LESSON 2
TOPIC: ELECTRICAL ENERGY
CONTENT: 1. Concept of electron flow.
2. Circuits- series and parallel.
3. Ammeter and Voltmeter.
4. House circuit; fuse and circuit breaker.
5. Electric meter- reading and billing.
PREAMBLE:
We already know various forms of energy. Can you mention them? Today, we are going to learn about Electrical energy in details.
Now, what is electrical energy?
Introduction: We make use of electricity in our towns and some villages, homes; schools etc. electricity is used for lighting, heating and cooling and in our industries. This electrical energy is the energy derived from the flow of electrons which is known as electric current.
How does electron flow, are there types of flow, how and with which device do we measure the flow, what is electrical circuit, how do we prevent the hazards, and read meter and billing system.
CONCEPT OF ELECTRON FLOW
In an electric flow, the current consist of a swarm of moving electrons. What causes electric current to flow is a chemical device called electric cells. Electric do this by producing an electric force which pushes the current along, and current will only flow if there is a complete circuit of conductors, by which the current will leave from one end of the cell and travel round to the other end. The current is the same at any point round the circuit and if the conductor is broken at any point, the current will stop flowing. Note that current flow a negatively charged end to the positively charged end. DEMONSTRATE an activity using unripe orange with zinc and copper plate; repeat the experiment using dilute sulphuric acid in a beaker.
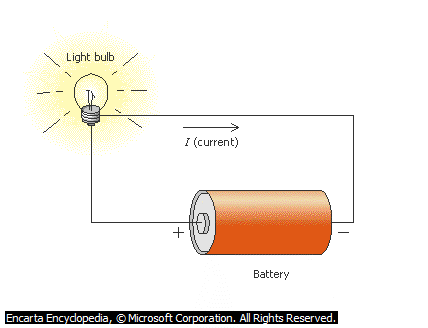
Example of Circuit
ELECTRICAL CIRCUITS
An electric circuit is a complete path of wires and electrical components through which electric current flows. Electric current can be made to flow from its source through metallic wires, back to their source. Electric current leaves the negatively charged rod of a cell, flows through a wire and then goes back to the cell through the positively charged rod. This complete path is referred to as electric circuit. This is represented by a sketch or symbol on the paper using arrow to indicate the flow of electron.
COMPLETE AND INCOMPLETE CIRCUIT
A circuit is said to be complete if the switch is closed (on), and the bulb will light because it is a closed circuit.
A circuit is said to be incomplete if the switch is opened (off), and the bulb will not light up because the circuit is not completed or closed.
SERIES PARALLEL CIRCUITS
When some components of a circuit are in series, it means that the components are connected end to end. They form a complete loop such that the same current flows through them.
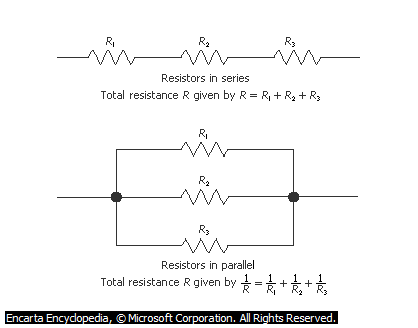
The above diagrams represent the series and parallel circuits
CIRCUIT IN PARALLEL
Components of a circuit are in parallel when the common terminals are connected to common points. Hence, cells are said to in parallel when all the positive terminals of the cells are connected together, and all the negative terminals are connected together. The external electrical component is then connected across the two junctions of the terminals.
1. Calculate the total e.m.f and the internal resistance involved in 3 cells in series with e.m.f of 1.5V and internal resistance 0.5ohms.
2. Assuming a cell in parallel has the same value, calculate the e.m.f and internal resistance.
AMMETER AND VOLTMETER
An ammeter is an instrument used to measure electric current. It is always placed in series with the circuit component carrying the current to be measured. An ammeter should have low resistance, so that its introduction into the circuit would not affect the value of the electric current to be measured.
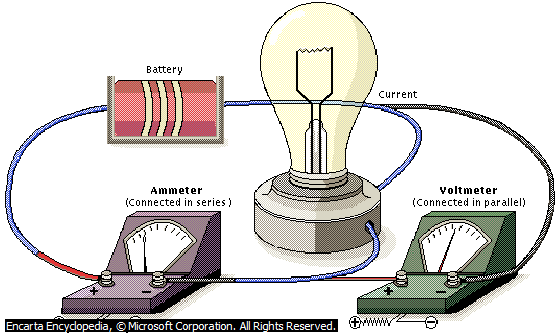 HOUSE CIRCUITS:
HOUSE CIRCUITS: Fuse and Circuit Breaker
House circuit can be divided into:
i. The lighting circuit
ii. The power circuit
A voltmeter on the other hand is an instrument used to measure the voltage across circuit components through which electric current is flowing. Voltmeters are always connected in parallel within circuit components across which the potential difference is to be measured.
Voltmeters should have high resistance so that when it is introduce into the circuit, current which ought to pass through the circuit component will not be diverted to pass through it and thereby disturbing the circuit.
The Lighting Circuit: The lighting circuit is the network of wires that connect all the bulbs in parallel in a house.
The power circuit: this consists of a complete circuit of three-core cables, which go round the whole house. Three-pin sockets are connected to the circuit at convenient points. Electrical appliances such as TV sets, radio sets, computer sets refrigerators, cooker, etc can be empowered by plugging them into these sockets.
Materials that can be easily seen or used in the house circuit are: Electric sockets and plugs. A typical socket has three holes:
1. The top hole is called the earth ( green or yellow),
2. The hole on the right side is called the live (brown or red)
3. The hole on the left side is called the neutral (blue or black).
FUSE AND CIRCUIT BREAKER
A fuse is a safety device containing a short length of thin conducting wire, which melts and breaks the circuit, if the current exceeds a certain safe value or maximum operating limit.
Circuit Breaker on the other hand works in the same way as the fuse. It is usually placed beside the electric meter such that the current enters it first before going into the meter.
ELECTRIC METER READING AND BILLING
To measure or read electricity consumed in order to bill the consumer accordingly, the standard unit commonly used is the kilowatt/hour.
1 unit of the electric power is the watt
1 watt= 1 volts x 1 ampere
Hence, the electrical meter is a device used for recording the number of units of electrical energy consumed in a house over a period of time.
1KWh = 1000 x 60 x60J
= 3.6 X 106 Joules of energy
The actual cost per unit to electrical energy varies with the nature of the use to which the energy is put.
The PHCN also charges a fixed charge and meter maintenance charge every month. This also varies according to the tariff rate of the consumer.
Example: 1. the tariff rate of a consumer is N4. 00 per unit. The present meter reading is 3760 while the reading was 3648.
a. What is the consumption of the household after one month?
b. If the fixed charge is N30 and the meter maintenance charge is N100. What is the current charge of the consumer?
SOLUTION: i. the consumption of the household is the difference between the present reading and the previous reading.
3760 – 3648 = 112units.
ii. The energy charge of the consumer = 112 x 4. 00 = N448. 00k
Fixed charges = N30
Meter maintenance charge = N100
Current charges = N(448 + 30 + 100) = N578 . 00
EVALUATION/ASSIGNMENT
1. A1600 Watts electric oven is used for 9 hours. Calculate the cost of using the N3. 00 per unit of energy. (Energy Consumed = power x time).What are the functions of the ammeter and voltmeter?
2. Read about Radioactivity in pgs 85- 88 of Basic SC. Made Easy by F. I. Kehinde.
Further Studies 1
Further Studies 2
Further Studies 3
Practice Test 1
Practice Test 2
Practice Test 3