LESSON 22
ASPECT: Grammar
TOPIC: The use of ‘even though’ and ‘at least’.

‘Even though’ and ‘at least’ are subordinating conjunction used to introduce a subordinating clause. Its purpose is to contrast with the main clause.
For example:
1. Even though they were poor, they were always happy.
2. If they were poor, at least they were always happy.
3. Even though he had no parents, he sponsored himself to school.
4. If he had no parents, at least he sponsored himself to school.
5. I visited my relatives at the weekend even though I didn’t want to.
6. Even though I hadn’t slept much, I stayed awake to finish my work.
7. I know the answer, at least I think I do.
EVALUATION: Use ‘even though’ and ‘at least’ in two sentences each
Further Studies 1
Further Studies 2
LESSON 23
ASPECT: COMPOSITION
TOPIC: Narrative Essay (A journey I once made).

A guide to writing composition ‘A journey I once made’.
- When did you embark on the journey? Whom did you go with and where did you go?
Where were you based then?
What were the exciting things on the way?
Or what were the new things you saw?
How long did the journey take you?
How many days, weeks, or months did you spend there?
What were your experiences there?
Would you like to visit there over and over again?
EVALUATION: Use the above guidelines to write a comprehensive composition on ‘A Journey I Once Made’
A Journey I Will Always Remember
December 17, 2012
By Anonymous
Along with the rest of my family I am a competitor. Competing vigorously alongside my siblings in karate was my life. I had been invited to many tournaments, however none of them would match up to one that was about to take place.
Our unbelievable journey began once my brother, Chris and I got invited to compete at the World Championship for karate in China. Immediately, my mother prepared four children’s suitcases as well as her own for this once-in-a-lifetime getaway. Full of anxiety and nervousness my whole family(consisting of me, my brother, Nick, my brother, Chris, my sister, Samantha and my parents) took steps forward onto our 14 hour flight( the longest one we would ever take) to travel 7575 miles away from home. Already as a seven year old I would be a world traveler. Experiencing new culture, language, people and places.
Landing in Beijing, China after all the stretching, various movies, and eating was a dream come true, besides the jet lag. We soon greeted our new best friends for the next ten days as we stepped onto our charter bus and began our journey. Our trip started by learning bits and pieces of this new language, seeing know landmarks and learning its history and singing funny songs that I can still recall today.
Pulling up onto a cobble stone road, our charter bus jumbled around until it came to an immediate halt. Filing out of the bus, our tour guide yelled out in an Asian dialect to go over the commotion that was happening around him,
“Welcome to the Great Wall of China.”
Like a group of penguins, we inched closer to the ticket booths while our tour guide disclosed the guideline of one of the World’s Greatest Wonders. However, I fell behind while walking nervously hand in hand with my mom facing one of my biggest “obstacles.” My worried eyes swept across the busy streets and many people. Standing out like a sore thumb were the cherry blossom trees. These delicate trees produced soft snow-like petals that fell from the tree with just the smallest gust of wind. I was mesmerized by this scene in front of me until my mom yanked me to stay with the curious pack. The last thing she wanted was a lost kid in China! So we continued our way with our tour guide telling us in detail of everything that was around us.
Then, there it was, the man-made obstacle that would prove if I were a big girl now. While everyone around me hurriedly made their ways up those memorable steps, I stood their knees shaking pleading my mom not to make we go any further. Comforting me, my mom steadily inched me toward those steps telling me,
“Everything is going to be alright.”
Gradually, I made my way up those “enormous obstacles” that were in my way from reaching the top. Just like learning how to walk, I made my way slowly. Soon enough, my mom caught up with the rest of our family, we meandered over to the nearby outdoor vendors. Here the merchants reeked of a mixture of rice and sweat. This putrid smell that was overfilling my nose made me want to escape as soon as possible. In memory of this once in a life time day, we each purchased the ideal ‘I climbed the Great Wall of China’ shirts.
This trip was unbelievable and adventurous. Surrounded by a unique and diverse culture at such a young age has developed my character to be unique like no one else..
