/9rfL1xPPLco
EVALUATION:
1. Mention five drawing instruments required for good board practice.
2. What type of drawing instrument can be used for drawing parallel line?
3. What is lettering?
READING ASSIGNMENT: Students should read about Board Practice
TEXT: NERDC Basic Technology for Junior Secondary Schools 1 Chapter 6 Pages 43-48.
ASSIGNMENT:
1. __________ is an instrument used for drawing parallel line (a) compass (b) ruler (c) divider (d) tee-square
2. Pencils for lettering and freehand sketching should be sharpened to a ______ point (a) chisel (b) conical (c) pointed (d) curved
3. ________________ are also called margin (a) leaf (b) border lines (c) centre lines (d) thick line
4. _____________ and ________ are two styles of lettering.
5. Thin continuous line can be used _______ (a) edges (b) construction lines (c) hidden outlines (d) path lines.
THEORY
1. What is title block?
2. What is lettering?
Scheme
(1) D (2) A (3) B (4) vertical and inclined (5) B
Theory
1. Title block gives necessary information such as designers name, title, date, scale etc of the drawing.
2. Lettering is the art of writing of letters (alphabets) and numbers (figures) in bold form or lower case form on drawing.
Further Studies 1
TOPIC: Board Practice
SUB-TOPICS:
(i) The instrument required for a good board practice
(ii) Setting Drawing Paper on the Board
(iii) Sharpening pencil to conical point and knife edge
(iv) Using the tee and set squares for drawing boarder lines and other horizontal and vertical lines
(v) Positioning and drawing the title block.
(vi) Writing (freehand) legible letters and numerals

The instruments required for good board practice
The instruments required for good board practice are:
(1) Drawing board and Tee-square
(2) Set-square (30o, 60o , 45o angles)
(3) Compass and Dividers
(4) Protractor and French curves
(5) Drawing pencils (HB and 2H)
(6) Eraser and Drawing paper


Setting Drawing Paper on the Board
Step 1: The drawing board is conveniently placed on the table with the paper on the board, leaving equal size all round, with the Tee-square edge to the left hand side.
Step 2: Place the tee-square on the paper and gently move or slide the tee-square to the top edge of the paper. Set the top edge of the paper parallel to the edge of the tee-square with the stock of the tee-square firmly against the edge of the drawing board on the left-hand side.
Step 3: Hold the paper with four pieces of adhesive tape or two metal cups to hold the paper in position at four corners.
Step 4: Gently slide the tee-square down without moving the paper.
https://youtu.be/YE0oZZO7vbk
Sharpening of Drawing Pencils to conical point and knife edge
A well sharpened pencil is very essential to technical drawing. Pencils for lettering and freehand sketching should be sharpened to a ‘conical point’ while those for geometrical or engineering drawing should be sharpened to a ‘chisel point’.
All horizontal lines are drawn with the aid of tee-square. The set-square is used sitting squarely on the tee-square to draw vertical lines.
EVALUATION
1. Briefly explain how set-square can be used to draw vertical lines.
2. Mention five drawing instruments.
LESSON 2
Using the tee and set squares for drawing Lines
This is a practical topic. The teacher should DEMONSTRATE this as much as possible in class for the students
The various uses of setsquares are given below:

Types and Uses of Lines in Technical Drawing
TYPES OF LINES ...........................THEIR USES
Thick continuous line ..................For visible outlines and edges.
Thin continuous line ..................For dimension lines, projection lines and construction lines.
Thin long chain line ..................For cutting and viewing planes as centre lines and path lines for indicating movement
Thick continuous wavy line................. For short break lines and boundary lines.
Thin continuous wavy line ..................For limits of partial views.
Thin ruled line with short zig-zags ....................For long break lines.
Arrow heads ...................Used at the end of dimension lines
Dotted straight line ....................For hidden outlines and edges
Boarder lines are also called margins. A space of about 10-15mm is left all around the drawing paper and is demarcated with straight lines. These drawing paper are called border lines. They beautify the drawing paper and protect the drawing inside.
Positioning and drawing the title block
Title Block: It gives necessary information about the drawing such as name of designer, school, class, date, scale etc. The title block is usually at the bottom right-hand corner of the drawing paper.
Writing (freehand) legible letters and numerals
Lettering is the art of writing of letters (alphabets) and numbers (figures) in bold form or lower case form on drawing.
The most important point is that the characters of the lettering must be uniform, legible, equally spaced and well proportioned. Lettering can be done either by free hand or with an instrument. The two styles of lettering are vertical or inclined styles.
https://youtu.be/9rfL1xPPLco
EVALUATION:
1. Mention five drawing instruments required for good board practice.
2. What type of drawing instrument can be used for drawing parallel line?
3. What is lettering?
READING ASSIGNMENT: Students should read about Board Practice
TEXT: NERDC Basic Technology for Junior Secondary Schools 1 Chapter 6 Pages 43-48.
ASSIGNMENT:
1. __________ is an instrument used for drawing parallel line (a) compass (b) ruler (c) divider (d) tee-square
2. Pencils for lettering and freehand sketching should be sharpened to a ______ point (a) chisel (b) conical (c) pointed (d) curved
3. ________________ are also called margin (a) leaf (b) border lines (c) centre lines (d) thick line
4. _____________ and ________ are two styles of lettering.
5. Thin continuous line can be used _______ (a) edges (b) construction lines (c) hidden outlines (d) path lines.
THEORY
1. What is title block?
2. What is lettering?
Scheme
(1) D (2) A (3) B (4) vertical and inclined (5) B
Theory
1. Title block gives necessary information such as designers name, title, date, scale etc of the drawing.
2. Lettering is the art of writing of letters (alphabets) and numbers (figures) in bold form or lower case form on drawing.
Further Studies 1
WEEK 2
LESSON 3
TOPIC: Woodwork Handtools: Measuring and marking out tools
SUB-TOPIC:
(i) Measuring tools
(ii) Setting and marking out tools
Measuring tools
Measuring is one of the activities carried out on wood or metal in the workshop to get the accurate size of the work done. Examples of measuring tools are metric rule, inside calipers, outside calipers, pairs of dividers etc. Metal or wood has to be measured into the required lengths relevant to the expected construction before cutting and construction can be done.
Metric Rule – Is the simplest measuring tool in a woodwork workshop. It is made of metal, wooden, plastic or coiled tape rule.
Calipers are measuring instruments that are used to measure the diameters of circular shapes. There are three types of calipers.
(i) Inside caliper is used for measuring the diameter of the inner parts of a circular object.
(ii) Outside caliper is used to measure the diameter of a cylindrical bar.
(iii) Odd-leg caliper is used to measure the centre lines of round bars. This caliper is also called Jenny’s Caliper.
(iv) Divider is similar to the actual place where it is needed.



Setting and Marking out tools – are try-square, sliding bevel, mitre rule, square, compass etc.
The next operation after measurements in woodwork or metalwork is marking out of the beginning and end of such measured lengths.
1. Try Square – It is used to mark lines that form a right angle. It is used to test the square-ness of an edge.

2. Sliding bevel – It is used for duplicating angles and for setting out bevels. The lines of such angles should not be 450
3. Mitre square – The mitre square is also used to mark angles, particularly angle 450

4. Compass – It is used to mark the arcs of a circle.
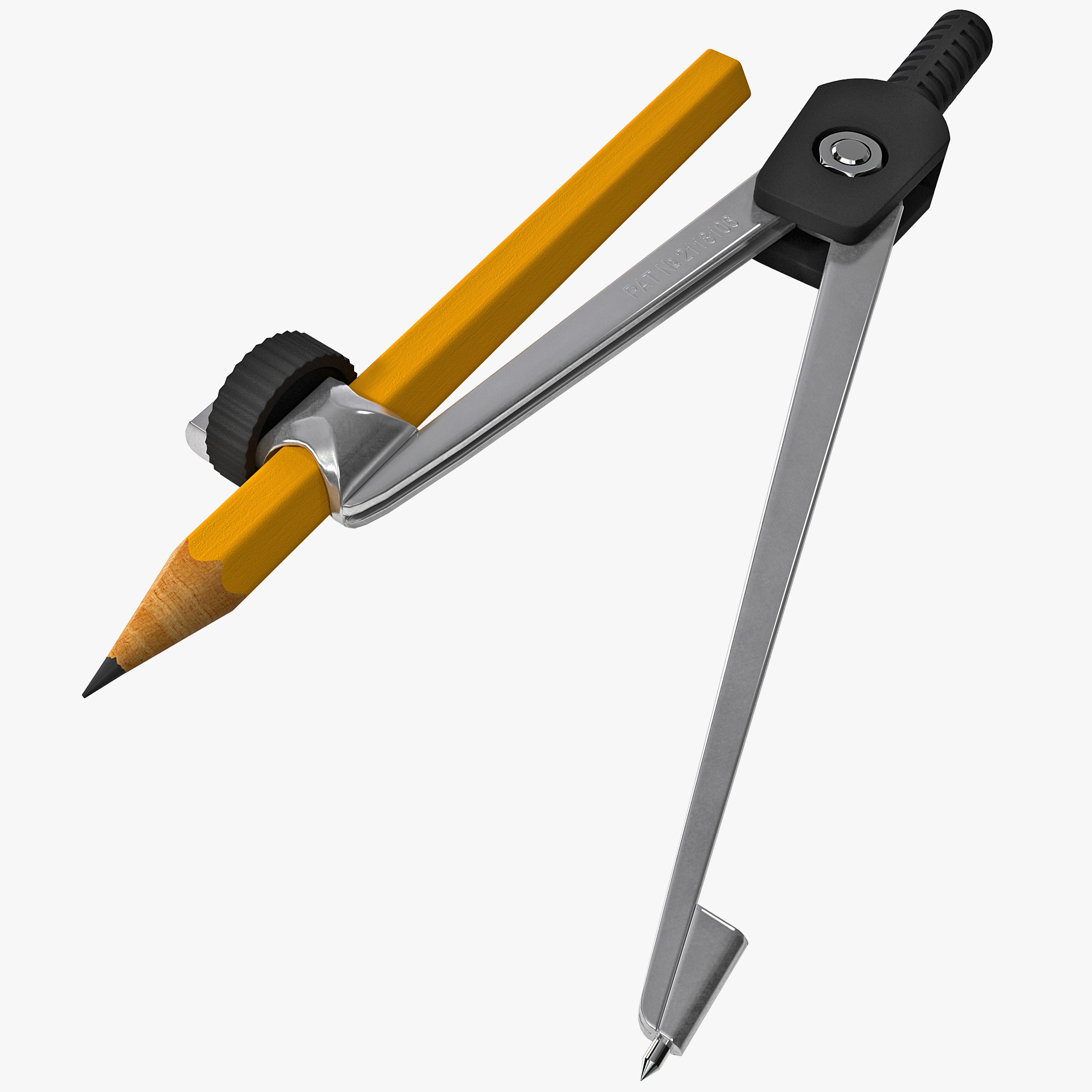

EVALUATION
1. What is measuring tools?
2. What are calipers?
3. Explain the function of try square
4. What is next operation after measurement?
Reading Assignment – Students should read about the driving tools.
TEXT: NERDC Introductory Technology for Junior Secondary School 1 Chapter 9, pages 64 – 78
ASSIGNMENT
1. ____ is used to mark the arcs of a circle.
2. ______ is used to measure the diameter of a circular shape.
3. Odd-leg caliper is also called ______________
4. Tools used to measure the diameter of a cylindrical bar is _________
MARKING SCHEME
1. Compass
2. Caliper
3. Jenny’s caliper
4. Outside caliper
5 marks each = 20 marks
LESSON 4
MAIN TOPIC : Wood working machines
SPECIFIC TOPIC : Types and uses
REFERENCE BK :Basic technology for JSS by Evans and Nation Building Basic Technology by E.K AJAYI.
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVES : At the end of the lesson the students should be able to:
(1) mention all the woodworking machines
(2) state the uses of the woodworking
CONTENT : WOODWORKING MACHINE
Woodworking machines are the machines that are powered electrically and used for woodwork operation .The common wood work operations are: planning, drilling turning and sawing.
WOOD WORK MACHINES
1. Sawing machine


2. Surface planer

3. Thicknesser

Potable Circular sawing machine
https://youtu.be/4jpOYxRyTFY
Turning machine
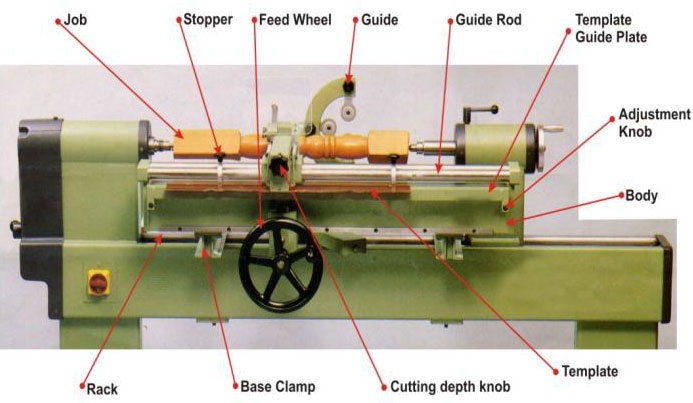
Drill press
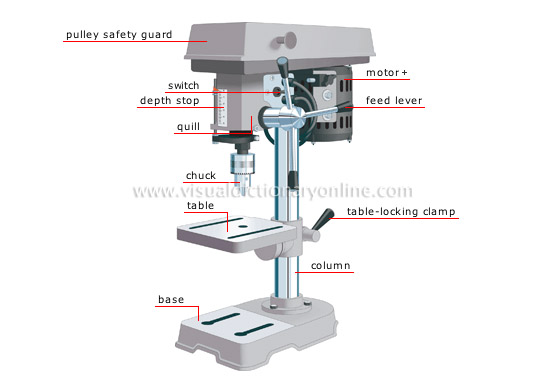
https://youtu.be/Q2gv59aeMAQ
EVALUATION/CLASSWORK
(1)Describes Woodwork machines
(2)Mention the common woodwork machines
ASSIGNMENT
Draw all the common woodwork machines
State the advantages of using woodwork machines and its disadvantages
more woodworking tools


LESSON 5
MAIN TOPIC : Woodworking machines
SPECIFIC TOPIC : Types of woodworking machines
REFERENCE BK : Basic Technology for JSS by Evans and Nation Building Basic Technology by E.K AJAYI.
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVES: At the end of the lesson the students should be able to:
(1) Mention the common types of woodwork machines
(2) State the uses of the woodwork machines
CONTENT
WOODWORKING MACHINE
Sawing machines are wood work machines for cutting timber. The two important ones are
are : (a)Circular sawing Machines:-these saws are used for cutting timber into smaller
Sizes, the saw used by the circular saw blade is circular in shape.
(b)Band Sawing Machines:-these saws are used mostly for cutting curves.
Planning machines are machines used for planning the sides, faces and edges of timber.
There are two types:-(a)Surface planer

(b)Thicknesser

Drill press these are machines for making holes in wood.
Wood-turning lathes these are the machines for making designs in wood.
EVALUATION/CLASSWORK
1. Mention all the wood work machines
2. State the uses of all the woodwork machines
watch video
https://youtu.be/CQdDPiofh1A
https://youtu.be/k6SRVTBZIxU
practice test
http://www.funtrivia.com/playquiz/quiz1 ... 0cc10.html
http://woodsgood.ca/quiz.htm
http://www.funtrivia.com/newflash/trivia.cfm?qid=183823
TOPIC: Woodwork Handtools: Measuring and marking out tools
SUB-TOPIC:
(i) Measuring tools
(ii) Setting and marking out tools
Measuring tools
Measuring is one of the activities carried out on wood or metal in the workshop to get the accurate size of the work done. Examples of measuring tools are metric rule, inside calipers, outside calipers, pairs of dividers etc. Metal or wood has to be measured into the required lengths relevant to the expected construction before cutting and construction can be done.
Metric Rule – Is the simplest measuring tool in a woodwork workshop. It is made of metal, wooden, plastic or coiled tape rule.

Calipers are measuring instruments that are used to measure the diameters of circular shapes. There are three types of calipers.
(i) Inside caliper is used for measuring the diameter of the inner parts of a circular object.
(ii) Outside caliper is used to measure the diameter of a cylindrical bar.
(iii) Odd-leg caliper is used to measure the centre lines of round bars. This caliper is also called Jenny’s Caliper.
(iv) Divider is similar to the actual place where it is needed.



Setting and Marking out tools – are try-square, sliding bevel, mitre rule, square, compass etc.
The next operation after measurements in woodwork or metalwork is marking out of the beginning and end of such measured lengths.
1. Try Square – It is used to mark lines that form a right angle. It is used to test the square-ness of an edge.

