LESSON 4
TOPIC: WORKSHEET I
Definition of a Worksheet:
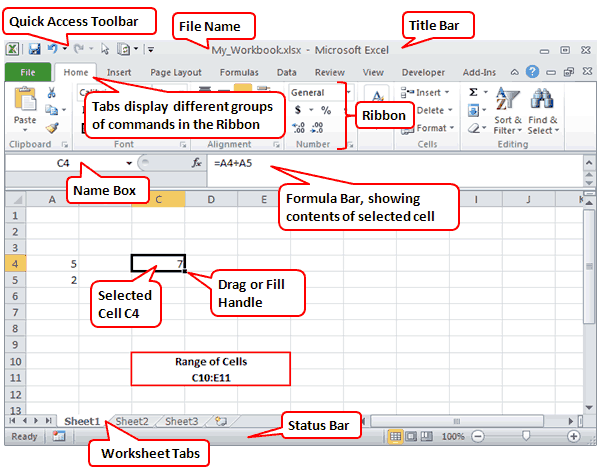
A Worksheet can be defined as the working area of the program where entering of data and calculations are handled. It consists of rows, columns, cells and a cell pointer.
Starting Excel worksheet: This entails the following
(i) opening a worksheet (ii) Data entry (iii) Editing (iv) saving (v) Retrieving worksheet
Opening a worksheet:
To create a new worksheet, follow the steps below:
Open Microsoft Excel from the Start button
