LESSON 17
TOPIC: MAINTENANCE
CONTENT:
(a) Definition of Periodic Maintenance
(b) Planning short, medium and long term maintenance
(c) Need for periodic maintenance
(d) Simple maintenance methods
(e) Keeping Maintenance records.
Maintenance is the work carried out to keep or restore an equipment to an acceptable working standard at a minimum cost. If an equipment is not properly taken care of, it breaks down. Breakdown of equipment is very expensive and causes a lot of inconvenience and sometimes causes loss of life. To avoid breakdown, an organization or individual should formulate an appropriate maintenance policy or plan.

(a)
DEFINITION OF PERIODIC MAINTENANCE:
It is a work undertaken from time to time in order to keep, restore or improve a facility to an acceptable standard. It can also be defined as the combination of all technical and associated administrative action carried out from time to time with the intention of retaining an item or restoring it to a state in which it can perform optimally.
Periodic Maintenance is the type of maintenance which is being carried out on machines, equipment and buildings at specified interval of time, whether they are in use or not.
(b)
PLANNING SHORT, MEDIUM AND LONG-TERM MAINTENANCE:
Periodic Maintenance is usually planned or scheduled according to the defined time frames. Periodic maintenance can be termed as:
a. Short term maintenance
b. Medium term maintenance
c. Long term maintenance
•
Short term maintenance comprises of those maintenance that are frequently carried out. For machines and vehicles which are continually used, these are carried out on daily or weekly or at two weeks interval. The machine and equipment which require short term maintenance are well laid out in the service manual. In motor vehicle maintenance, activities such as checking the water level, oil level, tyre pressure etc are parts of short term maintenance.
•
Medium-term maintenance: this comprises those maintenance processes which are not frequently carried out, but rather done at longer time interval. In motor vehicle maintenance, activities, such as changing of oil, changing of spark plugs; changing of fuel; changing of oil filter; as well as servicing of the engine are parts of medium term maintenance.
•
The Long-term maintenance: This comprises those maintenance which are rarely carried out, yet are carried out at longer term interval. Fixing of new tyres to the vehicle; the total overhauling of the engine; overall body work of the car are parts of long-term maintenance schedule.
(c)
NEED FOR PERIODIC MAINTENANCE:
To keep the machines or equipment in good working condition.
To obtain maximum possible output from the equipment.
To reduce the inconvenience of failure.
To preserve the usefulness of these equipment.
To maximize economic and financial turns in industries.
To mitigate the effects of elements of weather: when building and other structures are exposed to the elements of weather they depreciate over a time, so periodic maintenance takes care of the negative effects of harsh weather condition on the equipment.
(d)
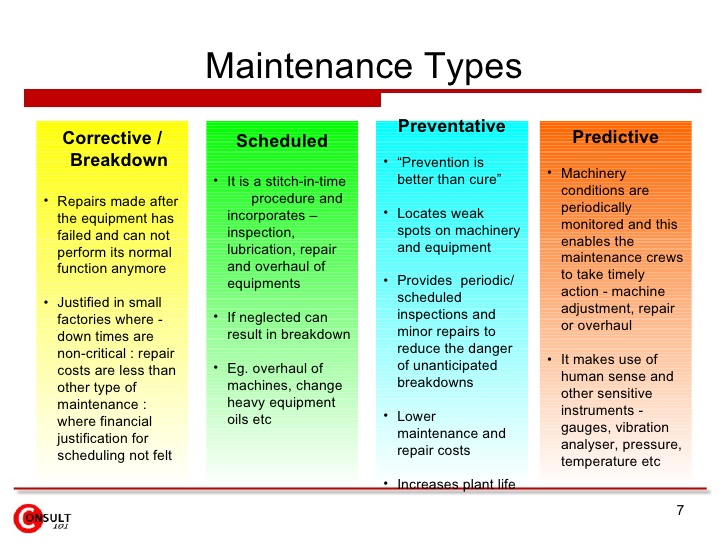
TYPES OF MAINTENANCE
There are three broad (3) types of maintenance:
(a)
Preventive Maintenance: This is a routine maintenance carried out at predetermined period or intervals to reduce or prevent the possibility of breakdown of equipment. Prevention is better than cure.
(b)
Predictive Maintenance: This is a type of maintenance whereby devices in the equipment trigger off danger signal predicting a fault. The danger signal could be in the form of red light or sound. Such predictive signals are common in motor cars, aeroplanes, computers and digital equipment.
(c)
Corrective Maintenance: This is done to correct faults which have already been developed. At this stage it will require replacement of damaged parts or procurement of a new equipment. Corrective maintenance is expensive and time consuming.
 REASONS FOR CHOOSING PREVENTIVE MAINTENANCE
REASONS FOR CHOOSING PREVENTIVE MAINTENANCE
• It prolongs the life span of the equipment
• It reduces the probability of failure and breakdown
• It ensures the safety of the users
• It maximizes the economic and financial returns in industries
• It always keeps the equipment in good working condition
• It reduces high cost of repair after breakdown
REASONS FOR CHOOSING PREDICTIVE MAINTENANCE
• It alerts the users when the equipment is about to have problem. For instance shortage of engine oil or fuel, weak battery or low voltage.
• It reduces the probability of failure or breakdown if the user goes for maintenance urgently.
• It ensures the safety of the user.
• It prolongs the life span of the equipment if urgent repair is carried out.
REASONS FOR NOT CHOOSING CORRECTIVE MAINTENANCE
• It is medicine after death
• It is costly and time consuming
• It does not maximize the economic and financial returns in industries.
• It does not reduce the probability of failure and breakdown.
• It does not prolong the life span of equipment.
(e)
SIMPLE MAINTENANCE METHODS
The Simple Maintenance Methods include:
(i)
Cleaning: This is the removal of dirts, with the use of clean cloth, the use of water with soap.
(ii)
Dusting: This is the removal of dust by the use of a small piece of cotton cloth called duster or brush
(iii)
Washing: This is the use of water and soaps. It may also involves the use of sponge or brush to apply the soapy water on the object which is being washed.
(iv)
Oiling: This is the application of oil to machine parts for the purpose of overcoming friction. This is done by using oil brush to spread engine oil on the desired surfaces of the machine, this process is called lubrication.
(v)
Greasing : This is the application of grease to maintain machine parts for the purpose of overcoming friction at the point of application.
(vi) Adjustment of selected parts
(vii) Changing of engine oil at least once in a month especially in motor cars.
(viii) Refilling of automatic transmission fluid, gear oil, axle oil, hydraulic oil, battery acid and electrolyte.
(ix) Alignment and wheel balancing of tyres.
(f)
MAINTENANCE RECORDS
These are the records of activities carried out on machines, vehicles and equipment which must be kept, in order to assist in proper planning of future maintenance activities and also to exercise economic control over the process of maintenance itself.
A typical maintenance record contains:
a. The name of the machine.
b. The date when the maintenance procedure was carried out.
c. The nature of the fault detected in the machine.
d. The processes that were carried out to rectify the fault identified.
e. Any useful recommendation for future maintenance of the machine.
f. The name of the officers who undertook the maintenance process.

EVALUATION
1. What is periodic maintenance?
2. Distinguish between short, medium and long term maintenance.
3. List all the information that a maintenance record is expected to contain.
4. Why is periodic maintenance necessary?
READING ASSIGNMENT
Read about fault detection techniques in your textbook: New Basic Technology for jss1,2,3 UBE Edition pages 204-205.