2. Sliding bevel – It is used for duplicating angles and for setting out bevels. The lines of such angles should not be 450


3. Mitre square – The mitre square is also used to mark angles, particularly angle 450

4. Compass – It is used to mark the arcs of a circle.

EVALUATION
1. What is measuring tools?
2. What are calipers?
3. Explain the function of try square
4. What is next operation after measurement?
Reading Assignment – Students should read about the driving tools.
TEXT: NERDC Introductory Technology for Junior Secondary School 1 Chapter 9, pages 64 – 78
ASSIGNMENT
1. ____ is used to mark the arcs of a circle.
2. ______ is used to measure the diameter of a circular shape.
3. Odd-leg caliper is also called ______________
4. Tools used to measure the diameter of a cylindrical bar is _________
MARKING SCHEME
1. Compass
2. Caliper
3. Jenny’s caliper
4. Outside caliper
5 marks each = 20 marks
LESSON 4
MAIN TOPIC : Wood working machines
SPECIFIC TOPIC : Types and uses
REFERENCE BK :Basic technology for JSS by Evans and Nation Building Basic Technology by E.K AJAYI.
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVES : At the end of the lesson the students should be able to:
(1) mention all the woodworking machines
(2) state the uses of the woodworking
CONTENT : WOODWORKING MACHINE
Woodworking machines are the machines that are powered electrically and used for woodwork operation .The common wood work operations are: planning, drilling turning and sawing.
WOOD WORK MACHINES
1. Sawing machine


2. Surface planer

3. Thicknesser

Potable Circular sawing machine
https://youtu.be/4jpOYxRyTFY
Turning machine

Drill press

https://youtu.be/Q2gv59aeMAQ
EVALUATION/CLASSWORK
(1)Describes Woodwork machines
(2)Mention the common woodwork machines
ASSIGNMENT
Draw all the common woodwork machines
State the advantages of using woodwork machines and its disadvantages
more woodworking tools


LESSON 5
MAIN TOPIC : Woodworking machines
SPECIFIC TOPIC : Types of woodworking machines
REFERENCE BK : Basic Technology for JSS by Evans and Nation Building Basic Technology by E.K AJAYI.
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVES: At the end of the lesson the students should be able to:
(1) Mention the common types of woodwork machines
(2) State the uses of the woodwork machines
CONTENT
WOODWORKING MACHINE
Sawing machines are wood work machines for cutting timber. The two important ones are
are : (a)Circular sawing Machines:-these saws are used for cutting timber into smaller
Sizes, the saw used by the circular saw blade is circular in shape.
(b)Band Sawing Machines:-these saws are used mostly for cutting curves.
Planning machines are machines used for planning the sides, faces and edges of timber.
There are two types:-(a)Surface planer

(b)Thicknesser

Drill press these are machines for making holes in wood.
Wood-turning lathes these are the machines for making designs in wood.
EVALUATION/CLASSWORK
1. Mention all the wood work machines
2. State the uses of all the woodwork machines
watch video
https://youtu.be/CQdDPiofh1A
https://youtu.be/k6SRVTBZIxU
practice test
http://www.funtrivia.com/playquiz/quiz1 ... 0cc10.html
http://woodsgood.ca/quiz.htm
http://www.funtrivia.com/newflash/trivia.cfm?qid=183823
WEEK 3
LESSON 6
TOPIC: Freehand Sketching
SUB-TOPICS: (i) Definition or meaning
(ii) Techniques of Sketching
Definition or meaning
Freehand sketching is one of the quickest methods by which the shape of an object can be communicated to others without using any drawing instrument except a pen or a pencil. Examples of free hand sketches are:
Freehand sketching is of advantage because a good sketch reduces the amount of writing needed to describe an object.

EVALUATION
What is freehand sketching?
Name the instruments used in Freehand Sketching.
LESSON 7
Technique of Sketching
1. Sketching a Straight line: A straight line is defined as the shortest distance between two points. We can use freehand to draw a fairly straight line by the following procedures.
(i) Put a dash or dot far enough to the right-hand side of the paper.
(ii) Start to draw a line from the left-hand side to join the dash or dot with your eyes fixed on the point.
2. Sketching a curve: To draw a curve by freehand, it will be necessary to plot some points not too far from each other at different levels, like this --------- with the points in position attempt to draw curves by joining the dashes or dots.
3. Sketching a Circle: To draw circles, the easiest way is to draw lines which are equal in diameter to the circle in different directions. Each line must be as faint and straight as possible, each crossing one another at a central point. Now, join the points by little curves from the top of each line. Try to draw other circles by means of joining two large curves having half the size as radius and full size in diameter.
4. Sketching a Square Box: This can be sketched in an isometric or oblique view. Isometric views have the vertical height and the base lines included at 450 to the horizontal while the second base line is horizontal. Once it is decided which view to represent, the block is drawn by using a series of straight lines both vertical and horizontal, applying the techniques discussed earlier.
5. Sketching an Irregular Edge – Figures with irregular edges are best drawn by first sketching a regular or square block which can completely contain the object. The shape is then carefully shaped by using dotted lines joined to show the desired shape with appropriate curves.
https://youtu.be/ewMksAbgdBI
EVALUATION
1. Briefly describe the technique of sketching a straight line and circle.
2. What is freehand sketching?
READING ASSIGNMENT
Read about scale drawing against next lesson.
TEXT: NERDC Basic Technology for Junior Secondary Schools 1 Chapter 7 Pages 49 – 56.
ASSIGNMENT
(1) ____________ is a shortest distance between two points.
(2) A square box can be sketched in an _______ or __________
THEORY
1. What is freehand sketching?
2. State one advantage of freehand sketching.
MARKING SCHEME
1. A straight line
2. Isometric or oblique.
THEORY
1. Freehand sketching is one of the quickest methods by which the shape of an object can be communicated to others without using any drawing instrument except a pen or a pencil.
2. It reduces the amount of writing needed to describe an object.
Further Studies
LESSON 8
TOPIC: Scales and Scale Drawing
SUB-TOPICS:
i) Reading graduation on the meter rule
ii) Measuring and comparing given sizes
Reading graduation on the meter rule
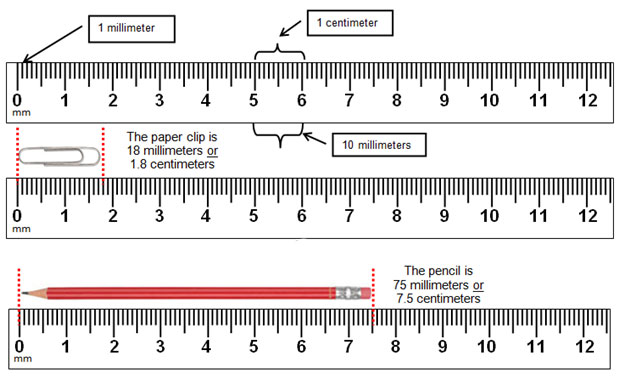
Meter Rule is a flat measuring device used to measure the length, height or width of an object. It is normally made of wood, plastic or metal. The meter rule is graduated in millimeters (mm) or centimeters (cm).
10mm = 1cm
Many kinds of meter rule are graduated between 0cm and 100cm. The straight parallel bars on the meter rule show the readings.
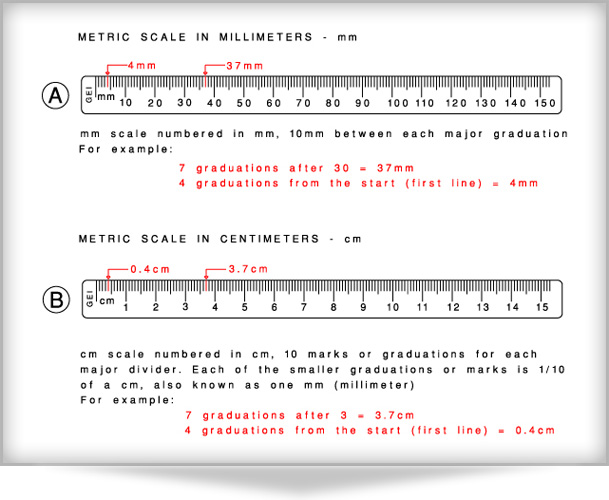
EVALUATION
The student should read the following points on the meter rule
(i) 54.5cm
(ii) 72.3cm
(iii) 38.7cm
(iv) 84.2cm
LESSON 9
Measuring and comparing given sizes
Measuring dimensions on the meter rule requires the following principles:
1) Do not take measurement directly with compass or dividers. Use the meter rule
2) Always place the meter rule along the line to be measured.
3) Always make a short dash at right angles to the meter rule during measurement
4) After setting off a dimension, always double-check your dimension to make sure that the distance is accurate
5) Small letters are used for the various units of measurement
6) For dimensions less than one, the decimal point comes after zero e.g. 0.25, 0.45, 0.85 etc
7) The units cm and mm are not written besides dimensions after measurement but a note is made on the drawing stating the unit of all the dimensions.
EVALUATION
Construct a plain scale of 100m to 1m to read 3m. Indicate the following dimensions on the scale:
a) 1.15m
b) 2.45m
READING ASSIGNMENT: Students should read about: Scales And Scale Drawing
TEXT: NERDC Basic Technology for Junior Secondary Schools 1 Chapter 8 Pages 58 – 63
ASSIGNMENT
1) Draw a line 68mm and an equivalent of it in cm indicating the dimension in cm
2) Construct a plain scale that can be read up to 15cm and on it indicate
i) 8.4cm ii) 7.4cm iii) 0.8cm
LESSON 10
TOPIC: Scales and Scale Drawing (contd.)
SUB-TOPICS:
(i) Scales and Scale Drawing
(ii) Materials for Scale Drawing
iii) Types of Scales used in Drawing
Scales and Scale Drawing
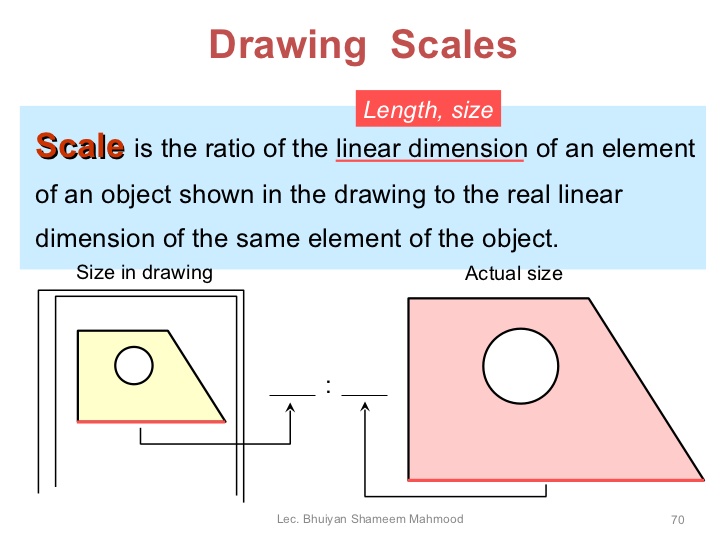
Scales drawing is different from ordinary drawing or sketching because it provides an accurate representation of the objects under consideration.
There are scales for reduction and for enlargement of the size of the object.
Materials for Scale Drawing
(i) Metric Rule: This has two flat straight edges. It is usually 30cm long.
(ii) Scale Rules: These have three straight edges and are triangular in shape. Each edge of the scale rule is graduated and each scale designation is marked on the rule.
EVALUATION
What is Scale Drawing?
Name two materials for Scale Drawing
LESSON 11
Scale Drawing (Types of Scales Used in Drawing)
Some objects are too big for the actual size to be contained on our drawing paper while some are too small for the parts to be clearly seen. We need to draw both of them to scale. Scale drawing is the drawing of a reduced size or an enlarged size of an object. Scale is usually given as a ratio and they are stated in the title block.
Types of Scales Used in Drawing
A scale is used to draw or to read the sale on a drawing.
(1) The full Scale/Size: In this case, an object is drawn to its size in all dimensions. Full size scale is 1:1
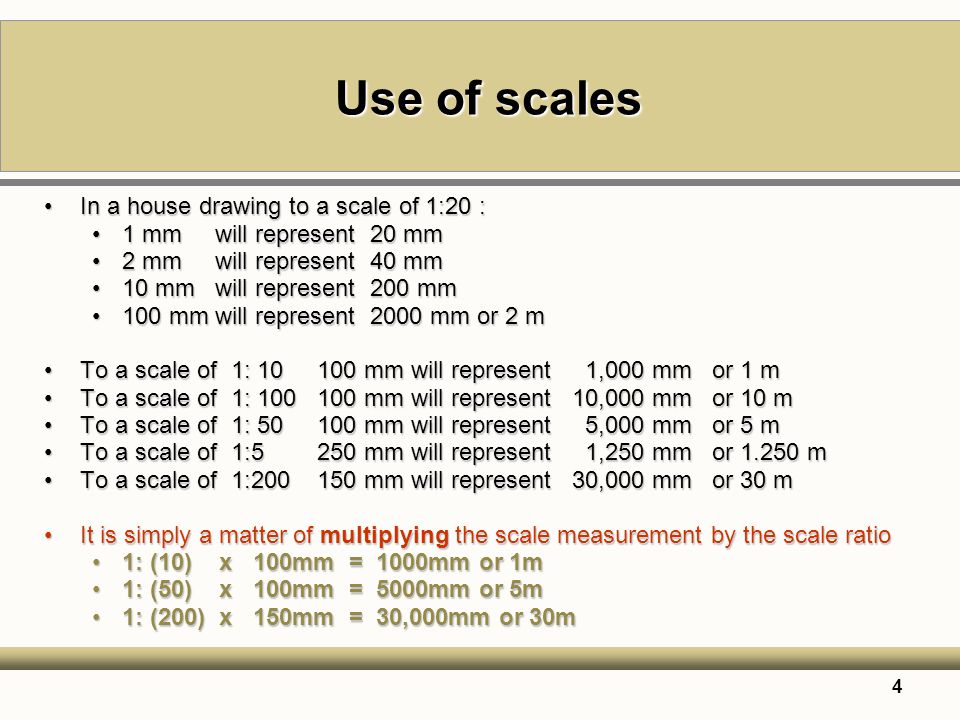
(2) Reduced Scale Drawing: The actual size of the object is reduced in proportion to the drawing. Reduced size is used when the object is too big. Reduced scale is used when the object is too big. Reduced scale ratios are 1:2; 1:5; 1:10; 1:100; 1:1000 etc.
(3) Enlarged Scale Drawing: This is used when the object to be drawn is too small to be clearly seen. Here, the normal size of the object is enlarged in proportion to the drawing. Enlarged scale ratios are 2:1; 10:1; 100:1; 500:1; 1000:1 etc. For example, 1000m:1mm means every 1000m on the drawing represents 1mm in actual size.
https://youtu.be/f-gCYOCFMYc
https://youtu.be/PgsSvBYAMJA
EVALUATION
(1) Define Scale Drawing
(2) What is the function of scale rule?
(3) Mention two types of scales used in drawing.
READING ASSIGNMENT: Students should read about: Scales And Scale Drawing
TEXT: NERDC Basic Technology for Junior Secondary Schools 1 Chapter 8 Pages 58 – 63
ASSIGNMENT
(1) ________ provides an accurate representation of the objects under construction.
(a) Board Practice (b) Technical Drawing (c) Scale Drawing (d) Woodwork
(2) _________ is the drawing of a reduced size or an enlarged size of the object.
(a) Scale drawing (b) Electrical Electronics (c) Hard wood (d) Metal work
(3) When the object to be drawn is too small to be clearly seen, we can use _______ scale
(a) Full Scale (b) reduced scale (c) medium scale (d) enlarged scale drawing
THEORY
1. Mention three types of scales used in drawing.
2. What is scale drawing?
MARKING SCHEME
1. (i) The Full Scale/Size
(ii) Reduced Scale drawing
(iii) Enlarged Scale drawing
(3 marks each) = 9 marks
2. (i) Scale drawing provides an accurate representation of the objects under consideration. (5 marks) OR
(ii) Scale drawing is the drawing of a reduced size or an enlarged size of an object.
Total = 20 marks
TOPIC: Freehand Sketching
SUB-TOPICS: (i) Definition or meaning
(ii) Techniques of Sketching
Definition or meaning
Freehand sketching is one of the quickest methods by which the shape of an object can be communicated to others without using any drawing instrument except a pen or a pencil. Examples of free hand sketches are:
Freehand sketching is of advantage because a good sketch reduces the amount of writing needed to describe an object.


EVALUATION
What is freehand sketching?
Name the instruments used in Freehand Sketching.
LESSON 7
Technique of Sketching
1. Sketching a Straight line: A straight line is defined as the shortest distance between two points. We can use freehand to draw a fairly straight line by the following procedures.
(i) Put a dash or dot far enough to the right-hand side of the paper.
(ii) Start to draw a line from the left-hand side to join the dash or dot with your eyes fixed on the point.
2. Sketching a curve: To draw a curve by freehand, it will be necessary to plot some points not too far from each other at different levels, like this --------- with the points in position attempt to draw curves by joining the dashes or dots.
3. Sketching a Circle: To draw circles, the easiest way is to draw lines which are equal in diameter to the circle in different directions. Each line must be as faint and straight as possible, each crossing one another at a central point. Now, join the points by little curves from the top of each line. Try to draw other circles by means of joining two large curves having half the size as radius and full size in diameter.
4. Sketching a Square Box: This can be sketched in an isometric or oblique view. Isometric views have the vertical height and the base lines included at 450 to the horizontal while the second base line is horizontal. Once it is decided which view to represent, the block is drawn by using a series of straight lines both vertical and horizontal, applying the techniques discussed earlier.
5. Sketching an Irregular Edge – Figures with irregular edges are best drawn by first sketching a regular or square block which can completely contain the object. The shape is then carefully shaped by using dotted lines joined to show the desired shape with appropriate curves.
https://youtu.be/ewMksAbgdBI
EVALUATION
1. Briefly describe the technique of sketching a straight line and circle.
2. What is freehand sketching?
READING ASSIGNMENT
Read about scale drawing against next lesson.
TEXT: NERDC Basic Technology for Junior Secondary Schools 1 Chapter 7 Pages 49 – 56.
ASSIGNMENT
(1) ____________ is a shortest distance between two points.
(2) A square box can be sketched in an _______ or __________
THEORY
1. What is freehand sketching?
2. State one advantage of freehand sketching.
MARKING SCHEME
1. A straight line
2. Isometric or oblique.
THEORY
1. Freehand sketching is one of the quickest methods by which the shape of an object can be communicated to others without using any drawing instrument except a pen or a pencil.
2. It reduces the amount of writing needed to describe an object.
Further Studies
LESSON 8
TOPIC: Scales and Scale Drawing
SUB-TOPICS:
i) Reading graduation on the meter rule
ii) Measuring and comparing given sizes
Reading graduation on the meter rule
Meter Rule is a flat measuring device used to measure the length, height or width of an object. It is normally made of wood, plastic or metal. The meter rule is graduated in millimeters (mm) or centimeters (cm).
10mm = 1cm
Many kinds of meter rule are graduated between 0cm and 100cm. The straight parallel bars on the meter rule show the readings.

EVALUATION
The student should read the following points on the meter rule
(i) 54.5cm
(ii) 72.3cm
(iii) 38.7cm
(iv) 84.2cm
LESSON 9
Measuring and comparing given sizes
Measuring dimensions on the meter rule requires the following principles:
1) Do not take measurement directly with compass or dividers. Use the meter rule
2) Always place the meter rule along the line to be measured.
3) Always make a short dash at right angles to the meter rule during measurement
4) After setting off a dimension, always double-check your dimension to make sure that the distance is accurate
5) Small letters are used for the various units of measurement
6) For dimensions less than one, the decimal point comes after zero e.g. 0.25, 0.45, 0.85 etc
7) The units cm and mm are not written besides dimensions after measurement but a note is made on the drawing stating the unit of all the dimensions.