Click on Office button to display a sub menu
Select New
Click on Create
A new workbook will be displayed.
Method II:
Open Microsoft Excel
Press Ctrl + N
Data Entry:
There are three types of data that can be entered into an excel worksheet. These are Labels, Numbers and Formula.
Labels are made up of texts that are entered into the active worksheet. Examples are letters of alphabets (A-Z)
Numbers / values consists of numerals 0 – 9
Formulas are mathematical expressions which return calculated value.
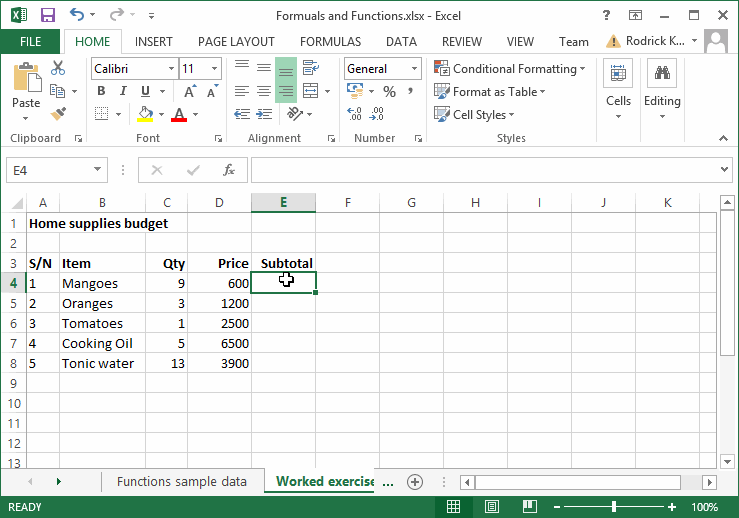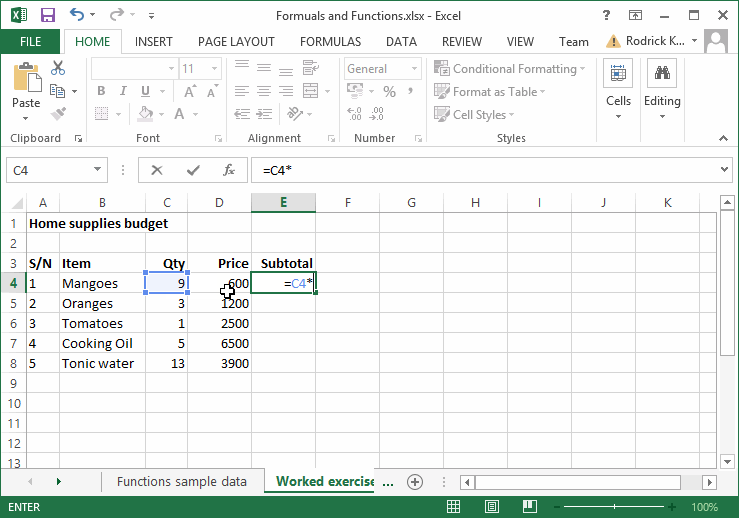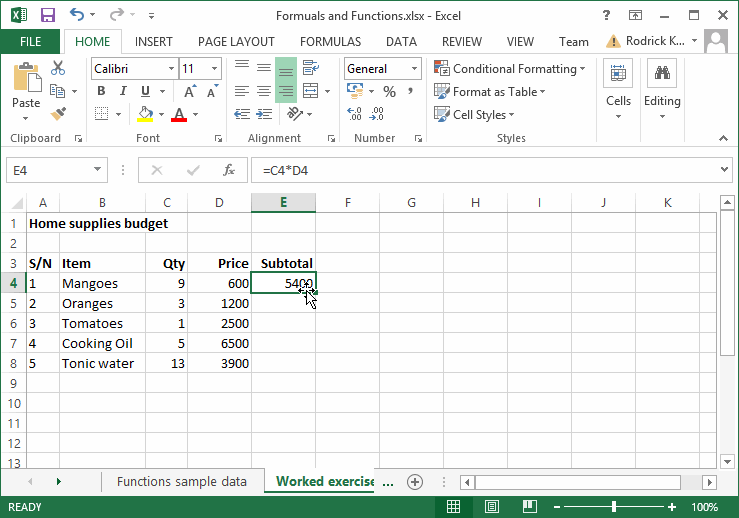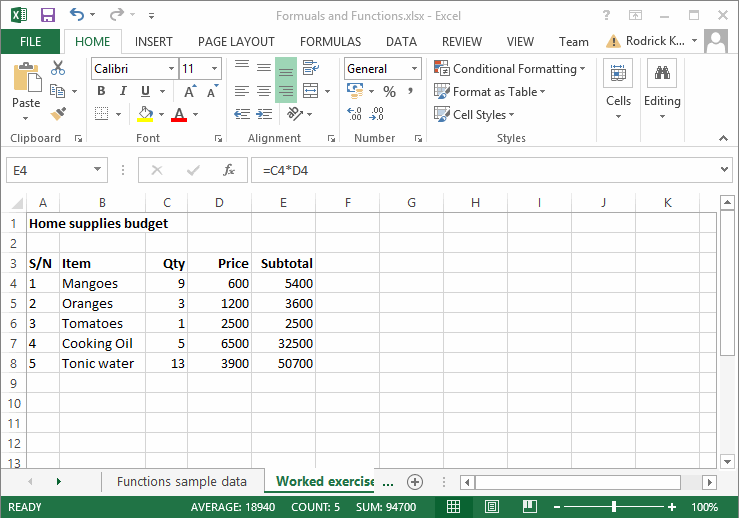
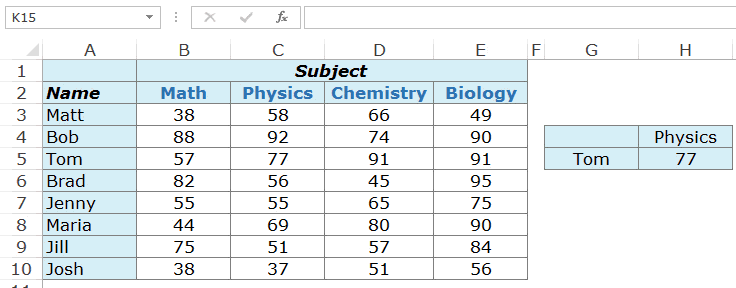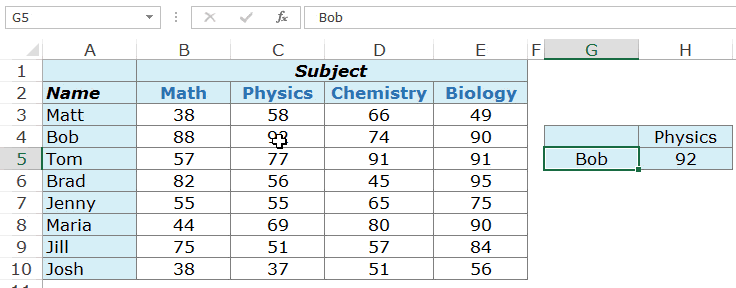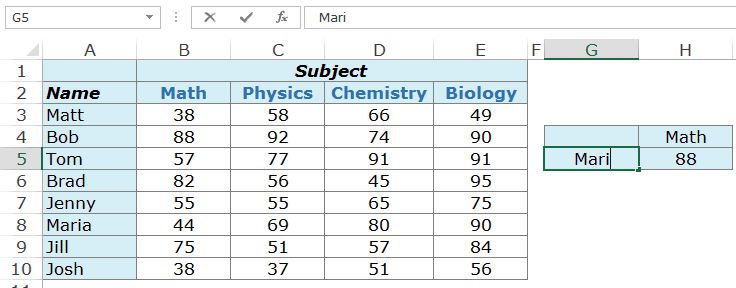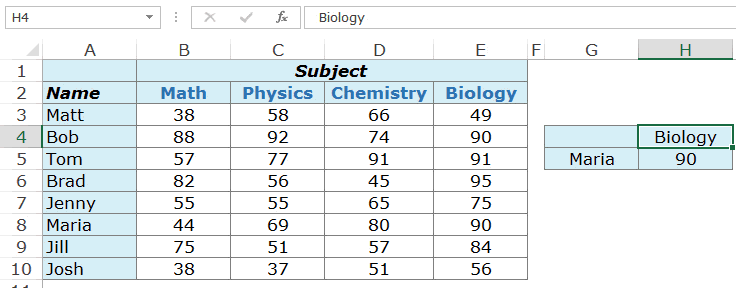
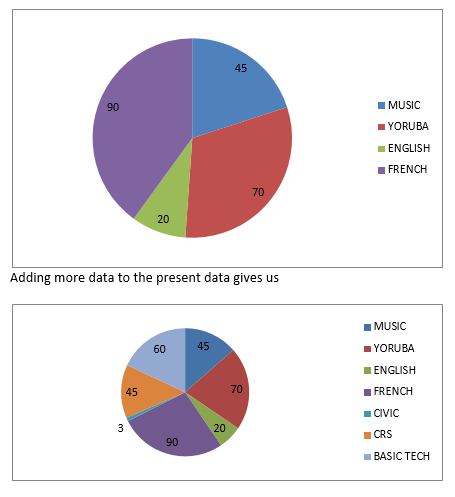
A typical example of data entry is shown below;
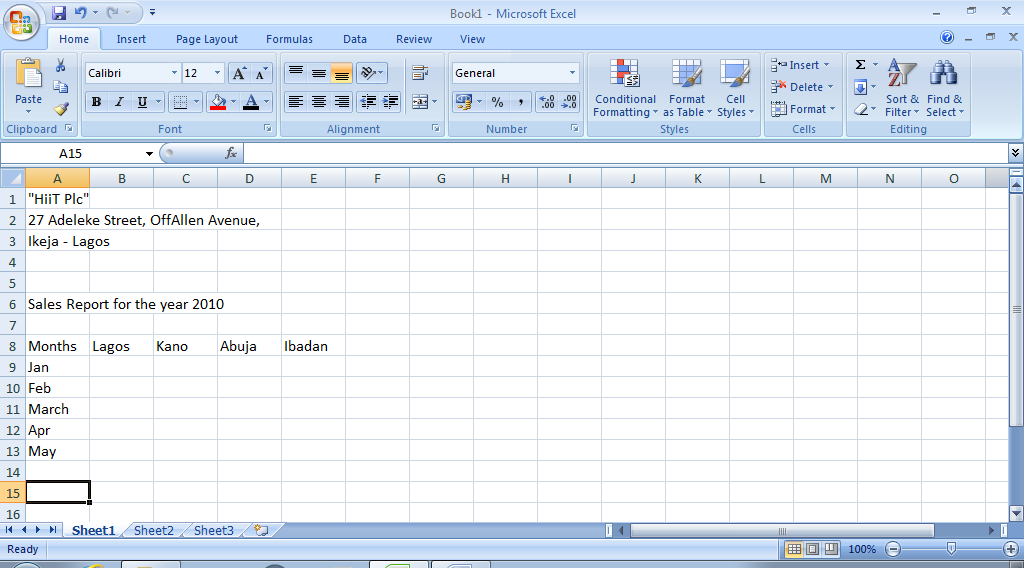
Fig. 4.1: Entering data into the worksheet.