LESSON 24
ASPECT: Speech work
TOPIC: Consonant sounds
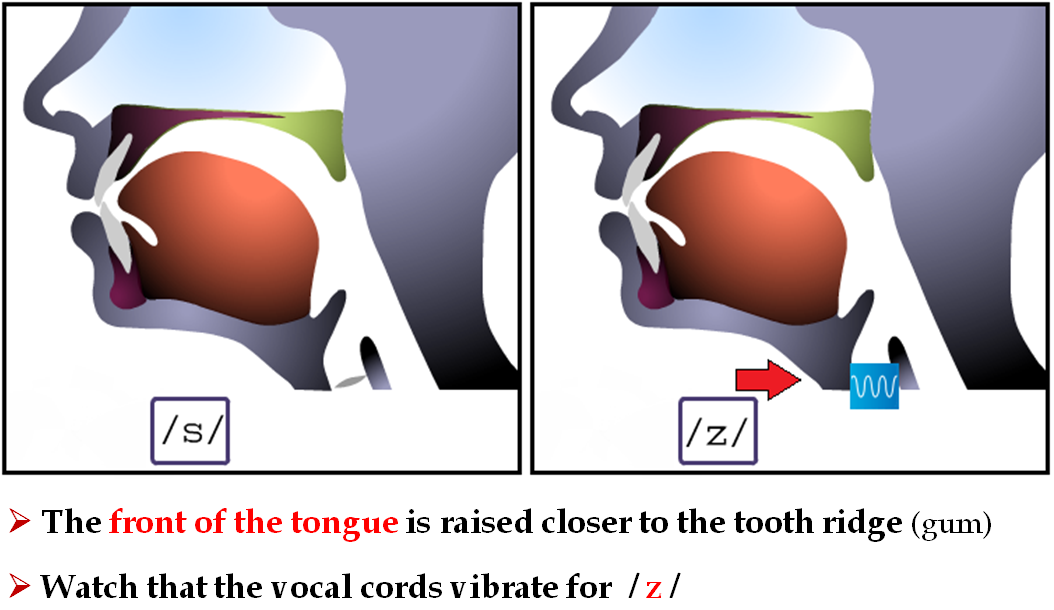
A consonant is a speech sound which is produced with the obstruction of airstream. The obstruction could be ‘partial’ or ‘total’.
There are 24 consonant sounds in English studies. They are:
/p/ /b/ /ʈ/ /d/ /k/ /g/ /ʧ/ /ʤ/ /f/ /v/ /Ө/ /ð/ /s/ /z/ /∫/ /Ӡ/ /h/ /Ɩ/ /r/ /m/ /ŋ/ /j/ /w/ /n/
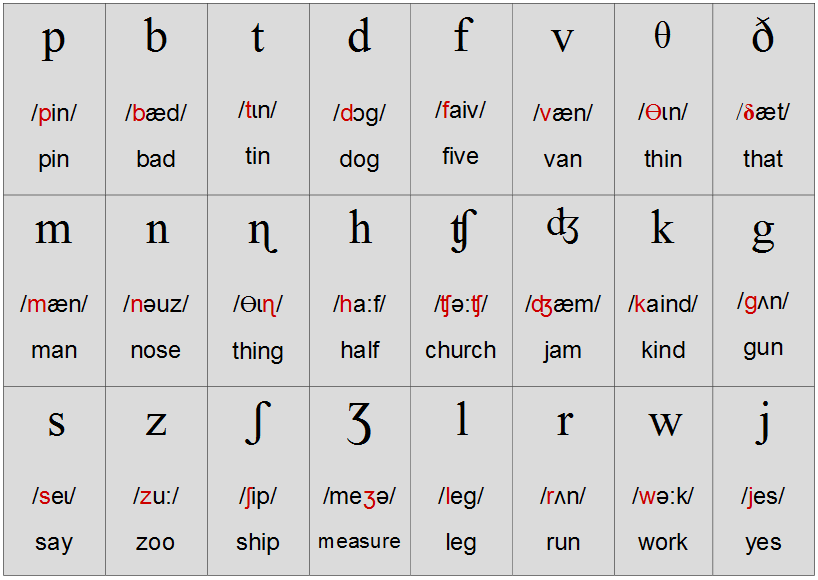
/p/----- put, pat, pot, peg, pit, push, wrapper, pass, place, happen, party
/b/---- but, bet, book, boom, boost, bay, baby, rob, bad, bat, back, abort, about, abide
/ʈ/--- ten, tap, tomb, table, take, tack, track
/d/---- dam, do, cord, draft, powder, advert, kid, deep, dim, divide, diary, dark, middle, paddle
/k/----- kid, kiss, cock, fix, six, choir, chord, require, back, calculate, kit, chasm
/g/ ----- game, goggle, got, gum, gay, guy, example, get, rogue, girl, grow
/ʧ/ ----fetch, match, march, rich, reach, nature, pasture, patch, chain, choice, children, Christ, Christians, character
/ʤ/ ---- gin, joy, edge, badge, jaw, jest, jeep, gem, general, gentle, page, judge, jam, giant
/f/------ tough, fall, phone, elephant, photo, food, fleet, fault
/v/ -------very, nephew, of, value, vice, voice, van, view, prove, visible
/Ө/ ------ thin, think, three, threw, though, length, breath, theatre, theme, thick, thicket, third, thrust
/ð/ ------- the, father, mother, them, that, thine, bathe, then, rather, this, there
/s/ ------- science, class, fast, slow, city, pass, dress, psychology, lace, face, pastor, taste, set
/z/ ------zoo, zoom, lazy, zigzag, zinc, close, rose, represent, reason, candies, laze, raise, zebra, easy
/∫/ ------ chalet, chateau, charade, machine, education, social, palatial, mission, short, sure, passion pressure
/Ӡ/------ garage, measure, treasure, leisure, television, vision, confusion, decision, fusion, pleasure, division, closure, usual
/h/ ----- house, home, harrow, harassment
/Ɩ/------- look, late, life, lake, lift, later, letter, local, lion, low, love, lame, lie
/r/------ robe, right, reflex, run, carry, merry, bright, story, bury, rite, wrong, wrote, radio
/m/------ flame, hammer, man, malt, make, come, mother, magic
/ŋ/------- bang, uncle, bank, sing, long, king, zinc, single, thank
/j/-------- you, yawn, yellow, yam, union, use, yes, university
