WEEK 10
Posted: Fri Jun 19, 2015 8:42 pm
LESSON 17
MAIN TOPIC: INTRODUCTION TO BOOK-KEEPING
SPECIFIC TOPIC: Meaning and importance
REFERENCE BOOKS:
Macmillan JSS1 Business Studies by Awoyokun A.A et al .Pages 54-55
WABP JSS Business Studies 1by Egbe T. Ehiametalor. Pages 47-48
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVES: At the end of the lesson, students should be able to:
define book-keeping
mention importance of book-keeping
CONTENTS:
Very few traders know the art of keeping proper record of their business transactions. that is, what they buy and sell and the amount of profit they make from it.
Book-keeping is the art of recording business transactions in a regular and systematic manner such that the record would be in a permanent form.
Transfer means the transfer of goods and services from one person to another.

IMPORTANCE OF BOOK-KEEPING
It provides the systematic recording of business transactions
It provides a means by which an enterprise can be conducted in an orderly manner
It provides a basis for recording and referring to at any point in time.
It shows at the end of a period whether a business has recorded any profit or loss or break even.
EVALUATION:
What is book-keeping?
Mention three importance of book-keeping.
HOME-WORK: mention three qualities of a book-keeper
SPECIFIC TOPIC: Qualities of a book-keeper
REFERENCE BOOKS:
Macmillan JSS1 Business Studies by Awoyokun A.A et al .Pages 54-55
WABP JSS Business Studies 1by Egbe T. Ehiametalor. Pages 47-48
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVES: At the end of the lesson, students should be able to:
mention the job qualities of a book-keeper
mention the personal qualities of a book-keeper
CONTENTS:
PERSONAL QUALITIES
Must possess minimum of high school education to enhance reading and writing legibly
Must be honest
Must be reliable
Must have self confidence
JOB QUALITIES
Must be accurate- a mathematical ability is essential
Must be intelligent and alert to issues concerning his job
Must be tactful
Must possess accounting skills
EVALUATION:
Mention four job qualities of a book-keeper.
Mention three personal qualities of a book-keeper.
HOME-WORK: Briefly mention three book-keeping ethics.
SPECIFIC TOPIC: Book-keeping ethics
REFERENCE BOOKS:
Macmillan JSS1 Business Studies by Awoyokun A.A et al .Pages 54-55
WABP JSS Business Studies 1by Egbe T. Ehiametalor. Pages 47-48
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVES: At the end of the lesson, students should be able to:
mention common book-keeping ethics
mention book-keeping ethics
CONTENTS:
COMMON BOOK-KEEPING PRACTICE
Issuing of receipts to a customer after sales.
Entering of sales transaction into sales book on a daily basis
Entering the amount of goods returned into the appropriate book.
BOOK-KEEPING ETHICS
Accurate keeping of records
Avoid cancelling
Keep all records safe and tidy
Make information available as at when needed.
EVALUATION:
mention three common book-keeping practice and four book- keeping ethics
HOME-WORK: what are daybooks?
LESSON 18
MAIN TOPIC: SOURCE DOCUMENTS
SPECIFIC TOPIC: Meaning and importance
REFERENCE BOOKS:
Macmillan JSS1 Business Studies by Awoyokun A.A et al .Pages 56-58
WABP JSS Business Studies 1by Egbe T. Ehiametalor. Pages 49-52
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVES: At the end of the lesson, students should be able to:
state the meaning of source documents
give examples of source documents
mention some of the uses of source documents
CONTENTS:
In order to keep records of business transaction documents are issued to show that certain transactions has taken place. E.g. when you pay school fees, receipt is given.
The book-keeper uses these documents {such as receipt} to prepare books of accounts of the business.
These documents are called source documents because they are the first source of information from which accounting books are prepared.
