LESSON 6
TOPIC: SENSE ORGANS
OBJECTIVE: At the end of the lesson, the students should be able to:
1. Mention the sense organs.
2. State the functions of the eye.
3. Mention the three layers of the eye.
CONTENT:
SENSE ORGANS
These are organs which help us to detect changes in our environment, they are specialized parts of the body that give information about the world around us and help to avoid danger. All the stimuli received by all the sense organs are coordinated and interpreted by the brain and spinal cord.
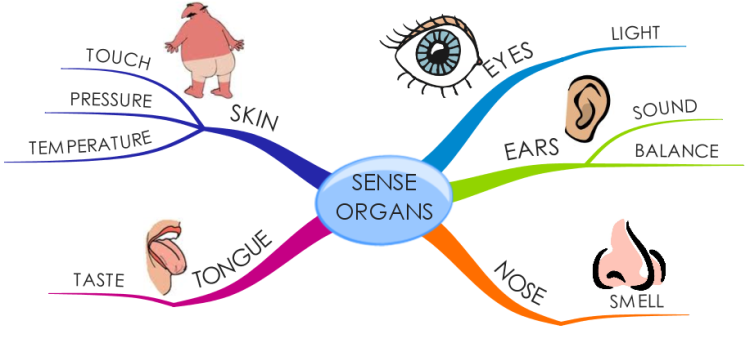
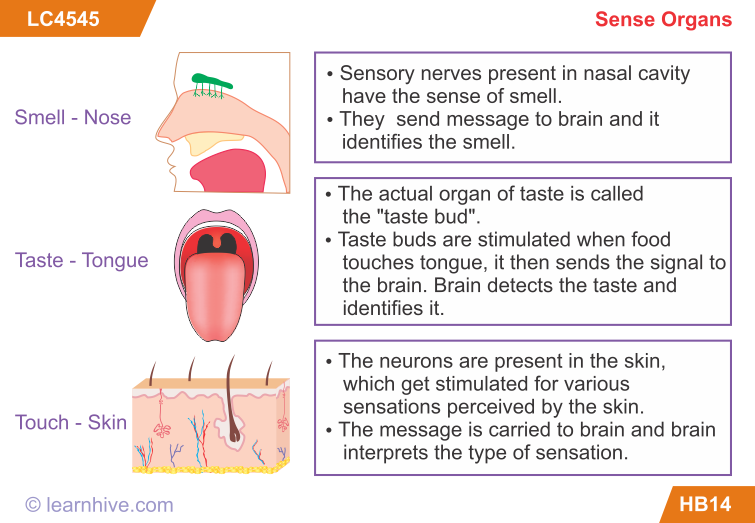
The sense organs are:
1. The eye for sense of vision.
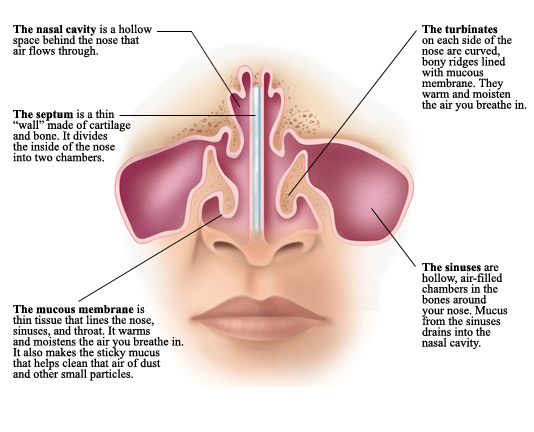
2. The nose for sense of smell.
3. The ear for sense of sound.
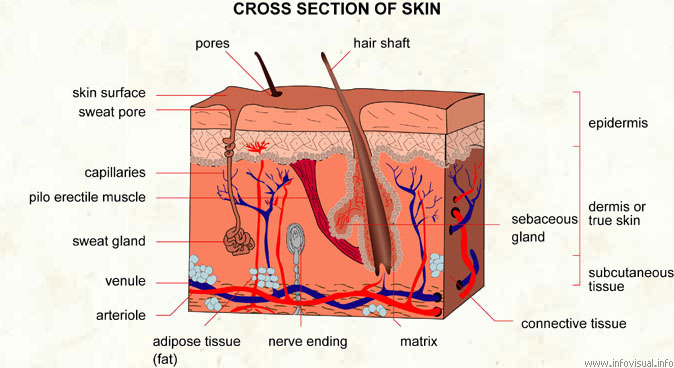
4. The skin for sense of touch, pressure, heat and cold.
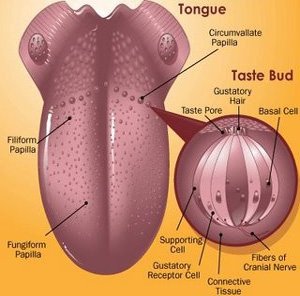
5. The tongue for sense of taste.
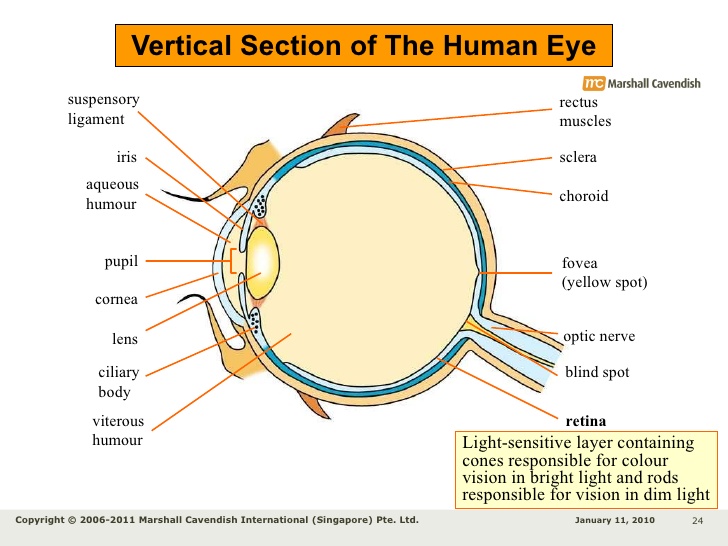
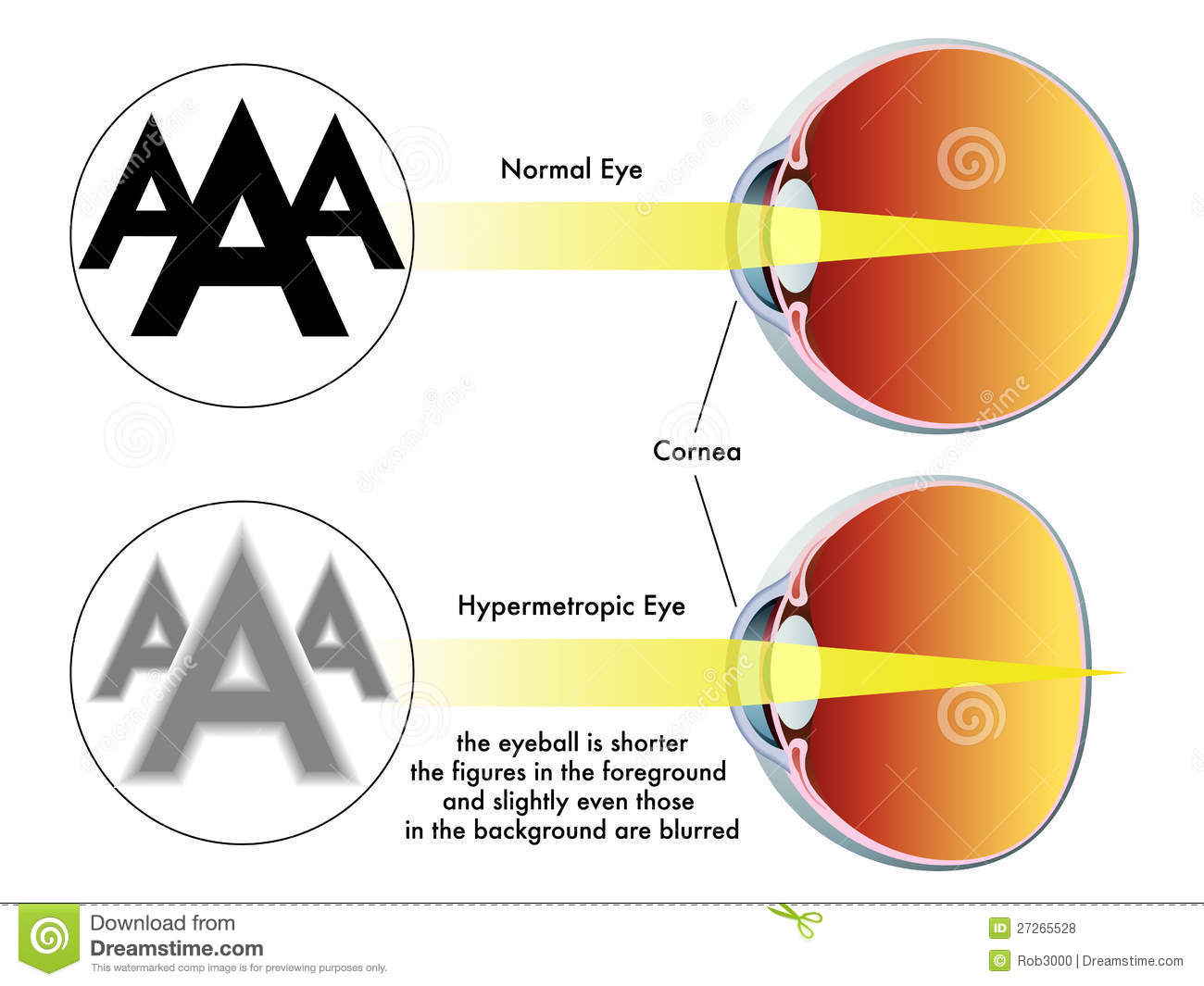
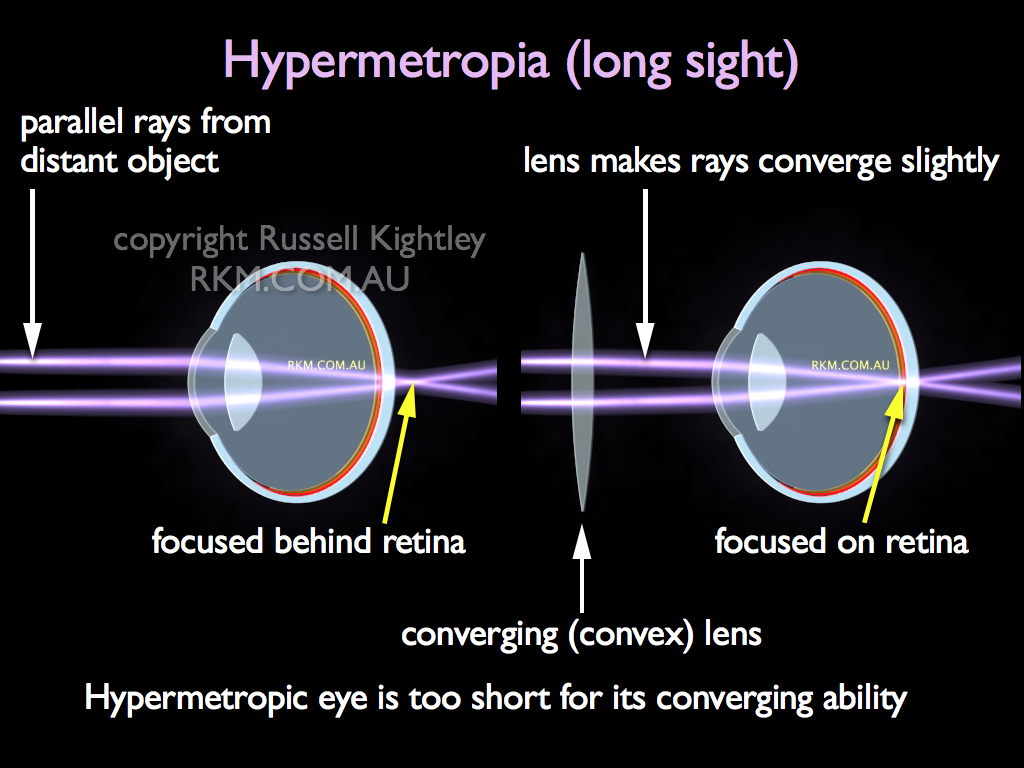
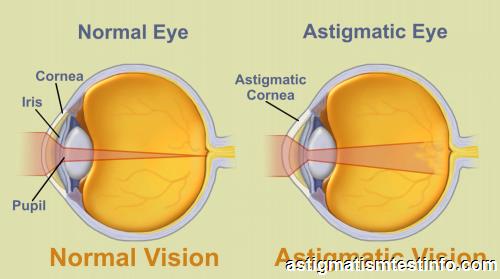
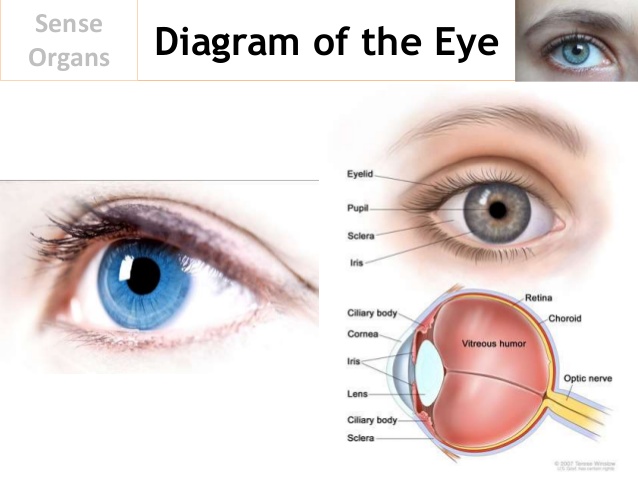
THE EYE
The eye is made up of three layers.