EVALUATION
Construct a plain scale of 100m to 1m to read 3m. Indicate the following dimensions on the scale:
a) 1.15m
b) 2.45m
READING ASSIGNMENT: Students should read about: Scales And Scale Drawing
TEXT: NERDC Basic Technology for Junior Secondary Schools 1 Chapter 8 Pages 58 – 63
ASSIGNMENT
1) Draw a line 68mm and an equivalent of it in cm indicating the dimension in cm
2) Construct a plain scale that can be read up to 15cm and on it indicate
i) 8.4cm ii) 7.4cm iii) 0.8cm
LESSON 10
TOPIC: Scales and Scale Drawing (contd.)
SUB-TOPICS:
(i) Scales and Scale Drawing
(ii) Materials for Scale Drawing
iii) Types of Scales used in Drawing
Scales and Scale Drawing
Scales drawing is different from ordinary drawing or sketching because it provides an accurate representation of the objects under consideration.
There are scales for reduction and for enlargement of the size of the object.
Materials for Scale Drawing
(i) Metric Rule: This has two flat straight edges. It is usually 30cm long.
(ii) Scale Rules: These have three straight edges and are triangular in shape. Each edge of the scale rule is graduated and each scale designation is marked on the rule.


EVALUATION
What is Scale Drawing?
Name two materials for Scale Drawing
LESSON 11
Scale Drawing (Types of Scales Used in Drawing)
Some objects are too big for the actual size to be contained on our drawing paper while some are too small for the parts to be clearly seen. We need to draw both of them to scale. Scale drawing is the drawing of a reduced size or an enlarged size of an object. Scale is usually given as a ratio and they are stated in the title block.
Types of Scales Used in Drawing
A scale is used to draw or to read the sale on a drawing.
(1) The full Scale/Size: In this case, an object is drawn to its size in all dimensions. Full size scale is 1:1
(2) Reduced Scale Drawing: The actual size of the object is reduced in proportion to the drawing. Reduced size is used when the object is too big. Reduced scale is used when the object is too big. Reduced scale ratios are 1:2; 1:5; 1:10; 1:100; 1:1000 etc.
(3) Enlarged Scale Drawing: This is used when the object to be drawn is too small to be clearly seen. Here, the normal size of the object is enlarged in proportion to the drawing. Enlarged scale ratios are 2:1; 10:1; 100:1; 500:1; 1000:1 etc. For example, 1000m:1mm means every 1000m on the drawing represents 1mm in actual size.

https://youtu.be/f-gCYOCFMYc
https://youtu.be/PgsSvBYAMJA
EVALUATION
(1) Define Scale Drawing
(2) What is the function of scale rule?
(3) Mention two types of scales used in drawing.
READING ASSIGNMENT: Students should read about: Scales And Scale Drawing
TEXT: NERDC Basic Technology for Junior Secondary Schools 1 Chapter 8 Pages 58 – 63
ASSIGNMENT
(1) ________ provides an accurate representation of the objects under construction.
(a) Board Practice (b) Technical Drawing (c) Scale Drawing (d) Woodwork
(2) _________ is the drawing of a reduced size or an enlarged size of the object.
(a) Scale drawing (b) Electrical Electronics (c) Hard wood (d) Metal work
(3) When the object to be drawn is too small to be clearly seen, we can use _______ scale
(a) Full Scale (b) reduced scale (c) medium scale (d) enlarged scale drawing
THEORY
1. Mention three types of scales used in drawing.
2. What is scale drawing?
MARKING SCHEME
1. (i) The Full Scale/Size
(ii) Reduced Scale drawing
(iii) Enlarged Scale drawing
(3 marks each) = 9 marks
2. (i) Scale drawing provides an accurate representation of the objects under consideration. (5 marks) OR
(ii) Scale drawing is the drawing of a reduced size or an enlarged size of an object.
Total = 20 marks
WEEK 4
LESSON 12
TOPIC: Driving and boring tools.
SUB-TOPICS:
(i) Driving tools
(ii) Boring tools
Driving tools
Driving tools are used to fix nails and screws into wooden and metal materials. Nails are the iron material with a flat head, smooth stem and sharp end. Screws look like nails but they have turned or twisted stem. Screws are driven into wood with screwdrivers while nails are driven into wood and metals with the use of hammers. Hammers are driving tools that have two parts – a head, which is made of iron and a wooden handle.
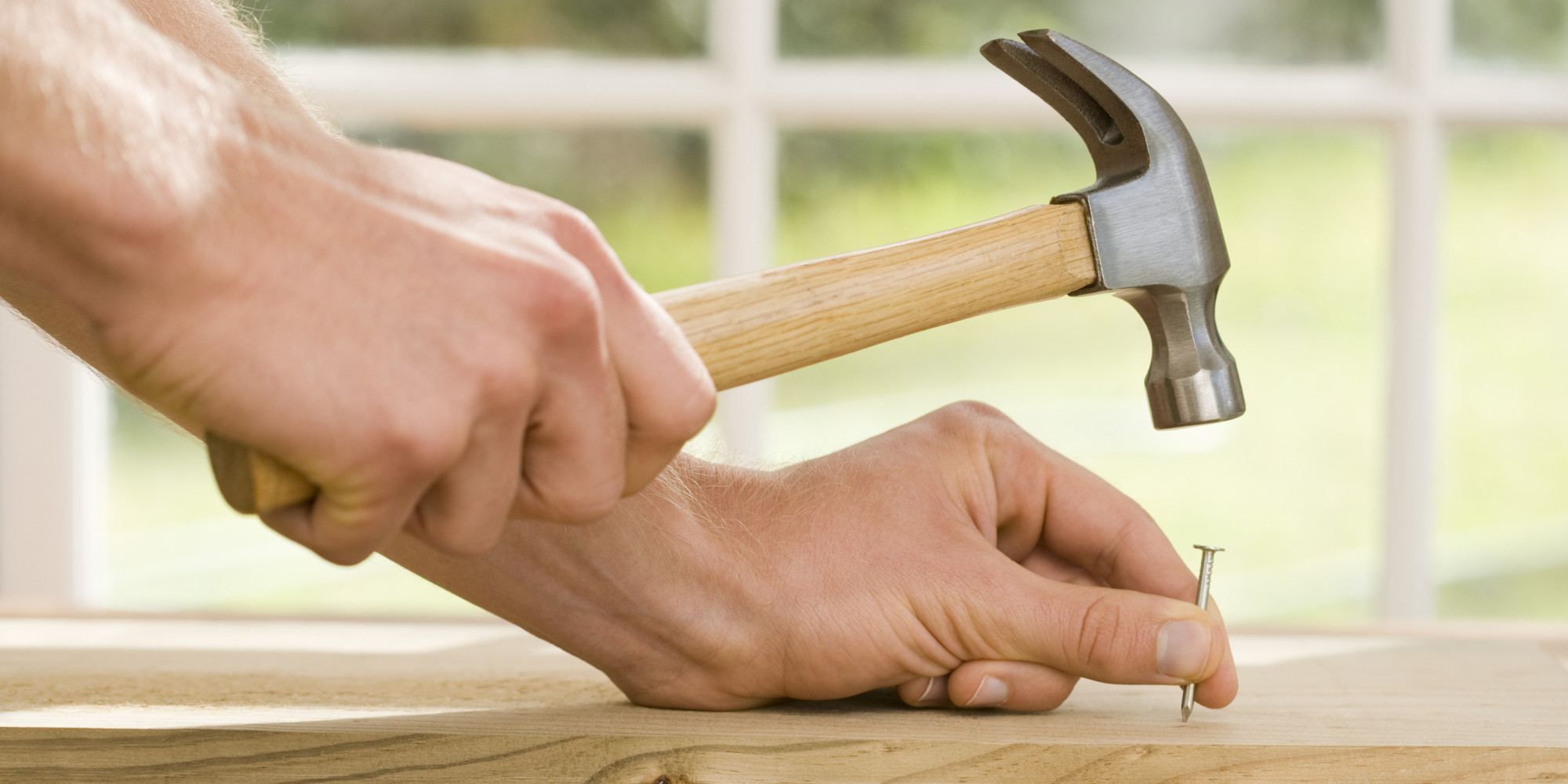

There are five types of hammers named according to the shape of the head.
1. Ball peen hammer.
2. Straight peen hammer
3. Cross peen hammer
4. Planishing hammer
5. Blocking head hammer
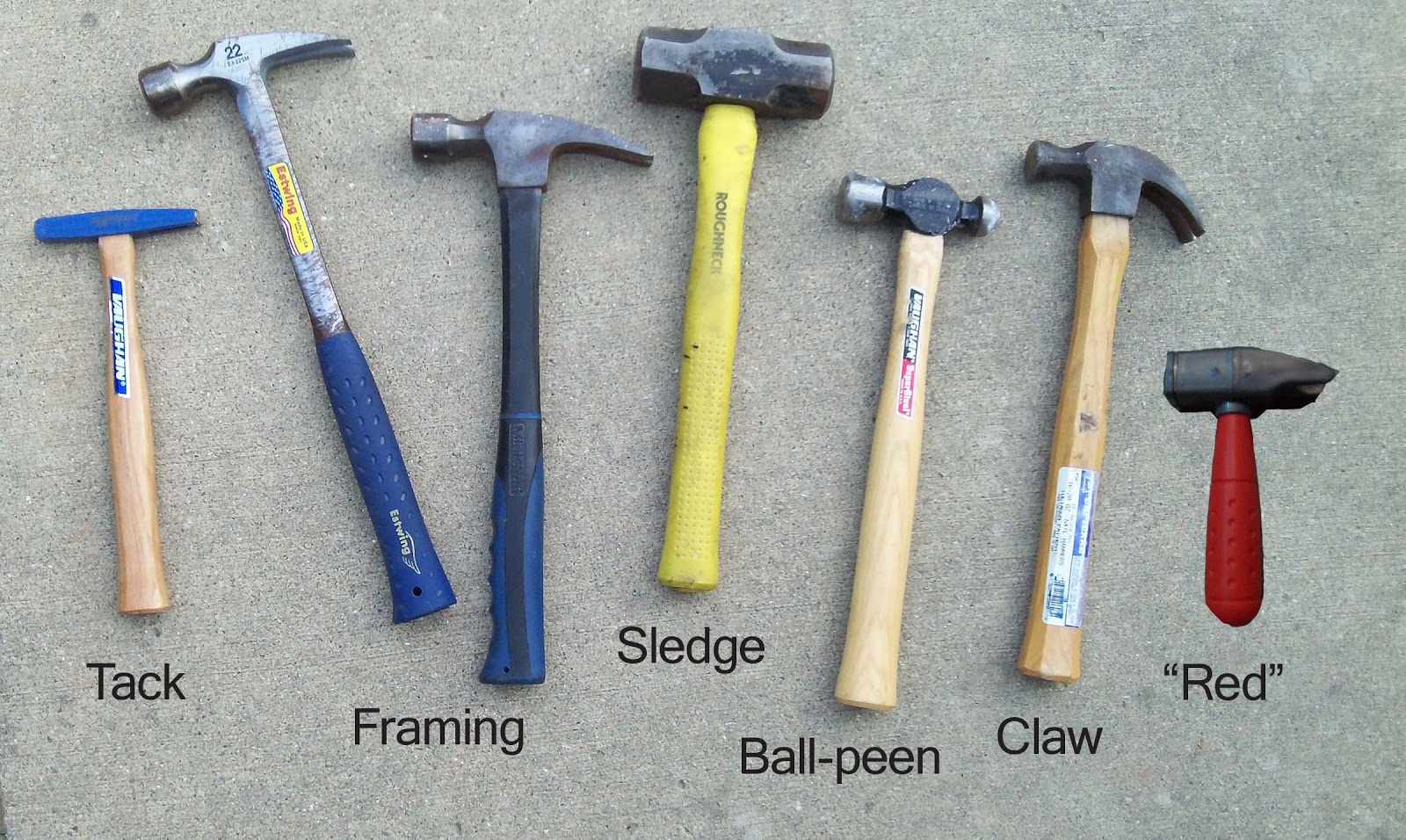

(a) Straight-peen hammer is used for riveting while other end is used for shaping sheet metals.
(b) Ball-peen hammer is used for general purposes.
(c) Blocking head hammer has polished faces. It is used for shaping sheet metal.
(d) Cross-peen hammer is used for drawing down and riveting.
(e) Planishing hammer is used by panel beaters for finishing.
Driving tools also include mallets. Mallets are soft-faced hammers, as shown in the figure below:


Screwdrivers are also driving tools and they have different shapes and sizes. They are used to drive screw in and out of wood or metals. They have a long blade with a tip that can fit into the slots (grooves) in the head of the screw with either wooden or plastic handle.
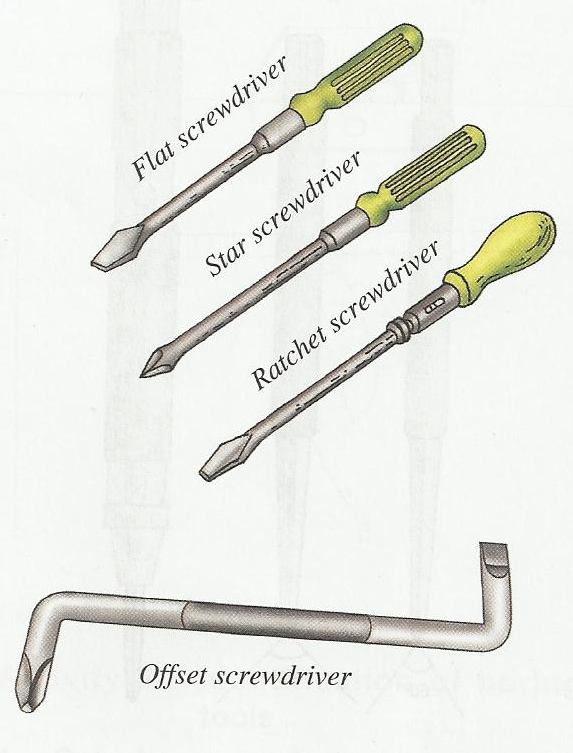

(a) Flat screwdriver used for screw having only one line slot on the head.
(b) Star screwdriver is used for screws having a star opening on the head
(c) Offset screwdriver is used whenever a straight screwdriver cannot be used.
(d) Allen screwdriver is used for driving in or removing screws which have a hexagonal or square slot in their head.
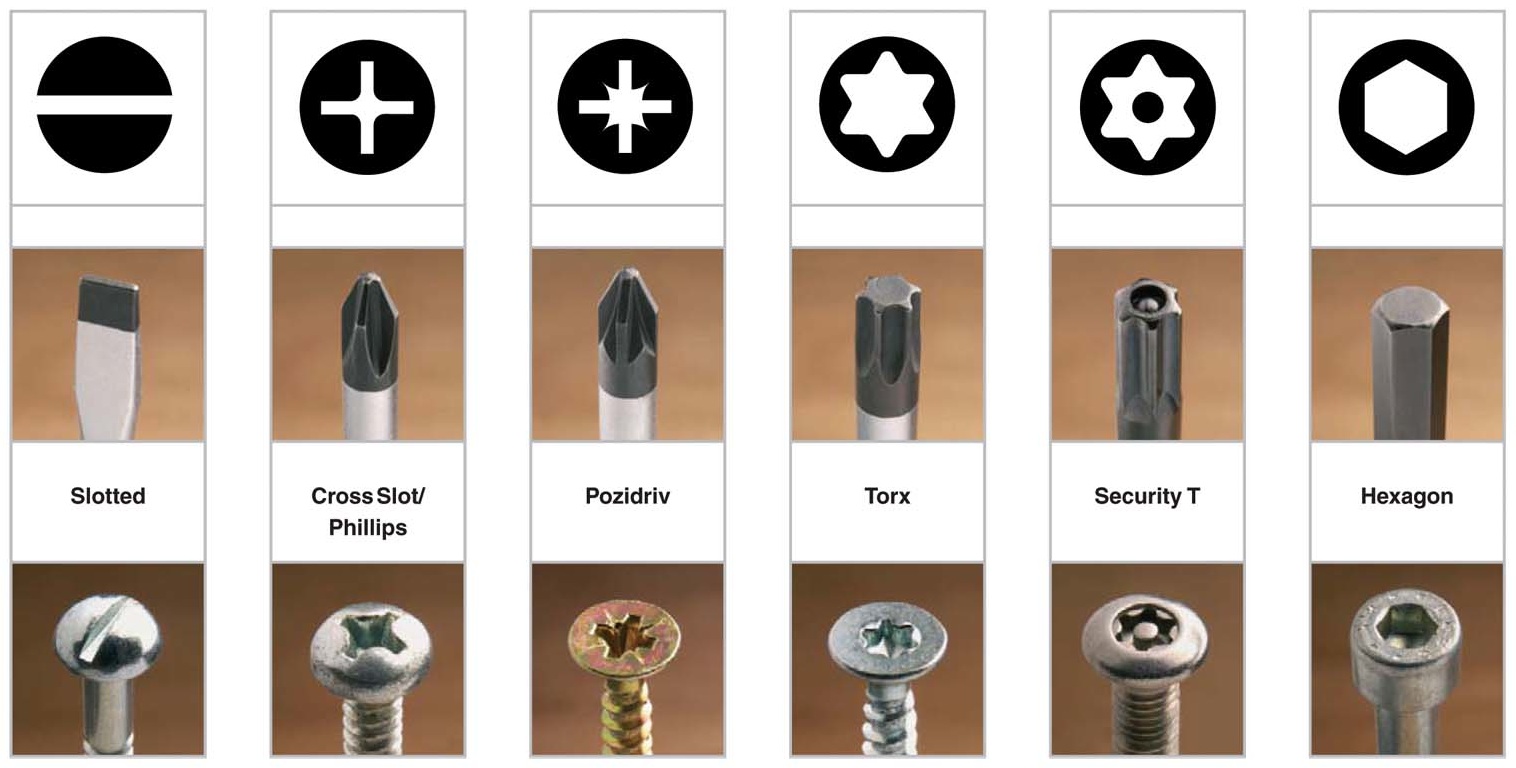

EVALUATION
1. What are driving tools?
2. Mention and explain two types of hammer.
3. What are screwdrivers?
LESSON 13
Boring tools
Boring is the act of making narrow holes in a material such as in wood or metal. Holes are bored in materials with tools called bits or drills. The boring tools are:
1. The ratchet brace: this is the tool used to hold bits of various sizes in the chucks. Some of the bits include:
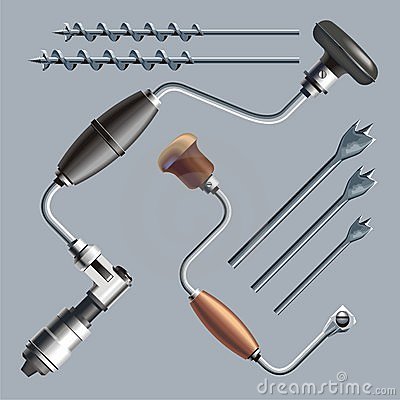
a. Centre bit: for boring shallow holes in wood.
b. Dowel bit : used where two components are to be held together by the dowel pin
c. Countersink bit: used to enlarge the existing holes in wood.
d. Double twist drill: used for boring deep hole in wood.