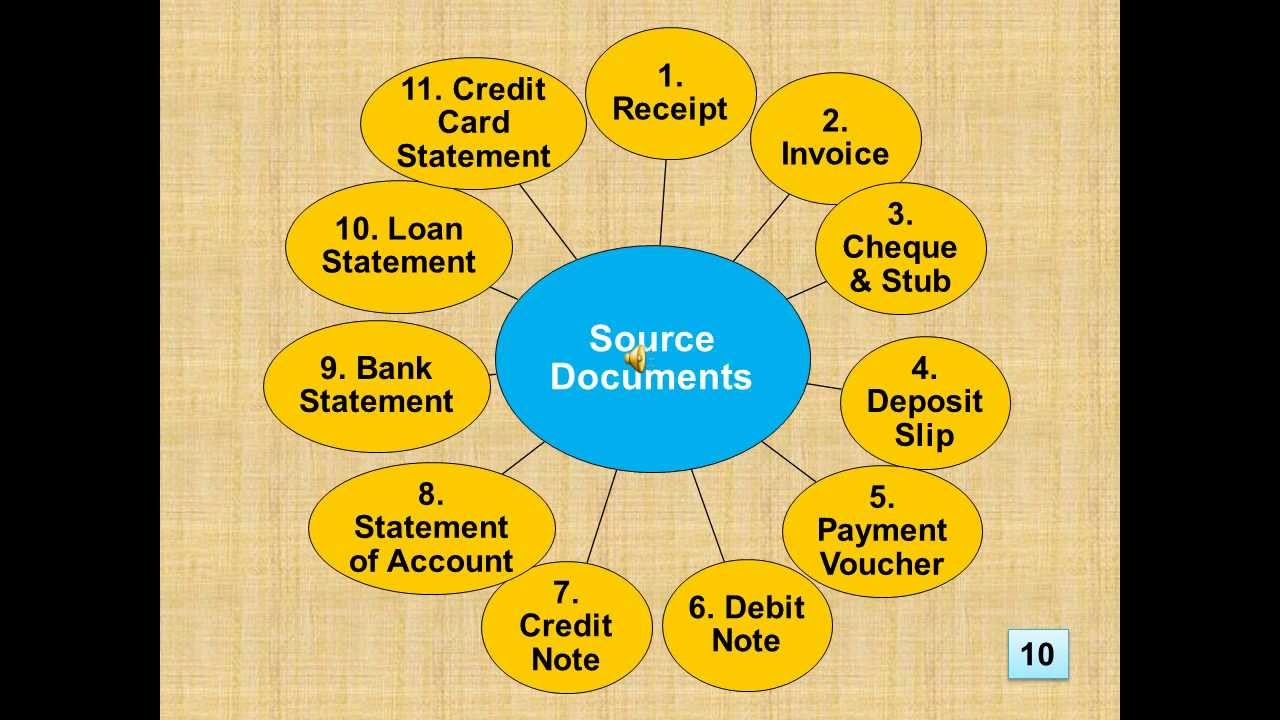
Source documents are the documents in which original business transactions are first recorded before been transferred into subsidiary books of accounts.
Examples of source documents include: invoice, voucher, cheque, receipt, credit note, debit note etc.
EVALUATION:
What are source document?
Mention three source documents that you know
Mention the purpose/ uses of source documents.
HOME-WORK: explain invoice, credit note and debit note.
SPECIFIC TOPIC: invoice, credit note and debit note.
REFERENCE BOOKS:
Macmillan JSS1 Business Studies by Awoyokun A.A et al .Pages 56-58
WABP JSS Business Studies 1by Egbe T. Ehiametalor. Pages 49-52
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVES: At the end of the lesson, students should be able to:
state the meaning and uses of an invoice
state the meaning and uses of credit note
state the meaning and uses of debit note
CONTENTS:
INVOICE
This is the document issued by the seller to the buyer showing the description of the goods purchased, the terms of agreement, quantity and price. It may also contain any deposit paid and the balance outstanding.
CREDIT NOTE
This is issued by a supplier when a buyer returns goods to the supplier. It may also be issued by a supplier to a buyer when the buyer has overcharged the buyer. It shows that the amount of money to be paid by the buyer has reduced.
DEBIT NOTE
This is a document that is issued by the seller to the buyer to show that the buyer has been undercharged.
EVALUATION:
Explain the following in details invoice, credit note and debit note.
HOME-WORK: write short notes on receipt, cheque and voucher
SPECIFIC TOPIC: Receipt, Cheque and Voucher
REFERENCE BOOKS:
Macmillan JSS1 Business Studies by Awoyokun A.A et al .Pages 56-58
WABP JSS Business Studies 1by Egbe T. Ehiametalor. Pages 49-52
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVES: At the end of the lesson, students should be able to:
state the meaning and uses of a receipt
state the meaning and uses of a cheque
state the meaning and uses of a voucher
CONTENTS:
RECEIPT
This is a document which the seller issues to the buyer in order to acknowledge receipt of payment for the goods sold.