1. The outer layer which is known as sclera. This layer is responsible for protecting the inner structure of the eye. The sclera transparent part is called the cornea.
2. Choroid: this is the middle coat of the eye, this part is rich in blood and nutrient and is responsible for the supply of food to the cells of the eye.
3. Retina is the innermost part of the eye, this layer is very sensitive to light and contains cells which are called rods and cones. The rods help us to see well at night and are also responsible for seeing objects in black and white,. The cones on the other hand are responsible for colour vision. Images are formed on the retina.
EVALUATION:
Mention the sense organs.
State the functions of the sense organs.
Mention and state the functions of the three layers of the eye.
further studies
http://faculty.washington.edu/chudler/eyetr.html
http://www.sciencekids.co.nz/sciencefac ... /eyes.html
http://www.scientificpsychic.com/workbook/chapter2.htm
practice test
http://www.proprofs.com/quiz-school/sto ... rgans-quiz
http://www.funtrivia.com/playquiz/quiz3 ... f5220.html
LESSON 7
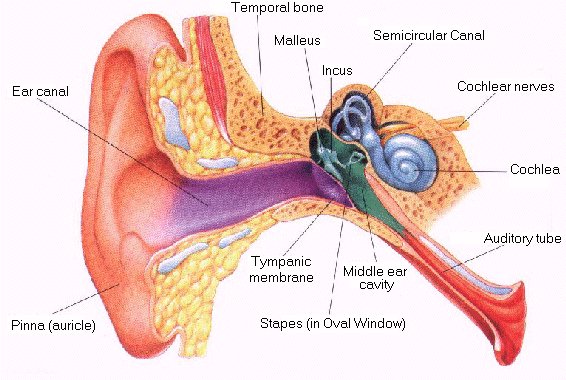
TOPIC: EAR
OBJECTIVE: At the end of the lesson, the students should be able to:
1. State the functions of the ear.
2. Mention the three parts of the ear.
CONTENT:
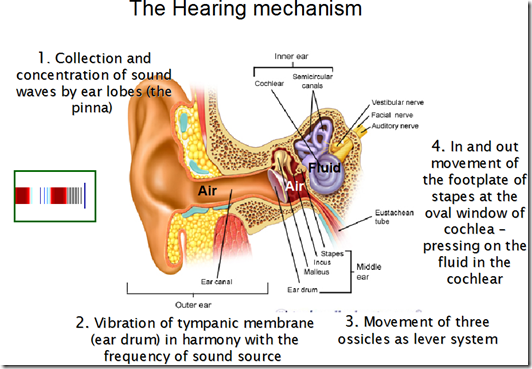
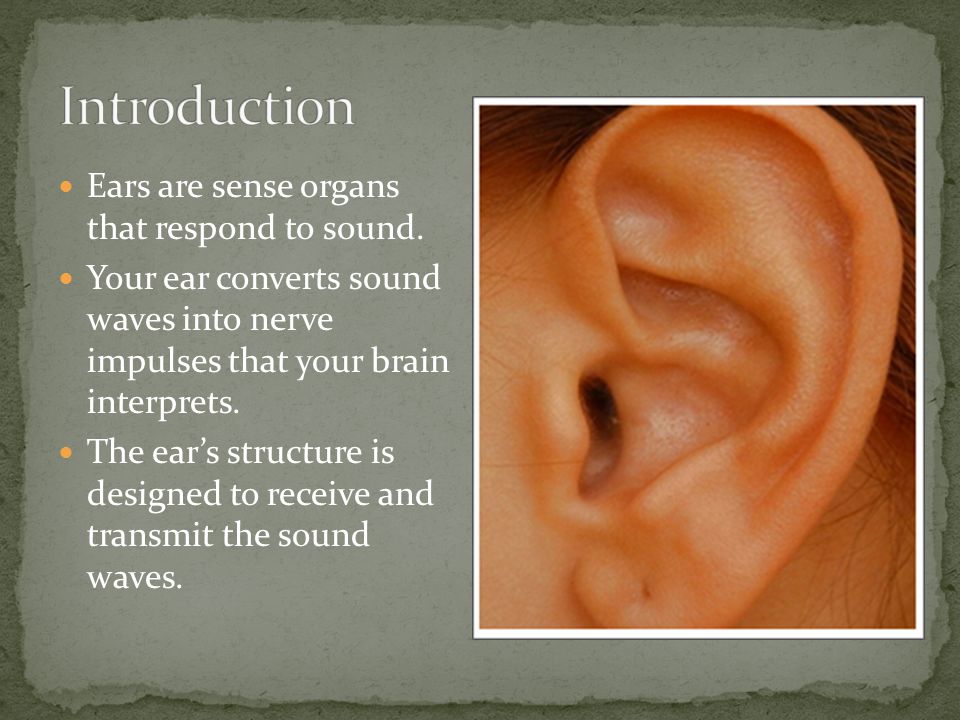
The ear is the sense organ for learning and balancing in mammals. The ear is made up of three parts.
i. Outer ear
ii. Middle ear
iii. Inner ear
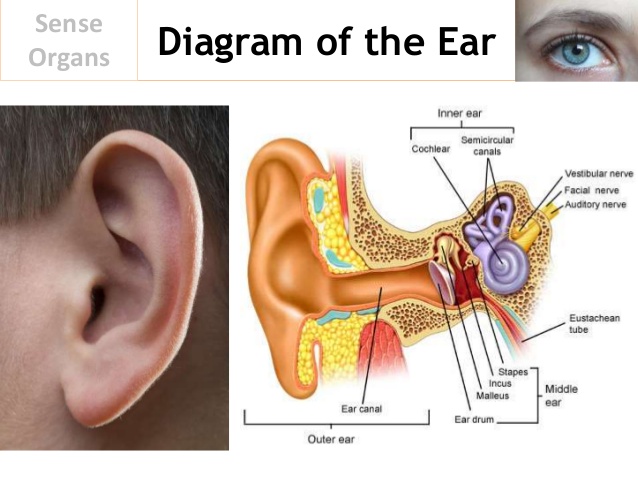
The outer ear consists of the pinna which is made of cartilage and the ear canal. The ear canal leads to the ear drum or tympanis membrane.
The middle ear contains the thypanic membrane, the three ear bones - auditory ossicles, made up of malleus (hammer) incus (anvil) and stapes (stirrup).