2. Gimlet: this is the tool used for boring holes in wood before inserting small nails and screws.

3. Bradawl: this tool can be used to replace gimlets, could be used as screw-driver to insert small screws, and could also be used for forming small holes before using screws or nails in the woodwork.

EVALUATION
1. Mention two types of screwdrivers and their uses.
2. Name and explain two types of hammer.
3. Define boring tools.
4. Give 5 examples of boring tools and state their uses.
READING ASSIGNMENT: Students should read about metal work holding devices.
TEXT: NERDC Basic Technology for schools Chapter 9 pages 64 – 70
ASSIGNMENT
1. Explain the uses of star screwdriver.
2. What is hammer?
Marking Scheme
1. Star screwdriver is used whenever a straight screwdriver cannot be used.
2. Hammers are driving tools that have two parts head made of iron and wooden handle. (5 marks each = Total 10 marks)
LESSON 14
TOPIC: Woodwork tools: Holding devices, cutting and paring tools.
SUB-TOPICS:
(i) Holding devices
(ii) Cutting and paring tools.
Holding devices
Woodworking holding devices are the tools used to hold work piece on the workbench. Woodworkers work on workbenches. It is on these benches that various woodwork constructions are carried out. The centre of the bench is usually lower than its two sides. This area is called a ‘well’ and its function is to accommodate the tools brought from the tool cupboard to the bench top during operations. The tools cannot fall or roll on to the floor or on anyone’s feet because this part is lower than other area of the bench.
The fittings are:
1. Bench vice: also called fitter’s vice. It is used to clamp or to hold jobs when the following operations are to be carried out on the bench, filling, bending, tapping, cutting, assembling parts etc.
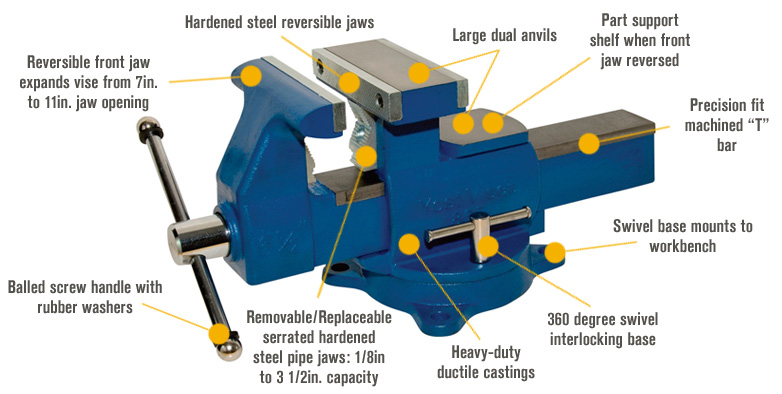
Other types of vice are:
Hand vice: used for holding work when performing operations such as drilling, riveting etc
Machine vice: It is fixed to the table of any machine tool.

The Care of the Vice
a. Always keep the vice clean.
b. The thread or the screw inside the vice should be oiled regularly.
c. Do not use the vice as an anvil for hammering a job
d. Always use hand force only to tighten the vice for holding the work piece.
2. Bench Stop – There are many types of bench stops. Some are made of wood while some are made of metals. It is a small strip of wood fixed on top of the bench. It is used to prevent wood from slipping off the bench top during planning.
3. Bench Hook – This is used for holding jobs during cutting and chiseling on the bench. At the same time, it protects the bench top.

4. The clamps
a. G-Clamp – This is a metal clamp used for clamping small jobs together. It is called a G-Clamp because of its shape which is in the form of letter ‘G’. The clamp is ideal for holding small pieces of wood together.
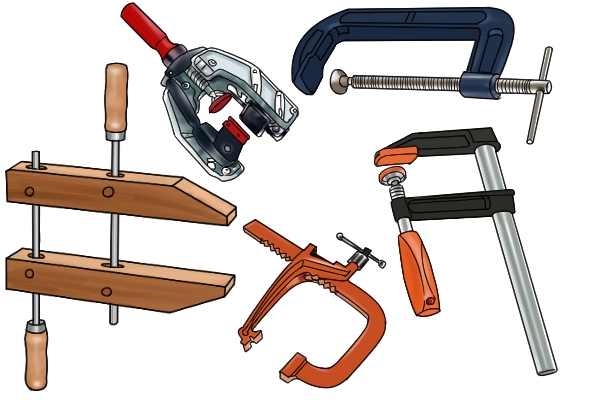
b. F-Clamp – This is used like the G-Clamp. The clamp is in the form of letter ‘F’.
c. Sash-Clamp – it is a larger clamp used for holding and drawing woods tightly together when assembling or gluing work.
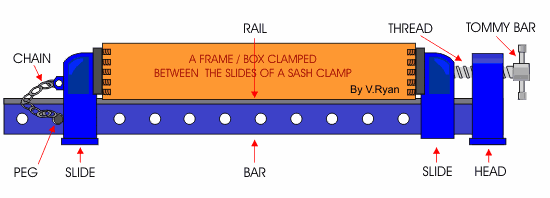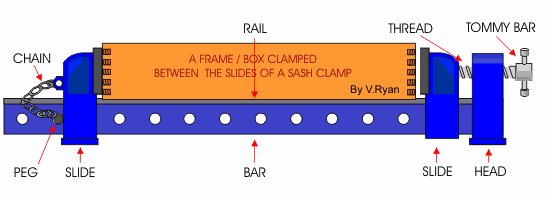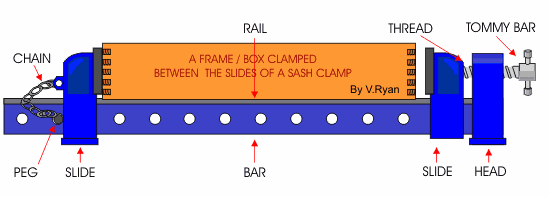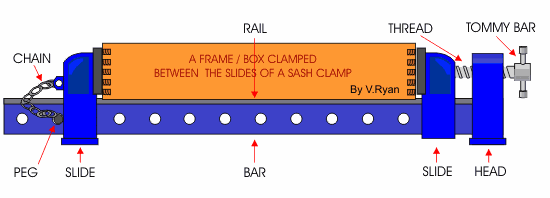
Cutting and Paring tools
Saws and Planes are used in cutting and smoothing wood in the workshop respectively. Saws are tools used for cutting wood. There are two main groups of saws: bench saw and curve cutting saws.

Curve cutting saws are:
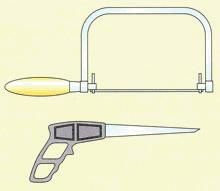
1. Coping Saw – This is used for cutting curve marked lines of wood. The blades can be adjusted to cut in any direction.
2. Fret Saw – This is used to cut curves in thin wood of 8mm thick or less. It is used to cut plywood.
3. Bow Saw – is used to cut along curve marked lines but the wood has to be 50mm thick.
4. Compass Saw – It is used for cutting large interior curves.
5. Keyhole – It is used mainly for internal curves where the bow saw cannot be used.
6. Rip Saw – Is used for cutting along the grain of the wood.
7. Tenon saw – Is used for cutting shoulders to tenon and recesses in board
8. Dovetail saw – Is also similar to tenon saw but it is much shorter. It is used for cutting fine joints and also light sawing.
9. Panel Saw – Is used for sawing thin timber across the wood.
10. Cross-cut saw – Is used for cutting across the grain.
Types and Uses of planes
Bench planes are used to obtain a good, smooth surface and to get the correct size required. Bench planes are:
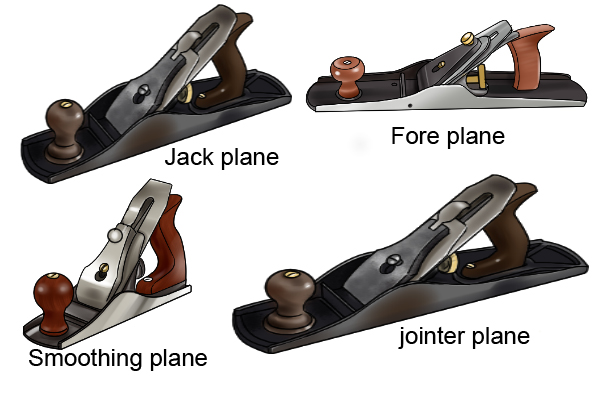
1. Jack Plane – It is used to smoothen or remove marks from timber. It is used to dress the surface and edges.
2. Trying plane – It is used to produce flat surface and perfectly straight edges.
3. Smoothing plane – It is used for clearing the surfaces and edges of timbers ready for assembling.
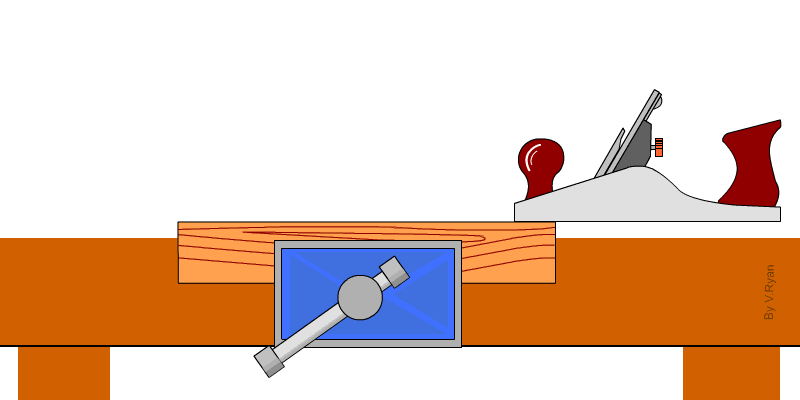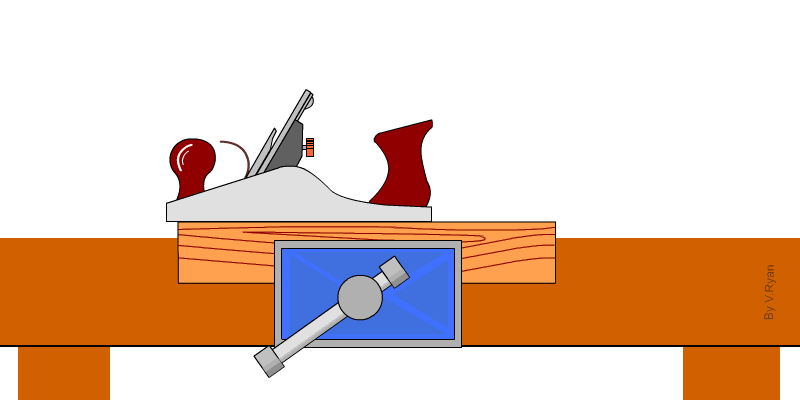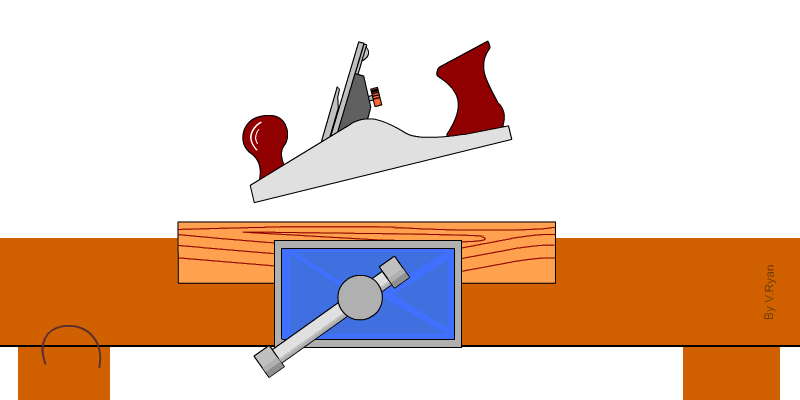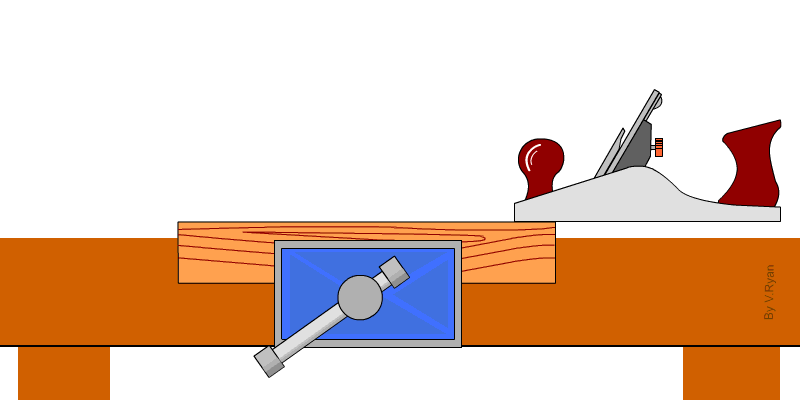
4. Block plane – It is used for planing small work that is not easily accessible.
5. Spoke shave – This is an example of a curve cutting plane used to produce smooth curve surfaces and edges.
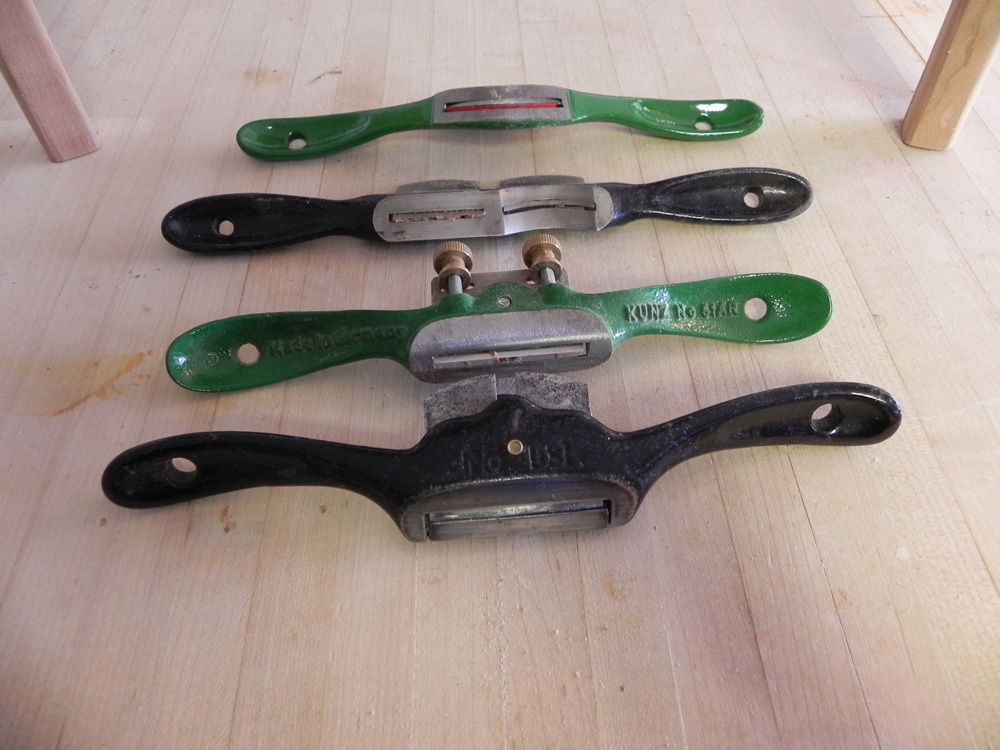

EVALUATION
1. Explain the three types of clamp
2. Explain the structure of a workbench
3. What is the main use of a saw?
4. Mention 8 curve cutting saws
READING ASSIGNMENT – Students should read about concept of energy and power
TEXT: NERDC Basic Technology for Junior Secondary School 1 Chapter 9, Pages 70-78
ASSIGNMENT –
1. _________ is used for holding jobs during cutting and chiseling on the bench
2. _________ is used to prevent wood from slipping off the bench top during planning
3. _________ is made of cast iron, it is used to hold work piece securely while working
4. _________ is ideal for holding small pieces of wood together
5. ________ is used for holding and drawing woods tightly together when gluing work
THEORY
1. List three different types of clamps you know.
2. Mention three fittings in work bench.
MARKING SCHEME
1. Bench hook
2. Bench stop
3. Vice
4. G-clamp
5. Sash-clamp
TOPIC: Driving and boring tools.
SUB-TOPICS:
(i) Driving tools
(ii) Boring tools
Driving tools
Driving tools are used to fix nails and screws into wooden and metal materials. Nails are the iron material with a flat head, smooth stem and sharp end. Screws look like nails but they have turned or twisted stem. Screws are driven into wood with screwdrivers while nails are driven into wood and metals with the use of hammers. Hammers are driving tools that have two parts – a head, which is made of iron and a wooden handle.