CHEQUE
A cheque is a written order to a bank to pay a certain some of money to another person or to the owner of the cheque.
VOUCHER
Any document which is used to support an entry in the books of account is called a voucher.
EVALUATION:
mention three common book-keeping practice and four book- keeping ethics
HOME-WORK: what are daybooks?
LESSON 19
MAIN TOPIC: DOUBLE ENTRY BOOK-KEEPING
SPECIFIC TOPIC: Meaning and format
REFERENCE BOOKS:
Macmillan JSS1 Business Studies by Awoyokun A.A et al .Pages 61-67
WABP JSS Business Studies 1by Egbe T. Ehiametalor. Pages 58-65
Spectrum Business Studies by Eno L.Inanga and Ebun C.Ojo Pages 67-74
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVES: At the end of the lesson, students should be able to:
state the meaning of double entry
state the principle of double entry
draw the format of double entry account
CONTENTS:
Double entry is a system of book-keeping in which transactions are first recorded in both the debit and credit sides of the ledger at the same time.
The double entry principle states that - For every debit entry there must be a corresponding credit entry and vice versa.
Double entry records are kept in a book called a ledger and each page in a ledger is called an account.
EVALUATION:
What is book-keeping?
state double entry principle
Draw the format of a double entry account.
HOME-WORK: what are asset, liability and capital?
SPECIFIC TOPIC: Golden rule of double entry
REFERENCE BOOKS:
Macmillan JSS1 Business Studies by Awoyokun A.A et al .Pages 61-67
WABP JSS Business Studies 1by Egbe T. Ehiametalor. Pages 58-65
Spectrum Business Studies by Eno L.Inanga and Ebun C.Ojo Pages 67-74
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVES: At the end of the lesson, students should be able to:
state the meaning of asset, liability and capital
state and apply the golden rule in book-keeping
CONTENTS:
An Asset is anything of value that is owned by a business
A Liability is an amount owed by a business to others.
Capital is the total investment in a business.
GOLDEN RULE:
Debit- The account that receives
Credit- The account that gives
Capital account is always on the credit side
EVALUATION:
What are assets, liability and capital
Give examples of asset and liability
HOME-WORK: State the double entry principle
SPECIFIC TOPIC: Exercises on double entry book-keeping
REFERENCE BOOKS:
Macmillan JSS1 Business Studies by Awoyokun A.A et al .Pages 61-67
WABP JSS Business Studies 1by Egbe T. Ehiametalor. Pages 58-65
Spectrum Business Studies by Eno L.Inanga and Ebun C.Ojo Pages 67-74
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVES: At the end of the lesson, students should be able to:
solve questions relating to double entry book-keeping correctly
CONTENTS:
Question 3 Spectrum Business Studies by Eno L.Inanga and Ebun C.Ojo Page74
Question 1 and 2 WABP JSS Business Studies 1by Egbe T. Ehiametalor. Pages 64
EVALUATION:
Question 5 Spectrum Business Studies by Eno L.Inanga and Ebun C.Ojo Page74
HOME-WORK: what are ledgers?