Editing the Worksheet
Editing a worksheet means to either insert data, delete existing ones or to make corrections to the already existing data. Fig. 4.2 below shows the edited version of fig. 4.1
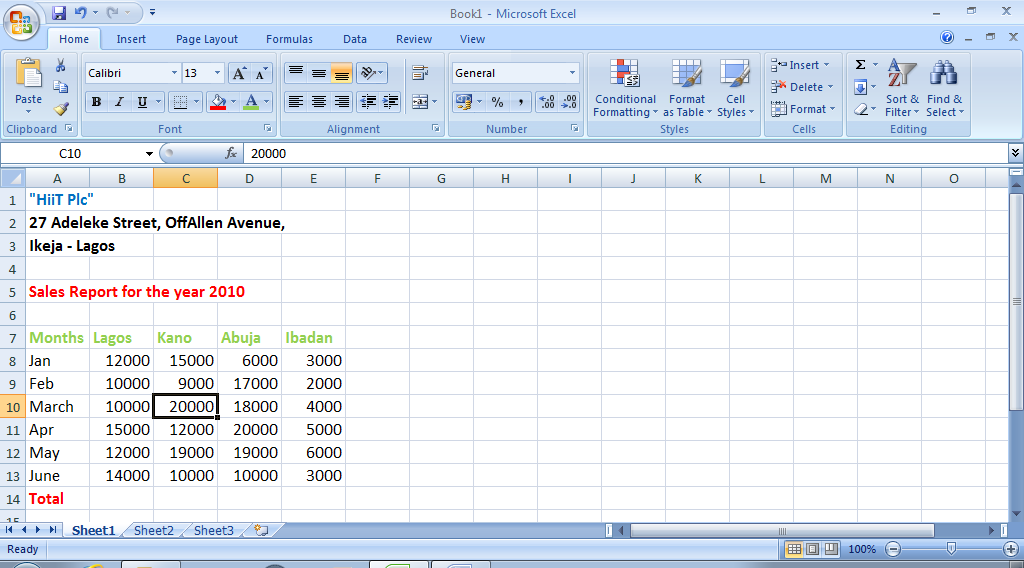
Fig. 4.2: Editing Worksheet
Saving a Worksheet
To save a worksheet for the first time, follow the steps below;
Click on the Microsoft office Button
Click on Save
When the dialog box appears, in the save in box click on the arrow, a drop down menu appears.
Select a location to save e.g My Document
Type a file name in the File name box.
Click on Save
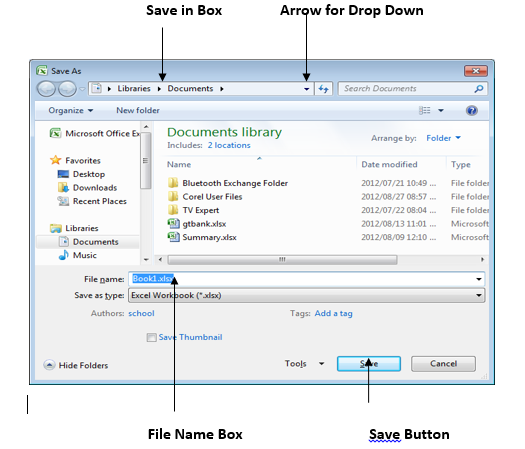
Fig 4.3: Save As Dialog Box
Subsequently, just press ctrl + S to continue saving the worksheet.
Retrieving a Worksheet
To retrieve an existing or saved worksheet, follow the steps below;
Load the spreadsheet package (Microsoft Excel in this case)
Click on the File menu or the Microsoft Office button
Click on Open, the open dialog box will be displayed
Click on the arrow beside the Look in box
Select My Document from the drop down menu
Click on the File Name
Click on Open
Formatting Worksheet:
The general arrangement of data is known as ‘Formatting’. The contents of selected cells can be formatted using the formatting tool bar. Formatting changes the way numbers and text are displayed in a worksheet.
Changing Fonts:
NOTE: practice the methods of changing font sizes, style, colour, attributes(bold, italics and underline), alignment(left, right, center), style, etc.
Formatting values in a range:
The number entered in the worksheet can be formatted to have currency symbols like the dollar ($). To follow numbers in a worksheet follow the under listed steps;
Highlight the number(s) in the desired range
Click on the arrow beside the number on the ribbon bar
When the dialog box appears, click on the number tab
Select Currency
Click on the arrow beside the symbol to get a drop down menu
Select the required symbol e.g dollar sign with 2 decimal places
Click on OK
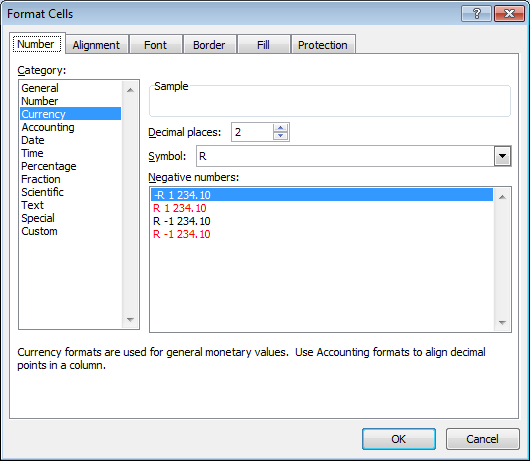
Fig. 4.4: The Format cells dialog box
Adjusting the Column Width:
To adjust the column width so as to accommodate the contents of the cell, follow the steps below;
Click on the cell to be adjusted
Position the cell pointer on the column tab,
The cell pointer changes to a cross
Click and drag to the right to increase the column width
Release the mouse button
NOTE: When the hash sign (#) is displayed inside a cell that contains data, it means the content of the cell is more than what the cell can accommodate. The column widths of that cell need to be adjusted.