There are five types of hammers named according to the shape of the head.
1. Ball peen hammer.
2. Straight peen hammer
3. Cross peen hammer
4. Planishing hammer
5. Blocking head hammer

(a) Straight-peen hammer is used for riveting while other end is used for shaping sheet metals.
(b) Ball-peen hammer is used for general purposes.
(c) Blocking head hammer has polished faces. It is used for shaping sheet metal.
(d) Cross-peen hammer is used for drawing down and riveting.
(e) Planishing hammer is used by panel beaters for finishing.
Driving tools also include mallets. Mallets are soft-faced hammers, as shown in the figure below:


Screwdrivers are also driving tools and they have different shapes and sizes. They are used to drive screw in and out of wood or metals. They have a long blade with a tip that can fit into the slots (grooves) in the head of the screw with either wooden or plastic handle.


(a) Flat screwdriver used for screw having only one line slot on the head.
(b) Star screwdriver is used for screws having a star opening on the head
(c) Offset screwdriver is used whenever a straight screwdriver cannot be used.
(d) Allen screwdriver is used for driving in or removing screws which have a hexagonal or square slot in their head.

EVALUATION
1. What are driving tools?
2. Mention and explain two types of hammer.
3. What are screwdrivers?
LESSON 13
Boring tools
Boring is the act of making narrow holes in a material such as in wood or metal. Holes are bored in materials with tools called bits or drills. The boring tools are:
1. The ratchet brace: this is the tool used to hold bits of various sizes in the chucks. Some of the bits include:

a. Centre bit: for boring shallow holes in wood.
b. Dowel bit : used where two components are to be held together by the dowel pin
c. Countersink bit: used to enlarge the existing holes in wood.
d. Double twist drill: used for boring deep hole in wood.

2. Gimlet: this is the tool used for boring holes in wood before inserting small nails and screws.

3. Bradawl: this tool can be used to replace gimlets, could be used as screw-driver to insert small screws, and could also be used for forming small holes before using screws or nails in the woodwork.

EVALUATION
1. Mention two types of screwdrivers and their uses.
2. Name and explain two types of hammer.
3. Define boring tools.
4. Give 5 examples of boring tools and state their uses.
READING ASSIGNMENT: Students should read about metal work holding devices.
TEXT: NERDC Basic Technology for schools Chapter 9 pages 64 – 70
ASSIGNMENT
1. Explain the uses of star screwdriver.
2. What is hammer?
Marking Scheme
1. Star screwdriver is used whenever a straight screwdriver cannot be used.
2. Hammers are driving tools that have two parts head made of iron and wooden handle. (5 marks each = Total 10 marks)
LESSON 14
TOPIC: Woodwork tools: Holding devices, cutting and paring tools.
SUB-TOPICS:
(i) Holding devices
(ii) Cutting and paring tools.
Holding devices
Woodworking holding devices are the tools used to hold work piece on the workbench. Woodworkers work on workbenches. It is on these benches that various woodwork constructions are carried out. The centre of the bench is usually lower than its two sides. This area is called a ‘well’ and its function is to accommodate the tools brought from the tool cupboard to the bench top during operations. The tools cannot fall or roll on to the floor or on anyone’s feet because this part is lower than other area of the bench.
The fittings are:
1. Bench vice: also called fitter’s vice. It is used to clamp or to hold jobs when the following operations are to be carried out on the bench, filling, bending, tapping, cutting, assembling parts etc.

Other types of vice are:
Hand vice: used for holding work when performing operations such as drilling, riveting etc
Machine vice: It is fixed to the table of any machine tool.

The Care of the Vice
a. Always keep the vice clean.
b. The thread or the screw inside the vice should be oiled regularly.
c. Do not use the vice as an anvil for hammering a job
d. Always use hand force only to tighten the vice for holding the work piece.
2. Bench Stop – There are many types of bench stops. Some are made of wood while some are made of metals. It is a small strip of wood fixed on top of the bench. It is used to prevent wood from slipping off the bench top during planning.
3. Bench Hook – This is used for holding jobs during cutting and chiseling on the bench. At the same time, it protects the bench top.

4. The clamps
a. G-Clamp – This is a metal clamp used for clamping small jobs together. It is called a G-Clamp because of its shape which is in the form of letter ‘G’. The clamp is ideal for holding small pieces of wood together.

b. F-Clamp – This is used like the G-Clamp. The clamp is in the form of letter ‘F’.
c. Sash-Clamp – it is a larger clamp used for holding and drawing woods tightly together when assembling or gluing work.

Cutting and Paring tools
Saws and Planes are used in cutting and smoothing wood in the workshop respectively. Saws are tools used for cutting wood. There are two main groups of saws: bench saw and curve cutting saws.

Curve cutting saws are:

1. Coping Saw – This is used for cutting curve marked lines of wood. The blades can be adjusted to cut in any direction.
2. Fret Saw – This is used to cut curves in thin wood of 8mm thick or less. It is used to cut plywood.
3. Bow Saw – is used to cut along curve marked lines but the wood has to be 50mm thick.
4. Compass Saw – It is used for cutting large interior curves.
5. Keyhole – It is used mainly for internal curves where the bow saw cannot be used.
6. Rip Saw – Is used for cutting along the grain of the wood.
7. Tenon saw – Is used for cutting shoulders to tenon and recesses in board
8. Dovetail saw – Is also similar to tenon saw but it is much shorter. It is used for cutting fine joints and also light sawing.
9. Panel Saw – Is used for sawing thin timber across the wood.
10. Cross-cut saw – Is used for cutting across the grain.
Types and Uses of planes
Bench planes are used to obtain a good, smooth surface and to get the correct size required. Bench planes are:

1. Jack Plane – It is used to smoothen or remove marks from timber. It is used to dress the surface and edges.
2. Trying plane – It is used to produce flat surface and perfectly straight edges.
3. Smoothing plane – It is used for clearing the surfaces and edges of timbers ready for assembling.

4. Block plane – It is used for planing small work that is not easily accessible.
5. Spoke shave – This is an example of a curve cutting plane used to produce smooth curve surfaces and edges.

EVALUATION
1. Explain the three types of clamp
2. Explain the structure of a workbench
3. What is the main use of a saw?
4. Mention 8 curve cutting saws
READING ASSIGNMENT – Students should read about concept of energy and power
TEXT: NERDC Basic Technology for Junior Secondary School 1 Chapter 9, Pages 70-78
ASSIGNMENT –
1. _________ is used for holding jobs during cutting and chiseling on the bench
2. _________ is used to prevent wood from slipping off the bench top during planning
3. _________ is made of cast iron, it is used to hold work piece securely while working
4. _________ is ideal for holding small pieces of wood together
5. ________ is used for holding and drawing woods tightly together when gluing work
THEORY
1. List three different types of clamps you know.
2. Mention three fittings in work bench.
MARKING SCHEME
1. Bench hook
2. Bench stop
3. Vice
4. G-clamp
5. Sash-clamp
WEEK 5
LESSON 15
MAIN TOPIC : Processing of Wood
SPECIFIC TOPIC : Processing of wood
REFERENCE BK :Basic technology for JSS by Evans and Nation Building Basic Technology by E.K AJAYI.
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVES: At the end of the lesson the students should be able to:
(1) Mention the steps in the processing of wood
(2) Explain the steps in processing of wood
CONTENT
The steps in processing of wood includes:-
Felling of tree
Wood conversion
Wood seasoning
Wood preservation
Felling of tree:- simply means cutting down of tree. Felling of trees is carried out with the use of chain saw.

In Nigeria Felling of tree is carried out in two places:-
I. Forest Reserve area : a reserved place by government where trees are planted, to cut down tree in this place the timber contractor will pay an amount called OTV out turn volume it means that they will pay for the volume of trees they take.
II. Free Area:- this is an area outside the Forest area e.g. farmland. To cut down tree in this area the amount paid is called Tariff which is paid to the government to obtain permit to cut the tree.
https://drive.google.com/file/d/11haSAA ... sp=sharing
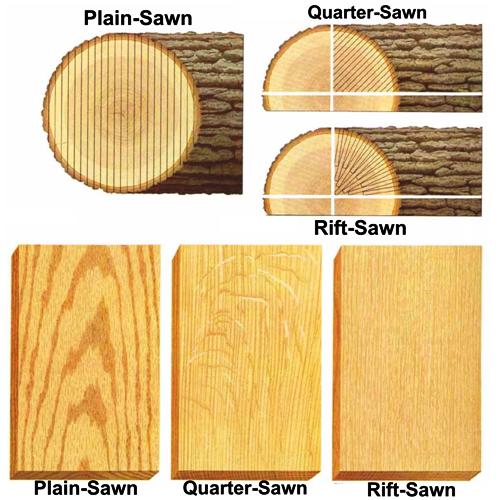
Wood conversion:-is the process of splitting the log into marketable sizes.

There are two methods of wood conversion
a. Plain sawn or tangential method or through and through methods
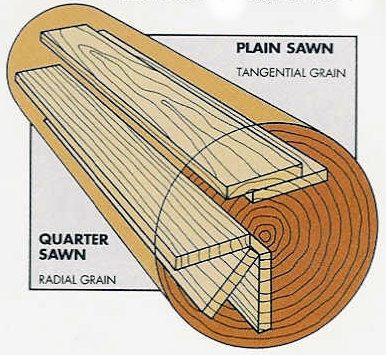
b. Quarter sawn.

EVALUATION/CLASSWORK
Mention the steps in processing of wood
Explain felling of tree and wood conversion
LESSON 16
SPECIFIC TOPIC : Processing of Rubber
REFERENCE BK :Basic technology for JSS by Evans and Nation Building Basic Technology by E.K AJAYI.
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVE : At the end of the lesson the students should be able to:
(1) explain the two types of rubber
(2) state the uses of rubber
CONTENT : RUBBER
Rubber, natural or synthetic substance characterized by elasticity, water repellent, and electrical resistance. Natural rubber is obtained from the milky white fluid called latex, found in many plants; synthetic rubbers are produced from unsaturated hydrocarbons.
Two types of rubber
1. Natural rubber.
2. Synthetic
Natural rubber, also called caoutchouc, is an elastomer (an elastic hydrocarbon polymer) that was originally derived from latex, a milky produced by rubber tree. The plants would be "tapped", that is, an incision made into the bark of the tree and the latex sap collected and refined into a usable rubber. The purified form of natural rubber is that which can also be produced synthetically. Natural rubber is used extensively in many applications and products, Natural rubber is an elastomer and a thermoplastic. However, it should be noted that once the rubber is vulcanized, it will turn into a thermo set. Most rubber in everyday use is vulcanized to a point where it shares properties of both; i.e., if it is heated and cooled, it is degraded but not destroyed.
https://drive.google.com/file/d/1RyW4UP ... sp=sharing
Vulcanized rubber: is the rubber treated with sulphur at high temperature in other to make it harder.

view picture below
https://drive.google.com/file/d/0Bz3Mh6 ... sp=sharing
Further Studies
EVALUATION/CLASSWORK
Explain processing of rubber.
Explain natural rubber
Mention uses of rubber.
LESSON 17
MAIN TOPIC : Processing of Materials
SPECIFIC TOPIC : Processing of Rubber
REFERENCE BOOK : Basic technology for JSS by Evans and Nation Building Basic Technology by E.K AJAYI.
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVE : At the end of the lesson the students should be able to:
(1) Explain the processing of rubber
(2) mention of rubber processing
CONTENT
Synthetic Rubber : is made petroleum . Synthetic rubbers are produced from unsaturated hydrocarbons

PROPERTIES OF RUBBER
1. Elastic - the ability to extend beyond its original state and return to its original state

2. Water resistance-ability to resist water from passing through
3. Rubber is light in weight and will float when put in water.
4. Poor conductor of electricity.-ability to resist the flow of electricity
USES OF RUBBER
The uses of rubber includes the following :
Tyre
Bumpers
Absorbers
Containers
Floaters
Electric insulators
Rubber Shoes and Sandal
Rubber Football
EVALUATION/CLASSWORK
1. Explain the processing of rubber.
2. Mention two types of rubber
practice test
http://science.howstuffworks.com/rubber-quiz.htm
MAIN TOPIC : Processing of Wood
SPECIFIC TOPIC : Processing of wood
REFERENCE BK :Basic technology for JSS by Evans and Nation Building Basic Technology by E.K AJAYI.
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVES: At the end of the lesson the students should be able to:
(1) Mention the steps in the processing of wood
(2) Explain the steps in processing of wood
CONTENT
The steps in processing of wood includes:-
Felling of tree
Wood conversion
Wood seasoning
Wood preservation
Felling of tree:- simply means cutting down of tree. Felling of trees is carried out with the use of chain saw.

In Nigeria Felling of tree is carried out in two places:-
I. Forest Reserve area : a reserved place by government where trees are planted, to cut down tree in this place the timber contractor will pay an amount called OTV out turn volume it means that they will pay for the volume of trees they take.
II. Free Area:- this is an area outside the Forest area e.g. farmland. To cut down tree in this area the amount paid is called Tariff which is paid to the government to obtain permit to cut the tree.
https://drive.google.com/file/d/11haSAA ... sp=sharing
Wood conversion:-is the process of splitting the log into marketable sizes.

There are two methods of wood conversion
a. Plain sawn or tangential method or through and through methods

b. Quarter sawn.

EVALUATION/CLASSWORK
Mention the steps in processing of wood
Explain felling of tree and wood conversion
LESSON 16
SPECIFIC TOPIC : Processing of Rubber
REFERENCE BK :Basic technology for JSS by Evans and Nation Building Basic Technology by E.K AJAYI.
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVE : At the end of the lesson the students should be able to:
(1) explain the two types of rubber
(2) state the uses of rubber
CONTENT : RUBBER
Rubber, natural or synthetic substance characterized by elasticity, water repellent, and electrical resistance. Natural rubber is obtained from the milky white fluid called latex, found in many plants; synthetic rubbers are produced from unsaturated hydrocarbons.
Two types of rubber
1. Natural rubber.
2. Synthetic
Natural rubber, also called caoutchouc, is an elastomer (an elastic hydrocarbon polymer) that was originally derived from latex, a milky produced by rubber tree. The plants would be "tapped", that is, an incision made into the bark of the tree and the latex sap collected and refined into a usable rubber. The purified form of natural rubber is that which can also be produced synthetically. Natural rubber is used extensively in many applications and products, Natural rubber is an elastomer and a thermoplastic. However, it should be noted that once the rubber is vulcanized, it will turn into a thermo set. Most rubber in everyday use is vulcanized to a point where it shares properties of both; i.e., if it is heated and cooled, it is degraded but not destroyed.
https://drive.google.com/file/d/1RyW4UP ... sp=sharing
Vulcanized rubber: is the rubber treated with sulphur at high temperature in other to make it harder.

view picture below
https://drive.google.com/file/d/0Bz3Mh6 ... sp=sharing
Further Studies
EVALUATION/CLASSWORK
Explain processing of rubber.
Explain natural rubber
Mention uses of rubber.
LESSON 17
MAIN TOPIC : Processing of Materials
SPECIFIC TOPIC : Processing of Rubber
REFERENCE BOOK : Basic technology for JSS by Evans and Nation Building Basic Technology by E.K AJAYI.
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVE : At the end of the lesson the students should be able to:
(1) Explain the processing of rubber
(2) mention of rubber processing
CONTENT
Synthetic Rubber : is made petroleum . Synthetic rubbers are produced from unsaturated hydrocarbons

PROPERTIES OF RUBBER
1. Elastic - the ability to extend beyond its original state and return to its original state

2. Water resistance-ability to resist water from passing through
3. Rubber is light in weight and will float when put in water.
4. Poor conductor of electricity.-ability to resist the flow of electricity
USES OF RUBBER
The uses of rubber includes the following :
Tyre
Bumpers
Absorbers
Containers
Floaters
Electric insulators
Rubber Shoes and Sandal
Rubber Football
EVALUATION/CLASSWORK
1. Explain the processing of rubber.
2. Mention two types of rubber
practice test
http://science.howstuffworks.com/rubber-quiz.htm
WEEK 6
LESSON 18
SPECIFIC TOPIC : Workbench
REFERENCE BK : Basic technology for JSS by Evans and Nation Building Basic Technology by E.K AJAYI.
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVES: At the end of the lesson the students should be able to:
(1) Describe a workbench
(2) State the functions of a work bench
CONTENT
Workbench is the carpenter's table where all the wood work operations are carried out. A wood worker cannot perform any operation satisfactorily. The centre of the bench is usually lower than its two sides. This area is called a WELL and its function is to accommodate the tools brought from the cupboard or the shelf during operations. Being lower the tools cannot fall or roll on the floor or on anyone's feet.
Fittings are attached to the work bench for proper woodwork operation.
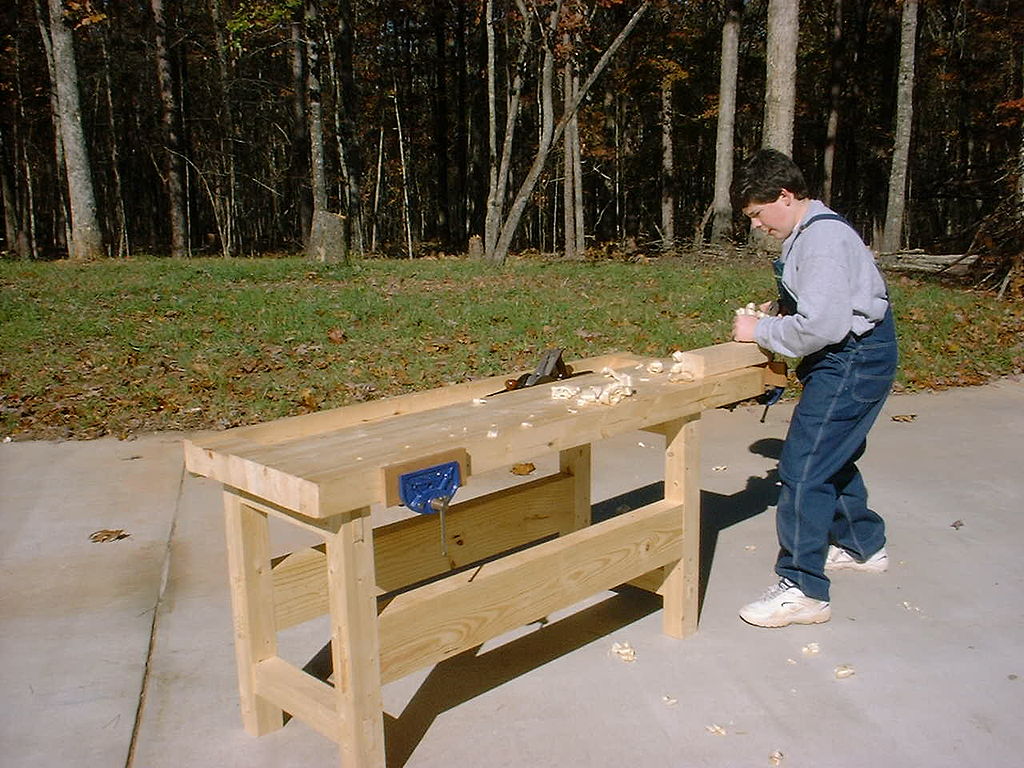

THE COMMON WORKBENCH FITTINGS
1. VICE
2. G.CLAMP
3. F.CLAMP
4. BENCH STOP
5. BENCH HOOK
6. SASH CLAMP
EVALUATION/CLASSWORK
Draw all the work bench fittings
LESSON 19
MAIN TOPIC : Workbench and Fitting
SPECIFIC TOPIC : Fittings
REFERENCE BK : Basic technology for JSS by Evans and Nation Building Basic1
Technology by E.K AJAYI.
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVES: At the end of the lesson the students should be able to:
(1)mention all the workbench fittings
(2)explain the function of the fittings
CONTENT :
Workbench fittings are:
1. Vice: This is fixed to the side of the bench, it is used for holding wood for operation such as planning and chiseling. It is made of metal and possesses a release lever which allows quick movement and grip.
https://youtu.be/4wmf5PVQZn8
2. G-clamp: This is a metal clamp used for holding small jobs to the bench while sawing or chiseling. It can also be used to hold other small jobs together because of its shape .It is in the form of letter G.