LESSON 20
MAIN TOPIC: LEDGER
SPECIFIC TOPIC: Meaning and classification
REFERENCE BOOKS:
Macmillan JSS1 Business Studies by Awoyokun A.A et al .Pages 65-67
WABP JSS Business Studies 1by Egbe T. Ehiametalor. Pages 61-65
Spectrum Business Studies by Eno L.Inanga and Ebun C.Ojo Pages 75-84
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVES: At the end of the lesson, students should be able to:
state the meaning of ledger
state the classification of ledger
draw the format of ledger
CONTENTS:
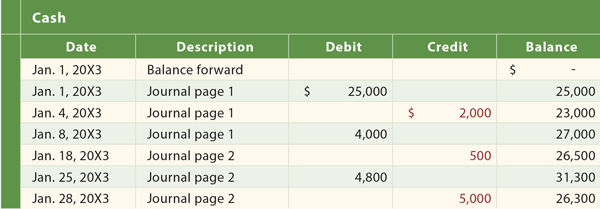
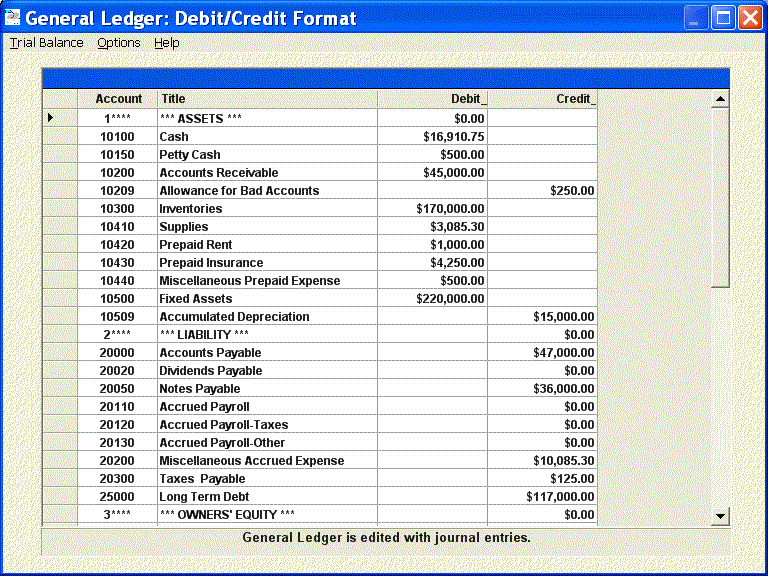
A general ledger account is an account or record used to sort and store balance sheet and income statement transactions. Examples of general ledger accounts include the asset accounts such as Cash, Accounts Receivable, Inventory, Investments, Land, and Equipment. Examples of the general ledger liability accounts include Notes Payable, Accounts Payable, Accrued Expenses Payable, and Customer Deposits. Examples of income statement accounts found in the general ledger include Sales, Service Fee Revenues, Salaries Expense, Rent Expense, Advertising Expense, Interest Expense, and Loss on Disposal of Assets.
Some general ledger accounts are summary records which are referred to as control accounts. The detail that supports each of the control accounts will be found outside of the general ledger in what is known as a subsidiary ledger. For example, Accounts Receivable could be a control account in the general ledger, and there will be a subsidiary ledger which contains each customer's credit activity. The general ledger accounts Inventory, Equipment, and Accounts Payable could also be control accounts and for each there will be a subsidiary ledger containing the supporting detail.
The ledger is a principal book of account in which all the transactions that take place in a business organisation are recorded.
CLASSIFICATION OF LEDGER
Ledger accounts can be divided into
Personal account: These are the accounts for debtors and creditors.
Impersonal account: This can further be divided into real and nominal account.
Nominal accounts: These are accounts of income and expenditure such as wages, rent, electricity etc. They cannot be seen or touched.
Real account: These are account relating to property or material objects. E.g land, car, plant etc.
EVALUATION:
What is ledger?
mention two classification of ledger with examples
Draw the format of a ledger.
HOME-WORK: what is typewriting?
MAIN TOPIC: INTRODUCTION TO BOOK-KEEPING
SPECIFIC TOPIC: Meaning and importance
REFERENCE BOOKS:
Macmillan JSS1 Business Studies by Awoyokun A.A et al .Pages 54-55
WABP JSS Business Studies 1by Egbe T. Ehiametalor. Pages 47-48
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVES: At the end of the lesson, students should be able to:
define book-keeping
mention importance of book-keeping
CONTENTS:
Very few traders know the art of keeping proper record of their business transactions. that is, what they buy and sell and the amount of profit they make from it.
Book-keeping is the art of recording business transactions in a regular and systematic manner such that the record would be in a permanent form.
Transfer means the transfer of goods and services from one person to another.

IMPORTANCE OF BOOK-KEEPING
It provides the systematic recording of business transactions
It provides a means by which an enterprise can be conducted in an orderly manner
It provides a basis for recording and referring to at any point in time.
It shows at the end of a period whether a business has recorded any profit or loss or break even.
EVALUATION:
What is book-keeping?
Mention three importance of book-keeping.
HOME-WORK: mention three qualities of a book-keeper
SPECIFIC TOPIC: Qualities of a book-keeper
REFERENCE BOOKS:
Macmillan JSS1 Business Studies by Awoyokun A.A et al .Pages 54-55
WABP JSS Business Studies 1by Egbe T. Ehiametalor. Pages 47-48
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVES: At the end of the lesson, students should be able to:
mention the job qualities of a book-keeper
mention the personal qualities of a book-keeper
CONTENTS:
PERSONAL QUALITIES
Must possess minimum of high school education to enhance reading and writing legibly
Must be honest
Must be reliable
Must have self confidence
JOB QUALITIES
Must be accurate- a mathematical ability is essential
Must be intelligent and alert to issues concerning his job
Must be tactful
Must possess accounting skills
EVALUATION:
Mention four job qualities of a book-keeper.