Renaming the Worksheets
When MS Excel is opened, the sheets are named Sheet 1, Sheet 2, etc. To rename a worksheet:
Right click on the sheet tab to be renamed
Select Rename
Type the name you wish to give to give to the sheet
Press the Enter key
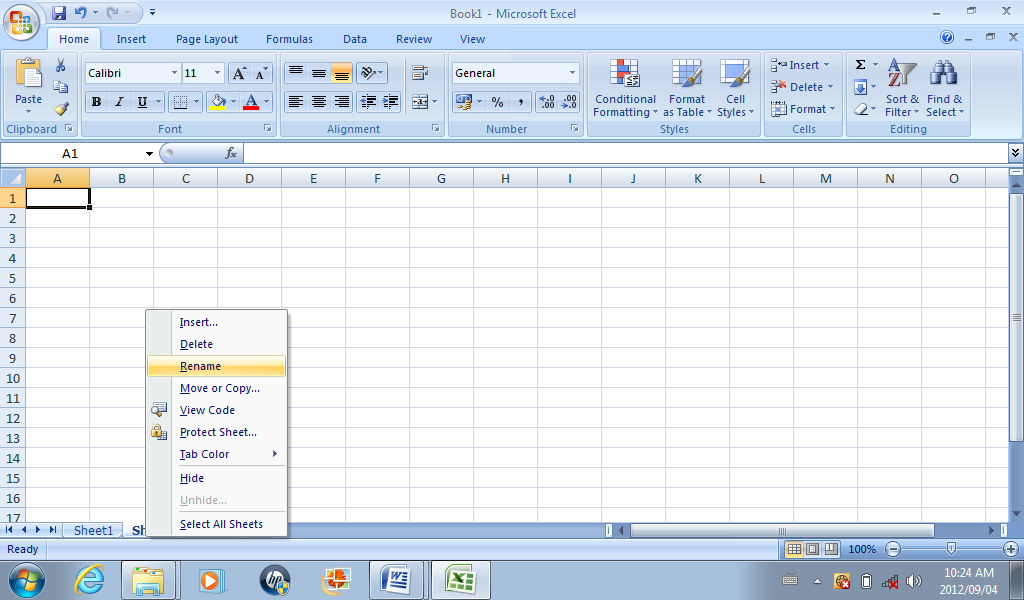
Fig. 4.4: Renaming the worksheet.
Inserting Rows or Columns:
To shift existing rows or columns to create blank rows or columns, follow the steps below;
Select the current row or column where the new row or column would be inserted
Click on Insert menu
Click on rows or columns
EVALUATION:
1. (a) Define a Worksheet.
(b) State the THREE types of data that can be entered into a worksheet.
2. Highlight the steps required to do the following;
(a) Open a worksheet (b) Save a worksheet (c) Retrieve a worksheet
(d) Rename a worksheet
ASSIGNMENT:
1. .................... can be defined as the working area of the program where entering of data and calculations are handled.
(a) Worksheet (b) Workbook (c) Workcell (d) row
2. Which of the following cannot be found in a worksheet?
(a) Cell pointer (b) Column (c) Animations (d) Row
3. .................... are mathematical expressions which return calculated value.
(a) MS Excel (b) Formula (c) Equation (d) Function
4. To save a workbook for future reference, a ...................... must be given to it.
(a) File name (b) File title (c) Reference name (d) Reference title
5. ..................... changes the way numbers and text are displayed in a worksheet.
(a) Arrangement (b) Decoration (c) Formatting (d) Highlighting
6. ................... sign is displayed when the content of the cell is more than what the cell can accommodate. (a) ₦ (b) (c) £ (d) #