3. F. clamp: This is used like the G. clamp. It has quick action adjustment. The clamp is in the form of letter F.

4. Sash clamp : This is a larger clamp used for holding and drawing woods tightly together when assembling or gluing work. Sash clamps are available in several sizes.

5. Bench stop: There are many types of bench stops. Some are made of wood while some are made of metal. Bench stop is a small strip of wood fixed on top of the bench to prevent wood from slipping off the top during planning.

6. Bench Hook : This is used for holding jobs during cutting and chiseling on the bench. At the same it protects the bench top.
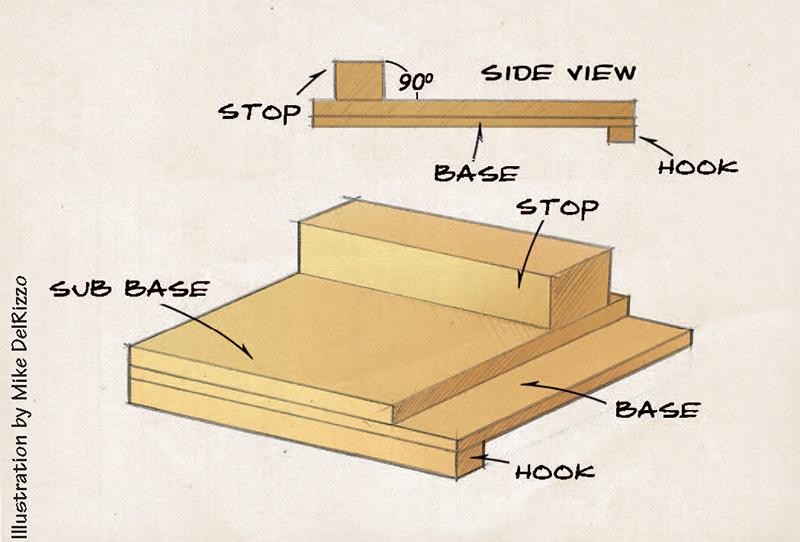
https://youtu.be/eBYG6OGGqcU
EVALUATION
1. Mention all the workbench fittings
2. Explain the functions of all workbench fittings
Watch video of workbench & fittings
https://youtu.be/3II1qLWOpRE
Further Studies
LESSON 20
MAIN TOPIC : Woodwork Appliance
SPECIFIC TOPIC : Saws
REFERENCE BK :Basic technology for JSS by Evans and Nation Building Basic Technology by E.K AJAYI.
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVES: At the end of the lesson the students should be able to:
I. State the meaning and uses of saw
II. Mention types of wood work saws
CONTENT
WOODWORK APPLIANCES
Saw: - a saw is a tool used for sawing or cutting wood into two or more parts . The teeth of saws are set alternately left and right to allow for clearance. There are different types of saws designed to perform different jobs.
The main types of woodwork hand saws are:
1) Rip saw
2) Crosscut saw
3) Panel saw
4) Tenor saw
5) Dovetail saw
6) Copping saw
7) Fret saw
8) Bow saw
EVALUATION/CLASSWORK
1. Describe Saw
2. Mention types of saws
ASSIGNMENT:
Draw all the types of woodwork hand saws
further studies
http://pinterest.com/teachcooklove/kids ... ing-tools/
http://woodworking-kids.com/
http://thejoyofwoodforkids.blogspot.com ... -wood.html
Watch Video
https://youtu.be/UUbOk36IPCg
LESSON 21
MAIN TOPIC : Woodwork appliances
SPECIFIC TOPIC : Types of woodwork hand saws
REFERENCE BK :Basic technology for JSS by Evans and Nation Building Basic Technology by E.K AJAYI.
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVE: At the end of the lesson the students should be able to:
i. Mention the types of woodwork hand saws
ii. State the function of the saws
CONTENT
RIP SAW: - This is used for sawing along the grain of wood, is the longest of all the saws.
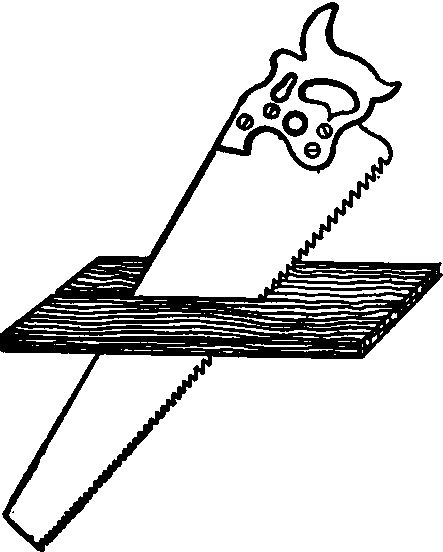

CROSS-CUT SAW: - This saw is used for cutting wood across the grain.

PANEL SAW: - This is a saw that is capable of doing the work of rip saw and crosscut saw. It is an all purpose saw.

FRET SAW: - This saw is used for complex shapes and curves in plywood and veneers. The blade of this saw is finer than that of the copping saw.
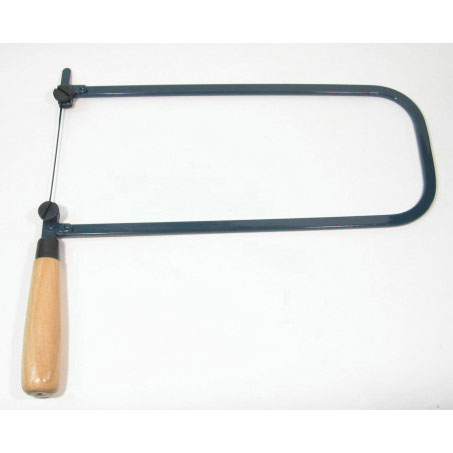

http://www.technologystudent.com/equip1/fretsw1.htm
COPPING SAW: - This saw is used for cutting accurate curves in thin wood and plywood. The blade can be adjusted to cut in any direction.
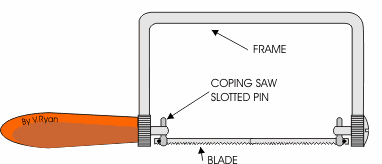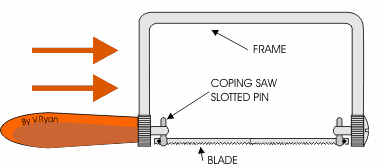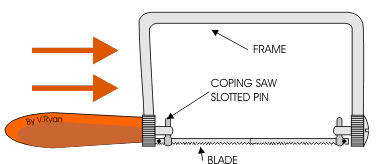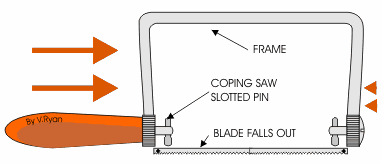
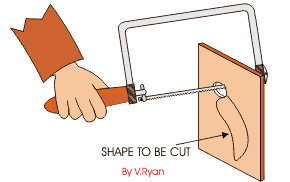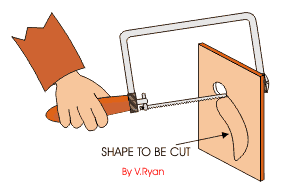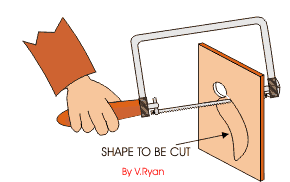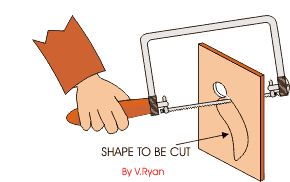
TENON SAW: - The tenon saw is used for cutting tenon joints and other small jobs on the bench.
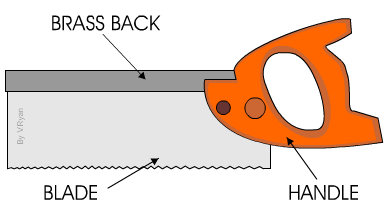
DOVETAIL SAW: - This saw is used for dovetailing and other small jobs on the bench. It is the smaller version of Tenon saw but has an open handle.
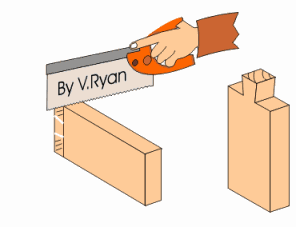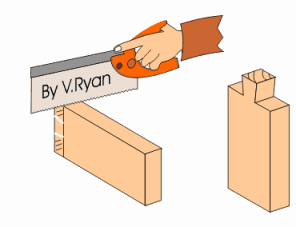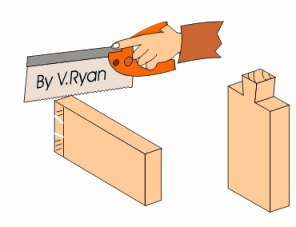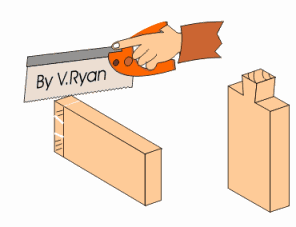
BOW SAW: - This saw is used for cutting circular or semi-circular curves. The blade can be turned to any direction by just moving the knob round.

EVALUATION/CLASSWORK
i. Mention all the woodwork hand saws
ii. State the function of these saws
further studies
http://home.howstuffworks.com/ripsaw.htm
http://home.howstuffworks.com/crosscut-saw.htm
http://www.woodworkbasics.com/hand-tools.html
Practice Test
http://www.proprofs.com/quiz-school/qui ... &quesnum=1
http://www.quia.com/quiz/1122314.html?A ... 1355849810
http://www.allthetests.com/quiz26/quiz/ ... rkers-quiz
SPECIFIC TOPIC : Workbench
REFERENCE BK : Basic technology for JSS by Evans and Nation Building Basic Technology by E.K AJAYI.
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVES: At the end of the lesson the students should be able to:
(1) Describe a workbench
(2) State the functions of a work bench
CONTENT
Workbench is the carpenter's table where all the wood work operations are carried out. A wood worker cannot perform any operation satisfactorily. The centre of the bench is usually lower than its two sides. This area is called a WELL and its function is to accommodate the tools brought from the cupboard or the shelf during operations. Being lower the tools cannot fall or roll on the floor or on anyone's feet.
Fittings are attached to the work bench for proper woodwork operation.

THE COMMON WORKBENCH FITTINGS
1. VICE
2. G.CLAMP
3. F.CLAMP
4. BENCH STOP
5. BENCH HOOK
6. SASH CLAMP
EVALUATION/CLASSWORK
Draw all the work bench fittings
LESSON 19
MAIN TOPIC : Workbench and Fitting
SPECIFIC TOPIC : Fittings
REFERENCE BK : Basic technology for JSS by Evans and Nation Building Basic1
Technology by E.K AJAYI.
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVES: At the end of the lesson the students should be able to:
(1)mention all the workbench fittings
(2)explain the function of the fittings
CONTENT :
Workbench fittings are:
1. Vice: This is fixed to the side of the bench, it is used for holding wood for operation such as planning and chiseling. It is made of metal and possesses a release lever which allows quick movement and grip.
https://youtu.be/4wmf5PVQZn8
2. G-clamp: This is a metal clamp used for holding small jobs to the bench while sawing or chiseling. It can also be used to hold other small jobs together because of its shape .It is in the form of letter G.

3. F. clamp: This is used like the G. clamp. It has quick action adjustment. The clamp is in the form of letter F.

4. Sash clamp : This is a larger clamp used for holding and drawing woods tightly together when assembling or gluing work. Sash clamps are available in several sizes.

5. Bench stop: There are many types of bench stops. Some are made of wood while some are made of metal. Bench stop is a small strip of wood fixed on top of the bench to prevent wood from slipping off the top during planning.

6. Bench Hook : This is used for holding jobs during cutting and chiseling on the bench. At the same it protects the bench top.

https://youtu.be/eBYG6OGGqcU
EVALUATION
1. Mention all the workbench fittings
2. Explain the functions of all workbench fittings
Watch video of workbench & fittings
https://youtu.be/3II1qLWOpRE
Further Studies
LESSON 20
MAIN TOPIC : Woodwork Appliance
SPECIFIC TOPIC : Saws
REFERENCE BK :Basic technology for JSS by Evans and Nation Building Basic Technology by E.K AJAYI.
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVES: At the end of the lesson the students should be able to:
I. State the meaning and uses of saw
II. Mention types of wood work saws
CONTENT
WOODWORK APPLIANCES
Saw: - a saw is a tool used for sawing or cutting wood into two or more parts . The teeth of saws are set alternately left and right to allow for clearance. There are different types of saws designed to perform different jobs.
The main types of woodwork hand saws are:
1) Rip saw
2) Crosscut saw
3) Panel saw
4) Tenor saw
5) Dovetail saw
6) Copping saw
7) Fret saw
8) Bow saw
EVALUATION/CLASSWORK
1. Describe Saw
2. Mention types of saws
ASSIGNMENT:
Draw all the types of woodwork hand saws
further studies
http://pinterest.com/teachcooklove/kids ... ing-tools/
http://woodworking-kids.com/
http://thejoyofwoodforkids.blogspot.com ... -wood.html
Watch Video
https://youtu.be/UUbOk36IPCg
LESSON 21
MAIN TOPIC : Woodwork appliances
SPECIFIC TOPIC : Types of woodwork hand saws
REFERENCE BK :Basic technology for JSS by Evans and Nation Building Basic Technology by E.K AJAYI.
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVE: At the end of the lesson the students should be able to:
i. Mention the types of woodwork hand saws
ii. State the function of the saws
CONTENT
RIP SAW: - This is used for sawing along the grain of wood, is the longest of all the saws.


CROSS-CUT SAW: - This saw is used for cutting wood across the grain.

PANEL SAW: - This is a saw that is capable of doing the work of rip saw and crosscut saw. It is an all purpose saw.

FRET SAW: - This saw is used for complex shapes and curves in plywood and veneers. The blade of this saw is finer than that of the copping saw.

http://www.technologystudent.com/equip1/fretsw1.htm
COPPING SAW: - This saw is used for cutting accurate curves in thin wood and plywood. The blade can be adjusted to cut in any direction.


TENON SAW: - The tenon saw is used for cutting tenon joints and other small jobs on the bench.

DOVETAIL SAW: - This saw is used for dovetailing and other small jobs on the bench. It is the smaller version of Tenon saw but has an open handle.

BOW SAW: - This saw is used for cutting circular or semi-circular curves. The blade can be turned to any direction by just moving the knob round.