The inner ear is a cavity that is filled with the liquid called perilymph. The perilymph surrounds the sensory structure in the ear. The sensory structures are cochlea and the semi-circular canals are concerned with balance. Both the cochlea and semi - circular canals are fitted with endolymph.
EVALUATION:
What are the functions of the ear?
Mention and describe the three layers of the ear.
ASSIGNMENT:
What is the name of the fluid in the ear and what is its function?
further studies
http://kidsresearchexpress-5.blogspot.c ... rgans.html
http://www.factmonster.com/ipka/A0932466.html
http://www.scientificpsychic.com/workbook/chapter2.htm
practice test
http://www.proprofs.com/quiz-school/sto ... rgans-quiz
http://www.funtrivia.com/playquiz/quiz3 ... f5220.html
LESSON 8
TOPIC:
ENVIRONMENTAL HAZARDS (SOIL EROSION AND FLOODING)
CONTENT: 1. Definition of Soil Erosion - Causes, Effects and Control of Soil Erosion
2. Definition of Flooding – Causes, Effects of Flooding on Communities and
Farmlands, Control of Flooding and Drainage Patterns
DEFINITION OF SOIL EROSION
Environmental hazard is a term used for any situation or state of events which poses a threat to the surrounding environment and adversely affect plants and animals
SOIL EROSION is the washing away of the soil by heavy rain or wind resulting to the formation of gully and landslides and leaving behind silt on which plants can no longer grow.
Soil erosion can also be defined as the removal of topsoil faster than the soil forming processes can replace it, due to natural, animal, and human activity (overgrazing, over cultivation, forest clearing, mechanized farming, etc.). Soil erosion results in land infertility, leads to desertification and devastating flooding.
 CAUSES OF SOIL EROSION
CAUSES OF SOIL EROSION
1. Excessive Rain fall: Due to excessive rain fall, top fertile soil is washed away.
2. Human activities: Human activities accelerate disappearance of protective cover of natural vegetation and cause soil erosion.
3. Over grazing: Over grazing leads to the absence of ground-vegetation, causes gradual depletion of soil organisms and soil erosion.
4. Land use: Humans play a major role in soil erosion through their use and abuse of natural resources, for example deforestation, grazing, arable land use, faulty farming systems, high crop intensity, construction, mining, etc.
5. Climate: The two most important climatic factors having a direct effect on erosion are precipitation and wind velocity.
6. Landforms: Slope, gradient, slope length and shape of slope are the important variables of landform that affect erosion processes for all types of soil erosion, e.g., splash, sheet, rill, and gully erosion.
7. Bush burning
 TYPES OF EROSION
TYPES OF EROSION
1.
WATER EROSION: Water erosion is the removal and carrying away of soil particles by rain, running water, melting ice running rapidly over an exposed soil surface.
2.
WIND EROSION: This is the blowing away of the soil particles or topsoil by wind. Wind erosion is common in arid or dry land where there is little or no rainfall.
 EFFECTS OF SOIL EROSION
EFFECTS OF SOIL EROSION
1. Reduction in soil quality which results from the loss of the nutrient-rich upper layers of the soil
2. Reduces water-holding capacity of soil.
3. Displacement of people from their homes
4. Destruction of farmlands
5. Collapse of building
6. Damage of soil surface and roads
 CONTROL OF SOIL EROSION
CONTROL OF SOIL EROSION
1. Planting of vegetative cover: Cover crops such as trees, grasses, shrubs can be planted to cover the soil surface. This will reduce the effect of rainfall on the soil. The roots of the vegetative plants help to bind the soil particles together.
2. Avoidance of indiscriminate bush burning: Bush burning exposes the soil to erosion because the vegetative covers are burnt.
3. Avoidance of overgrazing: Land should not be overgrazed to prevent water erosion
4. Mulching: This is the covering of ridges, beds and mounds in the farm with leaves, dry grasses and straw. Mulching reduces the impact of raindrops on the soil and thereby prevents erosion
5. Crop rotation: This is the growing of certain crops in an order and rotating them every planting season in order to maintain soil fertility and also prevent water erosion
6. Ridging across slope: Ridges should be constructed across and not along slopes to reduce the speed of run-off.
7. Application of organic manure: Organic matter prevents loss of water from the soil and makes the soil moist at all time. This makes the particles of the soil heavy for wind to blow away.