Mention three personal qualities of a book-keeper.
HOME-WORK: Briefly mention three book-keeping ethics.
SPECIFIC TOPIC: Book-keeping ethics
REFERENCE BOOKS:
Macmillan JSS1 Business Studies by Awoyokun A.A et al .Pages 54-55
WABP JSS Business Studies 1by Egbe T. Ehiametalor. Pages 47-48
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVES: At the end of the lesson, students should be able to:
mention common book-keeping ethics
mention book-keeping ethics
CONTENTS:
COMMON BOOK-KEEPING PRACTICE
Issuing of receipts to a customer after sales.
Entering of sales transaction into sales book on a daily basis
Entering the amount of goods returned into the appropriate book.
BOOK-KEEPING ETHICS
Accurate keeping of records
Avoid cancelling
Keep all records safe and tidy
Make information available as at when needed.
EVALUATION:
mention three common book-keeping practice and four book- keeping ethics
HOME-WORK: what are daybooks?
LESSON 18
MAIN TOPIC: SOURCE DOCUMENTS
SPECIFIC TOPIC: Meaning and importance
REFERENCE BOOKS:
Macmillan JSS1 Business Studies by Awoyokun A.A et al .Pages 56-58
WABP JSS Business Studies 1by Egbe T. Ehiametalor. Pages 49-52
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVES: At the end of the lesson, students should be able to:
state the meaning of source documents
give examples of source documents
mention some of the uses of source documents
CONTENTS:
In order to keep records of business transaction documents are issued to show that certain transactions has taken place. E.g. when you pay school fees, receipt is given.
The book-keeper uses these documents {such as receipt} to prepare books of accounts of the business.
These documents are called source documents because they are the first source of information from which accounting books are prepared.
Source documents are the documents in which original business transactions are first recorded before been transferred into subsidiary books of accounts.
Examples of source documents include: invoice, voucher, cheque, receipt, credit note, debit note etc.

EVALUATION:
What are source document?
Mention three source documents that you know
Mention the purpose/ uses of source documents.
HOME-WORK: explain invoice, credit note and debit note.
SPECIFIC TOPIC: invoice, credit note and debit note.
REFERENCE BOOKS:
Macmillan JSS1 Business Studies by Awoyokun A.A et al .Pages 56-58
WABP JSS Business Studies 1by Egbe T. Ehiametalor. Pages 49-52
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVES: At the end of the lesson, students should be able to:
state the meaning and uses of an invoice
state the meaning and uses of credit note
state the meaning and uses of debit note
CONTENTS:
INVOICE
This is the document issued by the seller to the buyer showing the description of the goods purchased, the terms of agreement, quantity and price. It may also contain any deposit paid and the balance outstanding.
CREDIT NOTE
This is issued by a supplier when a buyer returns goods to the supplier. It may also be issued by a supplier to a buyer when the buyer has overcharged the buyer. It shows that the amount of money to be paid by the buyer has reduced.
DEBIT NOTE
This is a document that is issued by the seller to the buyer to show that the buyer has been undercharged.
EVALUATION:
Explain the following in details invoice, credit note and debit note.
HOME-WORK: write short notes on receipt, cheque and voucher
SPECIFIC TOPIC: Receipt, Cheque and Voucher
REFERENCE BOOKS:
Macmillan JSS1 Business Studies by Awoyokun A.A et al .Pages 56-58
WABP JSS Business Studies 1by Egbe T. Ehiametalor. Pages 49-52
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVES: At the end of the lesson, students should be able to:
state the meaning and uses of a receipt
state the meaning and uses of a cheque
state the meaning and uses of a voucher
CONTENTS:
RECEIPT
This is a document which the seller issues to the buyer in order to acknowledge receipt of payment for the goods sold.
CHEQUE
A cheque is a written order to a bank to pay a certain some of money to another person or to the owner of the cheque.
VOUCHER
Any document which is used to support an entry in the books of account is called a voucher.
EVALUATION:
mention three common book-keeping practice and four book- keeping ethics
HOME-WORK: what are daybooks?