EVALUATION/CLASSWORK
i. Mention all the woodwork hand saws
ii. State the function of these saws
further studies
http://home.howstuffworks.com/ripsaw.htm
http://home.howstuffworks.com/crosscut-saw.htm
http://www.woodworkbasics.com/hand-tools.html
Practice Test
http://www.proprofs.com/quiz-school/qui ... &quesnum=1
http://www.quia.com/quiz/1122314.html?A ... 1355849810
http://www.allthetests.com/quiz26/quiz/ ... rkers-quiz
WEEK 7
LESSON 22
MAIN TOPIC : Woodwork appliances (planes)
SPECIFIC TOPIC : Planes
REFERENCE BK : Basic technology for JSS by Evans and Nation Building Basic Technology by E.K AJAYI.
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVE: At the end of the lesson the students should be able to:
i. Mention all the types of planes
ii. Demonstrate how to use the planes
CONTENT
Planes are tools or devices used to smooth the surfaces of wood.
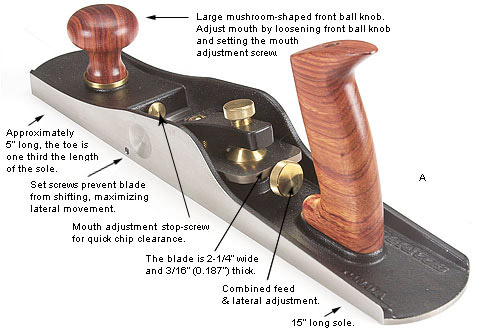
The common panes are :
i. Jack planes

ii. Smooth planes
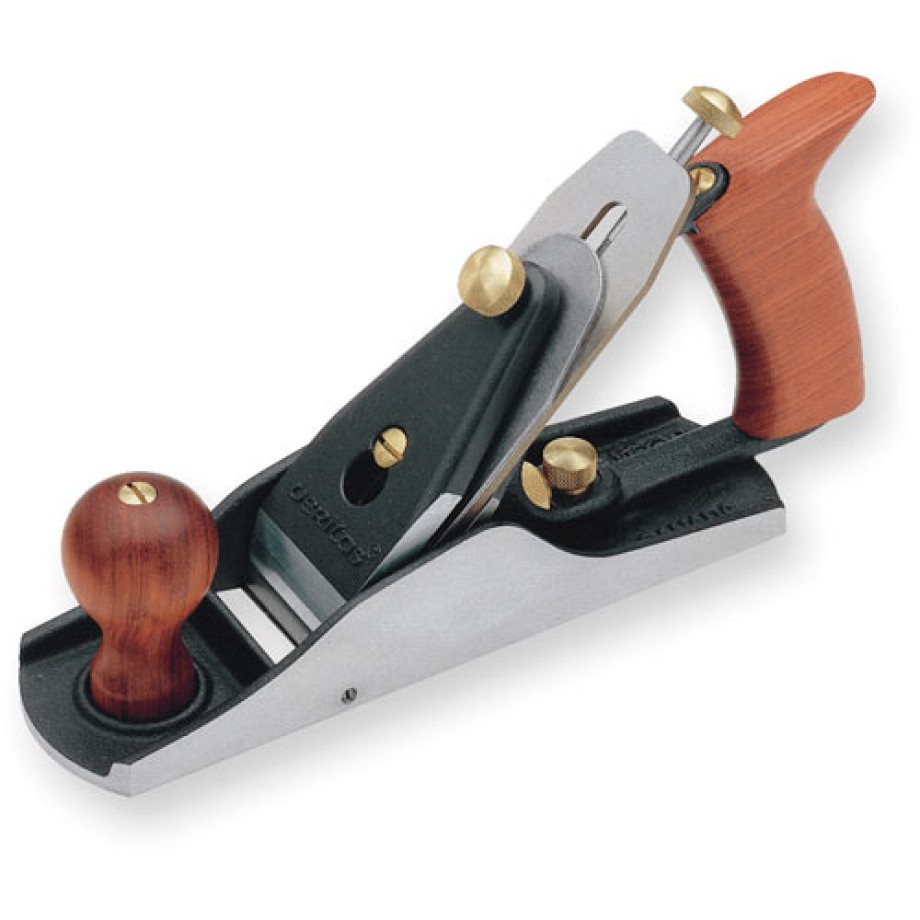

iii. Trying planes

iv. Spoke shaves
Jack planes are devices used for removing roughness from wood in other to prepare the timber to size. The length of the plane is between 290-380mm.
Smoothing planes are the tools used to smoothing the surfaces of wood .This planes are used to plane wood to the finer finish.
Spokeshaves are used to plane the edges of wood.
There are two types of spokeshaves
i. Flat face for convex shapes
ii. Round or curved face for concave
https://youtu.be/-YkNA24s4Ho
https://youtu.be/2ArFvwIQJ-4
EVALUATION/CLASSWORK
Describe planes
Mention the types of planes
ASSIGNMENT:
Draw the types of planes
further studies
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Plane_(tool)
practice test
http://www.proprofs.com/quiz-school/qui ... &quesnum=1
LESSON 23
MAIN TOPIC : Miscellaneous construction
SPECIFIC TOPIC : Locate the centre of a circle
REFERENCE BK :Basic technology for JSS by Evans and Nation Building Basic Technology by E.K AJAYI.
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVES: At the end of the lesson the students should be able to:
i. Describe a circle
ii. State the parts of a circle
CONTENT
Circle is a plane figure bounded by a curve line called circumference, which is always equidistance from the centre.
3
A diameter is a straight line drawn through the center, meeting the circumference at both side.
A radius is a straight line drawn from the center to the circumference.
An arc is any part of the circumference.
A chord is any straight line drawn across the circle, meeting the circumference at both ends.
A tangent is a straight line which touches the circumference. It is always at the right angles to the radius.
A segment is part of a circle bounded by an arc and a chord.
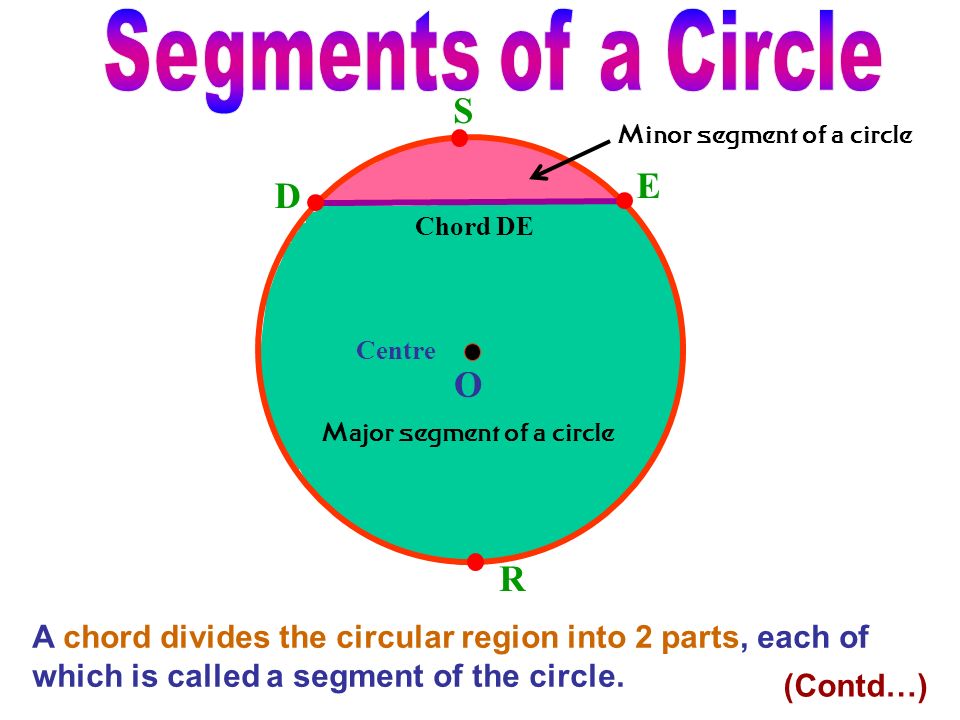
A sector is part of a circle bounded by two radii and an arc.
A quadrant is part of a circle bounded by two radii at right and an arc.
EVALUATION/CLASSWORK
Describe a circle
Mention all the parts of a circle
https://youtu.be/e2SnY19G5cM
https://youtu.be/xST3QUCjFBA
ASSIGNMENT: draw a circle and label all its parts
further studies
http://www.mathopenref.com/printinsquare.html
MAIN TOPIC : Woodwork appliances (planes)
SPECIFIC TOPIC : Planes
REFERENCE BK : Basic technology for JSS by Evans and Nation Building Basic Technology by E.K AJAYI.
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVE: At the end of the lesson the students should be able to:
i. Mention all the types of planes
ii. Demonstrate how to use the planes
CONTENT
Planes are tools or devices used to smooth the surfaces of wood.

The common panes are :
i. Jack planes

ii. Smooth planes

iii. Trying planes

iv. Spoke shaves

Jack planes are devices used for removing roughness from wood in other to prepare the timber to size. The length of the plane is between 290-380mm.
Smoothing planes are the tools used to smoothing the surfaces of wood .This planes are used to plane wood to the finer finish.
Spokeshaves are used to plane the edges of wood.
There are two types of spokeshaves
i. Flat face for convex shapes
ii. Round or curved face for concave
https://youtu.be/-YkNA24s4Ho
https://youtu.be/2ArFvwIQJ-4
EVALUATION/CLASSWORK
Describe planes
Mention the types of planes
ASSIGNMENT:
Draw the types of planes
further studies
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Plane_(tool)
practice test
http://www.proprofs.com/quiz-school/qui ... &quesnum=1
LESSON 23
MAIN TOPIC : Miscellaneous construction
SPECIFIC TOPIC : Locate the centre of a circle
REFERENCE BK :Basic technology for JSS by Evans and Nation Building Basic Technology by E.K AJAYI.
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVES: At the end of the lesson the students should be able to:
i. Describe a circle
ii. State the parts of a circle
CONTENT
Circle is a plane figure bounded by a curve line called circumference, which is always equidistance from the centre.
3
A diameter is a straight line drawn through the center, meeting the circumference at both side.

A radius is a straight line drawn from the center to the circumference.

An arc is any part of the circumference.

A chord is any straight line drawn across the circle, meeting the circumference at both ends.

A tangent is a straight line which touches the circumference. It is always at the right angles to the radius.

A segment is part of a circle bounded by an arc and a chord.

A sector is part of a circle bounded by two radii and an arc.

A quadrant is part of a circle bounded by two radii at right and an arc.

EVALUATION/CLASSWORK
Describe a circle
Mention all the parts of a circle
https://youtu.be/e2SnY19G5cM
https://youtu.be/xST3QUCjFBA
ASSIGNMENT: draw a circle and label all its parts
further studies
http://www.mathopenref.com/printinsquare.html
WEEK 8
LESSON 24
MAIN TOPIC : Metalwork hand tools
SPECIFIC TOPIC : Metalwork cutting Tools
REFERENCE BK : Basic technology for JSS by Evans and Nation Building Basic Technology by E.K AJAYI.
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVES: At the end of the lesson the students should be able to:
(1) Mention all the groups of metalwork hand tools
(2) Mention and state the uses of all the cutting tools
CONTENT
Metal work tools are grouped into stages according their functions and these stages includes
I. Metalwork hand cutting tools
II. Measuring tools
III. Marking out tools
IV. Metal holding devices
Metalwork hand cutting tools are those tools for cutting metals, the common hand cutting tools are:
1. Chisel
2. Hack saw
3. Files
Chisels : are used for cutting metal, there are made of high carbon steel, there are four types of chisels :
I. Flat chisel: - for general work

II. Half round nose chisel:- for making oil grooves in shaft or in a hole
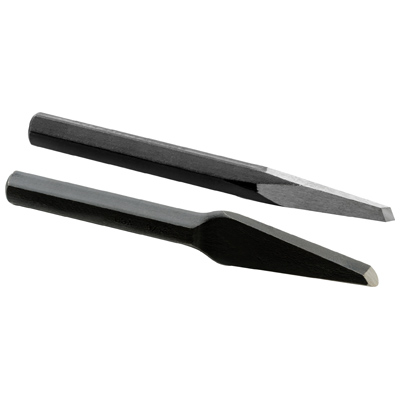

III. Cross cut chisel :- for making keyways and slots in shaft or in a hole

IV. Diamond nose chisel :- for chiseling inside corners and for cutting vee grooves

Hack saw: - is the chief tool for cutting metal and other engineering materials. There are two parts of hack saw (1) Hacksaw frame (2) Hacksaw blade and there are two types of hacksaw blade, the flexible and the all-hard blade.
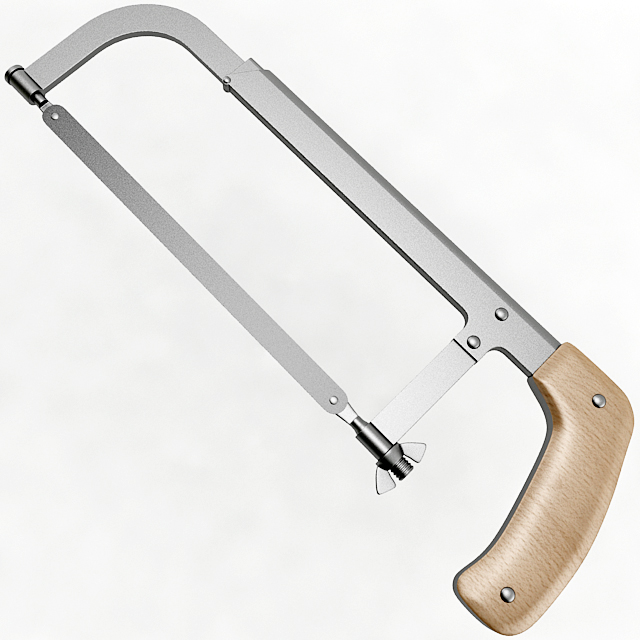

EVALUATION/CLASSWORK
Mention all the groups of metalwork hand tools
Mention and state the uses of all cutting tools
ASSIGNMENT:
Draw all the metal work cutting tools
further studies
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Category:M ... ting_tools
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Category:M ... hand_tools
http://www.technologystudent.com/equip_ ... cksw1.html
http://www.ehow.com/list_6539037_types- ... lades.html
LESSON 25
MAIN TOPIC : Metalwork hand Tools
SPECIFIC TOPIC : measuring tools
REFERENCE BK :Basic technology for JSS by Evans and Nation Building Basic Technology by E.K AJAYI.
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVES: At the end of the lesson the students should be able to:
(1) Mention all the driving tools
(2) State the functions of the driving tools
CONTENT
Measuring tools are tools for taking measurement. The common measuring instruments are:
1. Steel rule : for taking linear measurement
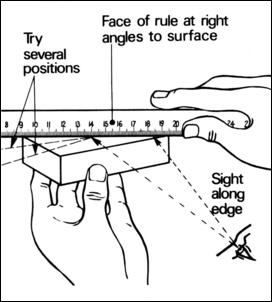
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=PoSQelBsLoY
2. Outside caliper : for measuring external diameter of a hole
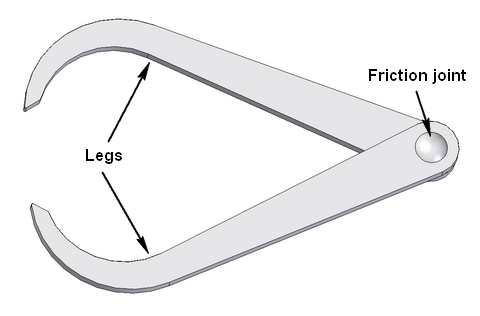
3. Inside caliper : for measuring internal diameter of a bar or the outside dimension of a work piece
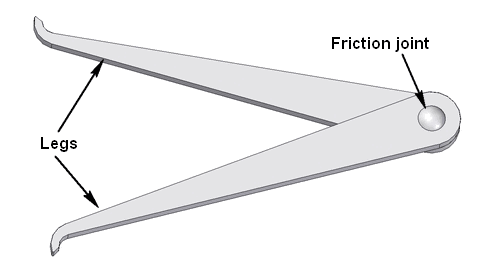
4. Vernier caliper : for measuring very small linear measurement
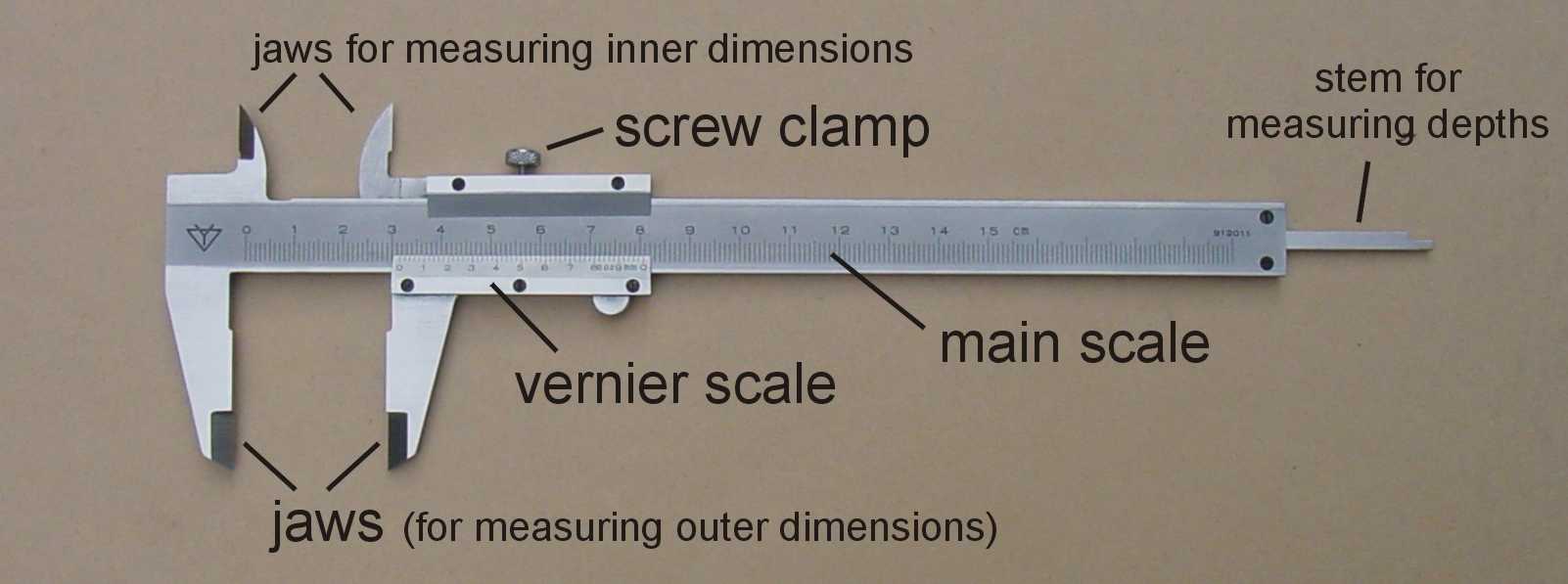
5. Centre Square : for testing for flatness and squareness of a work piece
6. Protractor : for measuring angles
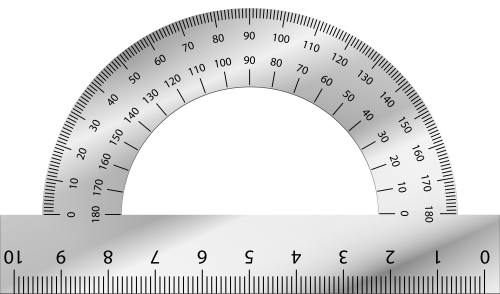
http://www.mathsisfun.com/geometry/prot ... using.html
7. Micrometre Screw Gauge : for measuring small diameter
EVALUATION/CLASSWORK
Describe measuring tools
Mention and state the functions of measuring tools
LESSON 26
MAIN TOPIC : Metalwork hand Tools
SPECIFIC TOPIC : Driving tools
REFERENCE BK :Basic technology for JSS by Evans and Nation Building Basic Technology by E.K AJAYI.
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVES: At the end of the lesson the students should be able to:
(1) Mention all the driving tools
(2) State the functions of the driving tools
CONTENT
Driving tools are the tools for driving or pushing in nails, screw and pins into wood, metal and other materials. The common driving tools are:
i. Hammer
ii. Punches
iii. Mallet
iv. Screw drivers
Hammers are used to drive in nails and pins into wood and other materials. There are different types of hammer
a. Ball Peen Hammer: for general purpose, the ball part is used for riveting
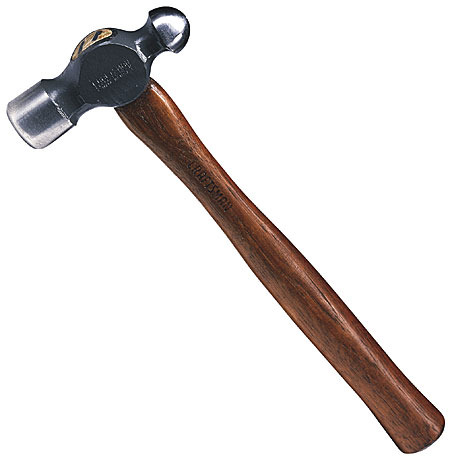

b. Straight Peen Hammer: it is used for riveting in awkward position, the other part is used for bending sheet metal.