8. Irrigation: Artificial application of water to the soil will make the soil moist, thereby binding the soil particles together and preventing the soil particles from being blown away by wind.
9. Planting of leguminous crops
10. Education

EVALUATION
1. Define erosion
2. List four causes of soil erosion
3. State five ways of controlling soil erosion
4. Mention five effects of erosion
LESSON 9
FLOODING
DEFINITION OF FLOODING
Flooding can be defined as an overflowing of water onto land that is normally dry. It also occurs when there is more water on the surface of the land than it can take. This may lead to river overflowing its banks.
 Causes of Floods
Causes of Floods
1.
Deforestation: When large areas of forests near the rivers are cleared, the land may be used for settlement, roads and farmland. Less vegetation protects the soil, the soil is quickly lost to rivers and sea. This raises the river bed, so the river overflows its banks easily, then flooding occurs
2.
Poor water management: when the dams are poorly constructed or maintained, they can easily collapse and this results in flooding.
3. Population pressure: Because of large amounts of people, more food, wood, etc are needed for consumption, thereby leading to over-cultivation of lands which lead to erosion and increases the risk of flooding.
4.
Amount of rainfall: The amount and intensity of rainfall determine the amount of run-off on the land and this will determine the amount of water available for flooding to occur.
5.
Closeness to sea or ocean: When the level of water rises above the bank of the sea or river, flooding occurs in areas close to the sea or river
6.
Social habit of the people: In areas where people tend to build structures to block drainage system, there may be blockage of water channels and free flow water is hindered which may lead to flooding.
7.
Type and condition of the soil: in some areas, the soil is too loose and cannot withstand heavy rainfall and are easily carried away leaving the ground eroded.
EFFECTS OR CONSEQUENCES OF FLOODING ON COMMUNITIES
1. Loss of human life
2. Damage to property
3. Deterioration of health conditions owing to waterborne diseases.
4. Communication links and infrastructure such as power plants, roads and bridges are damaged and disrupted, some economic activities may come to a standstill
5. People are forced to leave their homes and normal life is disrupted
6. Disruption of industry can lead to loss of livelihood.
7. Damage to infrastructure also causes long-term impacts, such as disruptions to supplies of clean water, wastewater treatment, electricity, transport, communication, education and health care.
8. Reduction in purchasing power and loss of land value in the floodplains can leave communities economically vulnerable.
9. Floods can also traumatise victims and their families for long periods of time.
 EFFECTS OF FLOODING ON FARMLAND
EFFECTS OF FLOODING ON FARMLAND
1. Widespread damage to crops and fencing
2. Loss of livestock
3. Waterlogged soils
4. Delay in harvesting are further intensified by transport problems due to flooded roads and damaged infrastructure.
5. Food prices increase due to shortage in supply.
6. Poverty
CONTROL OF FLOODING
1. Construction of dams to take excess water that may lead to flooding
2. Construction of reservoir that will hold excess water which can be used for other purposes
3. Clearing of gutters of waste that can prevent free flow of water
4. Prevention of construction of structures along river and sea banks
5. Having adequate and proper town planning which will bring about construction of adequate drainage system
6. Education

 DRAINAGE PATTERNS
DRAINAGE PATTERNS
Drainage is the process by which water or liquid waste is emptied from an area.