/w/------ one, wine, when, suite, quit, work, what, where, which, wife
/n/-------- know, night, knight, knowledge, banner
https://youtu.be/h4yrIuCE6UM
https://youtu.be/zoarwB-7O_c
EVALUATION:
From the words lettered A-E, choose the word that has the same consonant sound as the one represented by letters underlined.
1. Vain a. bane b. faint c. foil d. pain e. Stephen
2. Vice a. eat b. dress c. show d. chalk e. cool
3. Marry a. cart b. break c. river d. hurt e. curl
4. Time a. length b. thigh c. dime d. thyme e. width
5. Father a. matter b. murder c. further d. hunter e. fatter
LESSON 25
ASPECT: Literature in English.
TOPIC: Poetry (Types)
Prose is a piece of creative writing that is usually written in verse while poetry is collection of prose.
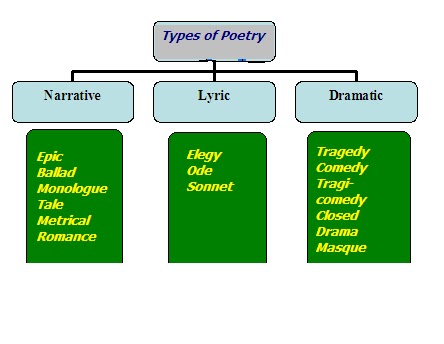
Types of poetry include:
1. Epic: Epic poems are long serious poems that tell story of a heroic figure.
2. Lyric: This poem can be sung. It expresses the poet’s thoughts and feelings.
3. Ode: Odes are poems which are serious in nature and written to a set a structure.
4. Ballads: Ballad poems are poems that tell story similar to a folk tale or legend and often has a repeated refrain. A ballad is often about love and often sung.
5. Dirge: This poem laments over the dead person.
6. Sonnets: Sonnets are lyric poems that are 14 lines long.
7. Elegy: A sad poem especially about someone who is dead.
8. ABC poem: An ABC poem has a series of lines that create a mood, picture, or feeling. Lines are made up of words and phrases.
The first word of line 1 begins with an A; the first word of line 2 begins with a B etc.
Example of ABC poem:
Although things are not perfect
Because of trial or pain
Continue in thanksgiving
Do not begin to blame
Even when the times are hard
Fierce winds are bound to blow…
9. Rhymes: Rhymes are types of poems which have the repetition of the same or similar sounds at the end of the two or more words most often at the end of lines.
EVALUATION: Mention five types of poems and explain any two?
From the words lettered A-D, choose the word that contains the SOUND represented by the given phonetic symbol.
1. /k/ (a) comb (b) kneel (c) cease (d) cell
2. /f/ (a) very (b) cough (c) love (d) off.
3. /m/ (a) comb (b) tanner (c) word (d) answer.
4. /r/ (a) girl (b) liver (c) year (d) worry.