c. Blocking Head Hammer: it is generally used for sheet metal work, the faces are well polished for shaping sheet metal.
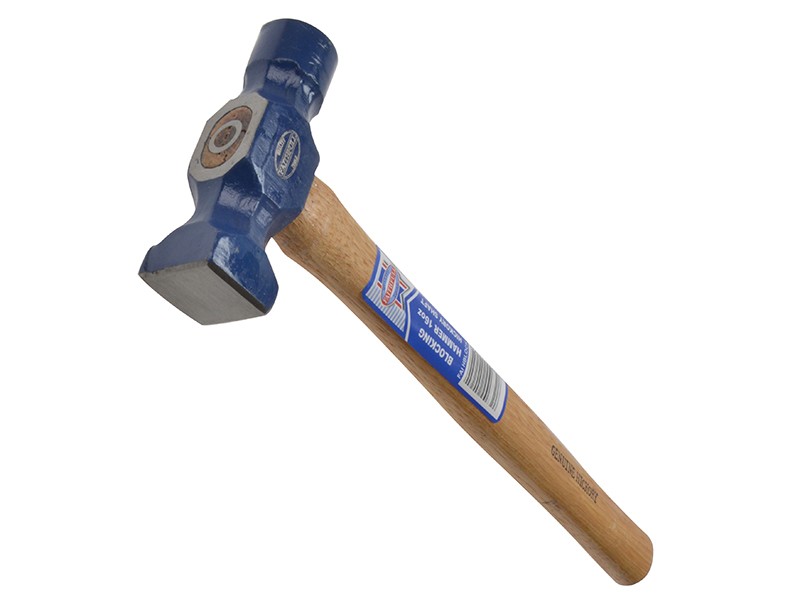

d. Cross peen Head Hammer: is used for drawing down and riveting.

e. Plainishing Head Hammer: this hammer is generally used by panel beater, one face is flat and the other convex .It is generally used for finishing.
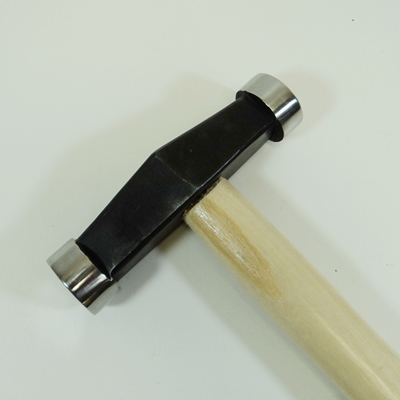

PUNCHES
Punches are used to drive nails and other fasteners below the surface of a work piece. In most cases punches are used along with hammer or mallet. There are three types of punches
1) Center punch
2) Pin punch
3) Bell punch
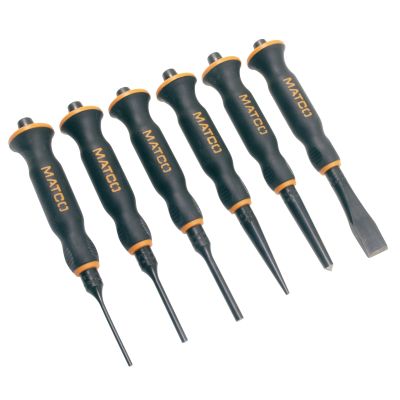

SCREW DRIVERS
Screw drivers are used to remove and tight screws, common types of screws are:
1. Flat screw drivers

2. Star screw drivers or Philips head screw driver

3. Offset screw drivers

4. Allen key screw drivers

EVALUATION/CLASSWORK
Describe driving tools
Mention and state the functions of driving tools
further studies
http://www.ehow.com/info-tip_8034733_wo ... tools.html
http://benjenkinsmaterialsprocesses.wee ... tools.html
http://benjenkinsmaterialsprocesses.wee ... tools.html
http://www.wagnermeters.com/top-40-wood ... -tools.php
http://www.woodworkbasics.com/hand-tools.html
practice test
http://www.mysafetysign.com/free-hand-a ... afety-quiz
http://www.the-warren.org/quiz/Metalwquiz.htm
MAIN TOPIC : Metalwork hand tools
SPECIFIC TOPIC : Metalwork cutting Tools
REFERENCE BK : Basic technology for JSS by Evans and Nation Building Basic Technology by E.K AJAYI.
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVES: At the end of the lesson the students should be able to:
(1) Mention all the groups of metalwork hand tools
(2) Mention and state the uses of all the cutting tools
CONTENT
Metal work tools are grouped into stages according their functions and these stages includes
I. Metalwork hand cutting tools
II. Measuring tools
III. Marking out tools
IV. Metal holding devices
Metalwork hand cutting tools are those tools for cutting metals, the common hand cutting tools are:
1. Chisel
2. Hack saw
3. Files
Chisels : are used for cutting metal, there are made of high carbon steel, there are four types of chisels :
I. Flat chisel: - for general work

II. Half round nose chisel:- for making oil grooves in shaft or in a hole

III. Cross cut chisel :- for making keyways and slots in shaft or in a hole

IV. Diamond nose chisel :- for chiseling inside corners and for cutting vee grooves

Hack saw: - is the chief tool for cutting metal and other engineering materials. There are two parts of hack saw (1) Hacksaw frame (2) Hacksaw blade and there are two types of hacksaw blade, the flexible and the all-hard blade.

EVALUATION/CLASSWORK
Mention all the groups of metalwork hand tools
Mention and state the uses of all cutting tools
ASSIGNMENT:
Draw all the metal work cutting tools
further studies
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Category:M ... ting_tools
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Category:M ... hand_tools
http://www.technologystudent.com/equip_ ... cksw1.html
http://www.ehow.com/list_6539037_types- ... lades.html
LESSON 25
MAIN TOPIC : Metalwork hand Tools
SPECIFIC TOPIC : measuring tools
REFERENCE BK :Basic technology for JSS by Evans and Nation Building Basic Technology by E.K AJAYI.
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVES: At the end of the lesson the students should be able to:
(1) Mention all the driving tools
(2) State the functions of the driving tools
CONTENT
Measuring tools are tools for taking measurement. The common measuring instruments are:
1. Steel rule : for taking linear measurement

http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=PoSQelBsLoY
2. Outside caliper : for measuring external diameter of a hole

3. Inside caliper : for measuring internal diameter of a bar or the outside dimension of a work piece

4. Vernier caliper : for measuring very small linear measurement

5. Centre Square : for testing for flatness and squareness of a work piece

6. Protractor : for measuring angles

http://www.mathsisfun.com/geometry/prot ... using.html
7. Micrometre Screw Gauge : for measuring small diameter

EVALUATION/CLASSWORK
Describe measuring tools
Mention and state the functions of measuring tools
LESSON 26
MAIN TOPIC : Metalwork hand Tools
SPECIFIC TOPIC : Driving tools
REFERENCE BK :Basic technology for JSS by Evans and Nation Building Basic Technology by E.K AJAYI.
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVES: At the end of the lesson the students should be able to:
(1) Mention all the driving tools
(2) State the functions of the driving tools
CONTENT
Driving tools are the tools for driving or pushing in nails, screw and pins into wood, metal and other materials. The common driving tools are:
i. Hammer
ii. Punches
iii. Mallet
iv. Screw drivers
Hammers are used to drive in nails and pins into wood and other materials. There are different types of hammer
a. Ball Peen Hammer: for general purpose, the ball part is used for riveting

b. Straight Peen Hammer: it is used for riveting in awkward position, the other part is used for bending sheet metal.

c. Blocking Head Hammer: it is generally used for sheet metal work, the faces are well polished for shaping sheet metal.

d. Cross peen Head Hammer: is used for drawing down and riveting.

e. Plainishing Head Hammer: this hammer is generally used by panel beater, one face is flat and the other convex .It is generally used for finishing.

PUNCHES
Punches are used to drive nails and other fasteners below the surface of a work piece. In most cases punches are used along with hammer or mallet. There are three types of punches
1) Center punch
2) Pin punch
3) Bell punch

SCREW DRIVERS
Screw drivers are used to remove and tight screws, common types of screws are:
1. Flat screw drivers

2. Star screw drivers or Philips head screw driver

3. Offset screw drivers

4. Allen key screw drivers

EVALUATION/CLASSWORK
Describe driving tools
Mention and state the functions of driving tools
further studies
http://www.ehow.com/info-tip_8034733_wo ... tools.html
http://benjenkinsmaterialsprocesses.wee ... tools.html
http://benjenkinsmaterialsprocesses.wee ... tools.html
http://www.wagnermeters.com/top-40-wood ... -tools.php
http://www.woodworkbasics.com/hand-tools.html
practice test
http://www.mysafetysign.com/free-hand-a ... afety-quiz
http://www.the-warren.org/quiz/Metalwquiz.htm
WEEK 9
LESSON 27
TOPIC: Energy and Power.
SUB-TOPICS:
(i) Concept of energy and power.
(ii) Forms of energy
(ii) Relationship between energy and power.
Concept of energy and power
Energy is defined as the ability to do work. Energy is not something we can touch or see. We can only see its effect. The standard unit for measuring energy is the Joule (J). It can also be measured in KiloJoule (KJ)
The following are the properties of energy:
- Energy exists in different forms. E.g. heat, chemical, kinetic etc
- Energy can neither be created nor destroyed.
- Energy can be converted from one form to another.eg electrical to heat as in pressing iron, chemical to heat as in gas cooker, etc
The concept of power is a scientific concept which makes it possible to rate appliances, machines and engineering system as regards to how they use energy or perform work. The concept of power can be specified as:
Electrical power: relates to electrical and electronics appliances and equipment. It is the rate at which electrical energy is consumed. It is measure in Watt (W).
Mechanical power relates to machines and mechanical system. Basically
Power = Energy/Time taken
Energy is used in the following ways:
Forms of Energy
The major forms of energy are:
1. Heat energy: This is the form of energy which leads to the rise in temperature of a body. It can be obtained from burning fire wood, coal, gas, kerosene e.tc. The heat generated from these sources is used mostly in cooking.

2. Mechanical energy: This is the energy of motion or potential for motion. Mechanical energy is used by falling objects, flying objects, flowing objects. There are two types of mechanical energy. These are :
Kinetic energy: energy possessed by a moving object. A hammer descending on a nail to drive it into wood has kinetic energy.
Potential energy: energy a body possesses because of its position. A body at a high position has higher potential energy than a body at a low position.
3. Electrical energy: this is the energy we use to operate electrical appliances like fans, radio, television set, electric irons etc. we obtain electrical energy from Power Holding Company of Nigeria which supplies electrical energy to our homes. We also obtain electrical energy from generators we use in our homes, batteries.

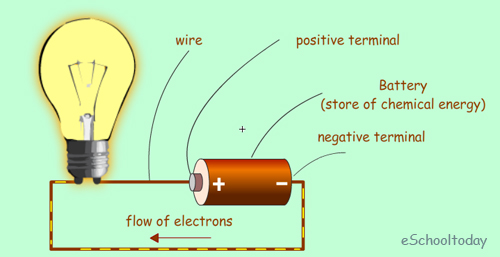
4. Chemical energy: this is the energy stored in chemical substances like food, kerosene, wood, animal dung, sawdust, etc. The chemical energy in the food produces muscular energy which keeps us going.
5. Sound energy: sound energy stimulates our ear and vibrates the air. Sound is energy because it vibrates the air and the vibrated air strikes our ear, which hear the sound.
6. Light / Solar energy:
Light / solar energy comes from the sun, which releases the energy through its rays. Solar energy from the sun dries clothes after they are washed. Without solar energy, photosynthesis cannot occur, without photosynthesis plants cannot grow, and without plants, human beings cannot and animals will not have food. Solar energy generates heat.
7. Nuclear energy: this is used to generate electricity in a nuclear power generating station. However, nuclear energy is very dangerous if not controlled. It can cause harm to both animals and plants. Hence nuclear power stations are not common.
EVALUATION
a. Define the term energy.
b. State the three properties of energy
c. Mention six major forms of energy
d. When fuel is burnt, the form of energy released is ---------
Relationship between energy and power
Work: Work is done when energy is used. To say that work is done means that a force has been used to move something through a distance. The force applied determines the amount of work done and the distance moved in the direction of the force. Work (w) is then a product of force (f) and distance (d).
It can be expressed as W = F x d.
The unit of force is Newton (N) while distance is measured in Newton metres (Nm) which is also called joule (j).
Power: is the rate at which work is done.
Power (P) = work done / Time taken
Power is measured Watt (w)
Example: A man lifts a load of 50kg from the ground to a height of 6metres within a time lift of 5 seconds. Calculate (i) the work done by the man.
(ii) The mechanical power consumed in lifting the load. Assuming g = 9.8m/s
SOLUTION
(i) Work done = force x distance
= 50 x 9.8 x 6
=2940 joules
=2.94KJ
(ii) Mechanical Power = work done
Time taken
= Force x distance /Time
= 50 x 9.8 x6 / 5
= 588watt.
EVALUATION
1a. List four forms of energy.
b. What is energy?
2. What is power?
3. Mention four sources of energy
READING ASSIGNMENT – Students should read over all the topics that have been thought for the preparation of their examination.
Further Study 1
Further Study 2
Further Study 3
TOPIC: Energy and Power.
SUB-TOPICS:
(i) Concept of energy and power.
(ii) Forms of energy
(ii) Relationship between energy and power.

Concept of energy and power
Energy is defined as the ability to do work. Energy is not something we can touch or see. We can only see its effect. The standard unit for measuring energy is the Joule (J). It can also be measured in KiloJoule (KJ)
The following are the properties of energy:
- Energy exists in different forms. E.g. heat, chemical, kinetic etc
- Energy can neither be created nor destroyed.
- Energy can be converted from one form to another.eg electrical to heat as in pressing iron, chemical to heat as in gas cooker, etc
The concept of power is a scientific concept which makes it possible to rate appliances, machines and engineering system as regards to how they use energy or perform work. The concept of power can be specified as:
Electrical power: relates to electrical and electronics appliances and equipment. It is the rate at which electrical energy is consumed. It is measure in Watt (W).
Mechanical power relates to machines and mechanical system. Basically
Power = Energy/Time taken
Energy is used in the following ways:
Forms of Energy
The major forms of energy are:
1. Heat energy: This is the form of energy which leads to the rise in temperature of a body. It can be obtained from burning fire wood, coal, gas, kerosene e.tc. The heat generated from these sources is used mostly in cooking.

2. Mechanical energy: This is the energy of motion or potential for motion. Mechanical energy is used by falling objects, flying objects, flowing objects. There are two types of mechanical energy. These are :
Kinetic energy: energy possessed by a moving object. A hammer descending on a nail to drive it into wood has kinetic energy.
Potential energy: energy a body possesses because of its position. A body at a high position has higher potential energy than a body at a low position.

3. Electrical energy: this is the energy we use to operate electrical appliances like fans, radio, television set, electric irons etc. we obtain electrical energy from Power Holding Company of Nigeria which supplies electrical energy to our homes. We also obtain electrical energy from generators we use in our homes, batteries.


4. Chemical energy: this is the energy stored in chemical substances like food, kerosene, wood, animal dung, sawdust, etc. The chemical energy in the food produces muscular energy which keeps us going.
5. Sound energy: sound energy stimulates our ear and vibrates the air. Sound is energy because it vibrates the air and the vibrated air strikes our ear, which hear the sound.
6. Light / Solar energy:
Light / solar energy comes from the sun, which releases the energy through its rays. Solar energy from the sun dries clothes after they are washed. Without solar energy, photosynthesis cannot occur, without photosynthesis plants cannot grow, and without plants, human beings cannot and animals will not have food. Solar energy generates heat.
7. Nuclear energy: this is used to generate electricity in a nuclear power generating station. However, nuclear energy is very dangerous if not controlled. It can cause harm to both animals and plants. Hence nuclear power stations are not common.
EVALUATION
a. Define the term energy.
b. State the three properties of energy
c. Mention six major forms of energy
d. When fuel is burnt, the form of energy released is ---------
Relationship between energy and power
Work: Work is done when energy is used. To say that work is done means that a force has been used to move something through a distance. The force applied determines the amount of work done and the distance moved in the direction of the force. Work (w) is then a product of force (f) and distance (d).
It can be expressed as W = F x d.
The unit of force is Newton (N) while distance is measured in Newton metres (Nm) which is also called joule (j).
Power: is the rate at which work is done.
Power (P) = work done / Time taken
Power is measured Watt (w)
Example: A man lifts a load of 50kg from the ground to a height of 6metres within a time lift of 5 seconds. Calculate (i) the work done by the man.
(ii) The mechanical power consumed in lifting the load. Assuming g = 9.8m/s
SOLUTION
(i) Work done = force x distance
= 50 x 9.8 x 6
=2940 joules
=2.94KJ
(ii) Mechanical Power = work done
Time taken
= Force x distance /Time
= 50 x 9.8 x6 / 5
= 588watt.
EVALUATION
1a. List four forms of energy.
b. What is energy?
2. What is power?
3. Mention four sources of energy
READING ASSIGNMENT – Students should read over all the topics that have been thought for the preparation of their examination.
Further Study 1
Further Study 2
Further Study 3