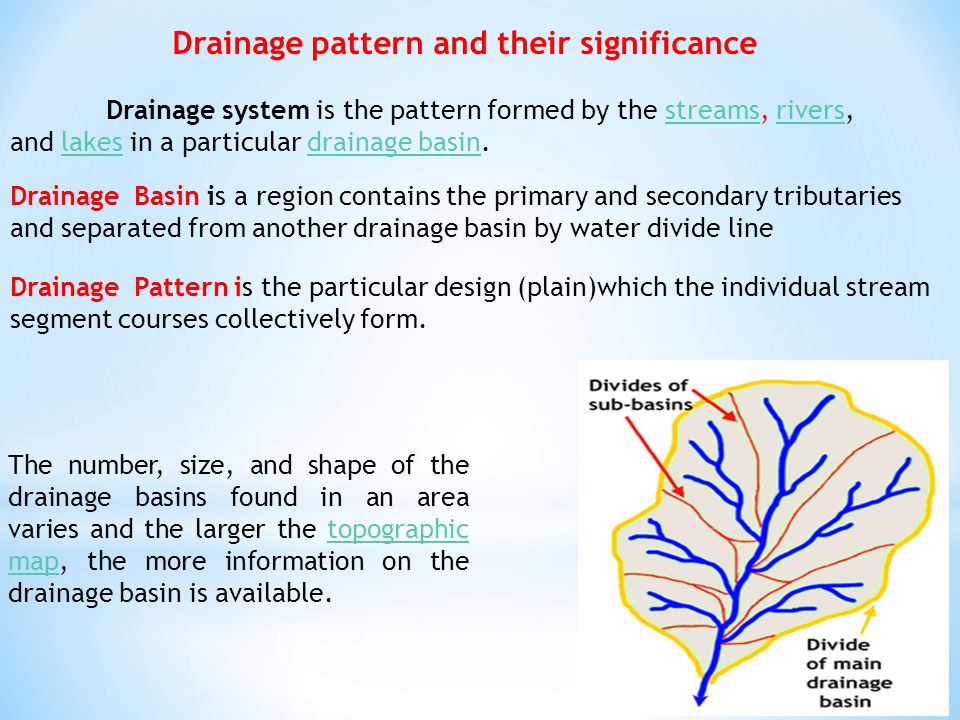 TYPES OF DRAINAGE PATTERNS
TYPES OF DRAINAGE PATTERNS
1.
SURFACE DRAINAGE SYSTEM: This type of drainage system is found in rural areas and it is not designed by qualified engineers. The drainage is exposed and water can easily overflow the drainage and flood the area.

2.
SUB-SURFACE DRAINAGE SYSTEM: The sub-surface system is covered with concrete while water flows underground, thereby preventing overflow of the boundaries. It is designed by qualified engineers. This type of drainage is usually found in cities such as Abuja, Lagos, e.t.c.
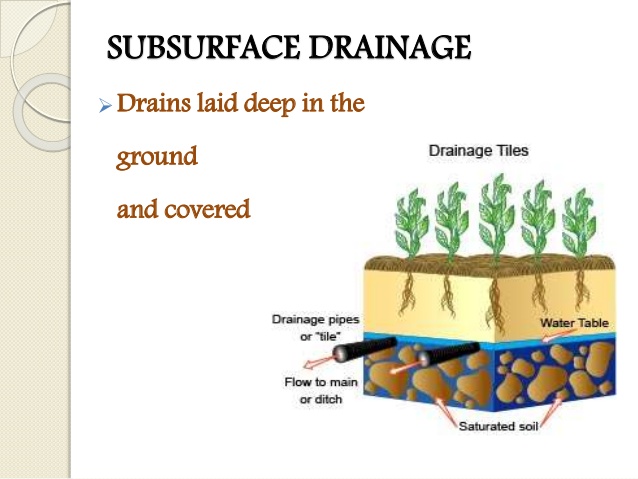
EVALUATION
1. Explain flooding
2. List five causes of flooding
3. Explain four effects of flooding
4. Mention and explain four activities of man that promote flooding
5. Explain how flooding can be prevented or controlled
6. Explain two types of drainage system
Further Studies 1
Further Studies 2
Reading assignment
Read Soil erosion and flooding
ASSIGNMENT
Read Basic Science made easy for Nigerian Junior Secondary Schools Bk3 by F. I. Kehinde pgs 102-103 and answer the following questions:
i. Define bush burning and deforestation
ii. State three causes of bush burning
iii. State three effects of deforestation
REFERENCES
1. Basic Science Made Easy for Nigerian Junior Secondary Schools Book 3 by F. I. Kehinde
2. Functional Basic Science for Junior Secondary Schools, Book 3 by c. U. Onyirioha et al.