LESSON 7
TOPIC:
FARMING SYSTEM
Contents: - definition and -types of farming systems
- advantages and disadvantages of farming systems.
Definition of Farming systems:
Farming systems refer to the types of technology adopted in farming operations. Any farming system adopted in an area depends on (a) the availability of farmland, (b) the culture of the people, (c) economic factor, (d) geographical factor.
 TYPES OF FARMING SYSTEMS:
TYPES OF FARMING SYSTEMS: These include Shifting cultivation/Bush fallowing, Land Rotation, Mixed Farming, Ley Farming, and Taungya Farming.
1.
Shifting Cultivation/ Bush Fallowing: It is a system whereby a farmer having farmed on a piece of land leaves it for another place . The land is therefore left to rest(fallow) for few years. During this period, the farmer moves or shift to a new place for farming and allows the former place to be covered with bush. After two to four years he returns back to the former place to cultivate the land. This time , the land has regained the lost nutrients.
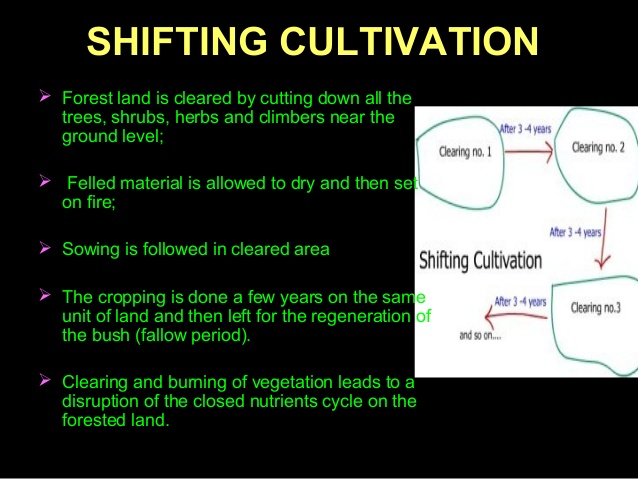
 Advantages:
Advantages:
a. It is simple and cheap to practice
b. It prevents the built up of pests and diseases
c. It allows the land to regain its lost nutrients in natural form.
d. The plant caver helps to check erosion.
Disadvantages:
a. Natural forest are often destroyed.
b. It is a slow process of maintaining soil fertility
c. The fallow period may not be enough for the soil to recover its lost nutrients
2.
Land Rotation: It is a system whereby a farmland is divided into portions or plots. The farmer cultivates one plot at a time and continues with the others in a definite order until all the plots are completely covered. He then starts all over again. The advantages and disadvantages are similar to that of bush fallowing.
 Advantages:
Advantages:
a. the legume crop included in the rotation, helps to add nitrogen to the soil
b. it helps to check erosion
c. pests and diseases attack is reduce
d. different crops are produced in a piece of land.
Disadvantages:
a. soil nutrients is gradually depleted.
b. It requires scientific knowledge
3.
Mixed Farming: It is a system whereby a farmer cultivates crops and rear animals on the same farmland. A portion of land is used for crop e.g maize production and a separate portion is used for keeping animals like fowl.
 Advantages
Advantages
a. Food is provided from both crops and animals
b. Income is realized from both crops and animals
c. the crops in the farmland can be used to feed the animals.
d. The manure (droppings or dung) is a source of organic fertilizer for the crops
e. Some of the large animals can be used to work in the farm
f. When there is crops failure, the farmer gains from the animals and vis-visa.
Disadvantages
a. The farmer attention is divided which could lead low production .
b. It requires large capital
c. Much labour and effort is needed
d. Animals could eat up the crops
LESSON 8
4.
Ley Farming : It is a system of farming which involves the planting of forage crops and food crops in alternation. The forage crops may include grasses and legumes and crops like maize , rice, cowpea.
 Advantages:
Advantages: the only advantage is that the farmer has forages to feed his animals and at the same time harvest the food crops from his farm.
Disadvantage: the system requires a lot of skills.
5.
TaungyaFarming: It involves the planting of food crops along side economic trees in government reserve areas(G.R.A) in the rural areas. When the farmers crops are harvested, the economic trees e.g Obeche, Mahogany or Afara are left on the soil for the government.
 Advantages:
Advantages:
a it provides income to the government when the trees are fell and sold.
b the land is always protected against erosion.
c unwanted forest can be replaced by desirable tree species.
Disadvantages:
a. it leads to the destruction of natural forest
b. the system does not allowed the cultivation of permanent crops.
c. at times the economic trees die off as a result of being neglected by the farmers.
PASTORAL FARMING: It is a system of farming in which a farmer keeps only livestock like cattle, sheep and goats. The two types of pastoral farming are Ranching and Nomadic herding.
(i)
RANCHING: The animals are kept in a fenced place where feed and water are supply to them.
 Advantages:
Advantages:
a. There is low incidence of pests and diseases
b. There is production of high quality animals
a. It is expensive to practice
b. There is the risk of total loss of animals if they attack by diseases.
(ii)
NOMADIC HERDING: It involves the movement of the herdsman with his animals from place to place in search of green pasture and water. This system is commonly practiced by the Fulani of Nigeria.
 Advantages:
Advantages:
a. There is no cost of feed for the animals.
b. Less labour is required as one man can cater for a large number of animals.
Disadvantages:
a. There is irregular supply of feed and water to the animal.
b. Animals are exposed to insect pests and diseases.
c. The animals and herdsmen are exposed to dangerous animals
d. The animals could be killed by moving vehicles.
EVALUATION:
1. Name 4 types of farming system
2. State 3 advantages and 2 disadvantages of mixed farming system.
3. Write 3 differences between Ley farming and Taungya farming systems.
REFERENCE TEXTS: -Essentials of Agricultural sc. By Earnest ChukwudiAnie
-Junior Sec. Agric. For Nigerian Schs. By Athony Youdeowei
-Prescribed Agric. Sc. For JSS. By Omoruyi S.A. et al
-New Intensive Agric.Sc.For UBE. By E.U. Okaro