LESSON 19
MAIN TOPIC: DOUBLE ENTRY BOOK-KEEPING
SPECIFIC TOPIC: Meaning and format
REFERENCE BOOKS:
Macmillan JSS1 Business Studies by Awoyokun A.A et al .Pages 61-67
WABP JSS Business Studies 1by Egbe T. Ehiametalor. Pages 58-65
Spectrum Business Studies by Eno L.Inanga and Ebun C.Ojo Pages 67-74
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVES: At the end of the lesson, students should be able to:
state the meaning of double entry
state the principle of double entry
draw the format of double entry account
CONTENTS:
Double entry is a system of book-keeping in which transactions are first recorded in both the debit and credit sides of the ledger at the same time.
The double entry principle states that - For every debit entry there must be a corresponding credit entry and vice versa.
Double entry records are kept in a book called a ledger and each page in a ledger is called an account.
EVALUATION:
What is book-keeping?
state double entry principle
Draw the format of a double entry account.
HOME-WORK: what are asset, liability and capital?
SPECIFIC TOPIC: Golden rule of double entry
REFERENCE BOOKS:
Macmillan JSS1 Business Studies by Awoyokun A.A et al .Pages 61-67
WABP JSS Business Studies 1by Egbe T. Ehiametalor. Pages 58-65
Spectrum Business Studies by Eno L.Inanga and Ebun C.Ojo Pages 67-74
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVES: At the end of the lesson, students should be able to:
state the meaning of asset, liability and capital
state and apply the golden rule in book-keeping
CONTENTS:
An Asset is anything of value that is owned by a business
A Liability is an amount owed by a business to others.
Capital is the total investment in a business.
GOLDEN RULE:
Debit- The account that receives
Credit- The account that gives
Capital account is always on the credit side
EVALUATION:
What are assets, liability and capital
Give examples of asset and liability
HOME-WORK: State the double entry principle
SPECIFIC TOPIC: Exercises on double entry book-keeping
REFERENCE BOOKS:
Macmillan JSS1 Business Studies by Awoyokun A.A et al .Pages 61-67
WABP JSS Business Studies 1by Egbe T. Ehiametalor. Pages 58-65
Spectrum Business Studies by Eno L.Inanga and Ebun C.Ojo Pages 67-74
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVES: At the end of the lesson, students should be able to:
solve questions relating to double entry book-keeping correctly
CONTENTS:
Question 3 Spectrum Business Studies by Eno L.Inanga and Ebun C.Ojo Page74
Question 1 and 2 WABP JSS Business Studies 1by Egbe T. Ehiametalor. Pages 64
EVALUATION:
Question 5 Spectrum Business Studies by Eno L.Inanga and Ebun C.Ojo Page74
HOME-WORK: what are ledgers?
LESSON 20
MAIN TOPIC: LEDGER
SPECIFIC TOPIC: Meaning and classification
REFERENCE BOOKS:
Macmillan JSS1 Business Studies by Awoyokun A.A et al .Pages 65-67
WABP JSS Business Studies 1by Egbe T. Ehiametalor. Pages 61-65
Spectrum Business Studies by Eno L.Inanga and Ebun C.Ojo Pages 75-84
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVES: At the end of the lesson, students should be able to:
state the meaning of ledger
state the classification of ledger
draw the format of ledger
CONTENTS:
A general ledger account is an account or record used to sort and store balance sheet and income statement transactions. Examples of general ledger accounts include the asset accounts such as Cash, Accounts Receivable, Inventory, Investments, Land, and Equipment. Examples of the general ledger liability accounts include Notes Payable, Accounts Payable, Accrued Expenses Payable, and Customer Deposits. Examples of income statement accounts found in the general ledger include Sales, Service Fee Revenues, Salaries Expense, Rent Expense, Advertising Expense, Interest Expense, and Loss on Disposal of Assets.
Some general ledger accounts are summary records which are referred to as control accounts. The detail that supports each of the control accounts will be found outside of the general ledger in what is known as a subsidiary ledger. For example, Accounts Receivable could be a control account in the general ledger, and there will be a subsidiary ledger which contains each customer's credit activity. The general ledger accounts Inventory, Equipment, and Accounts Payable could also be control accounts and for each there will be a subsidiary ledger containing the supporting detail.
The ledger is a principal book of account in which all the transactions that take place in a business organisation are recorded.


CLASSIFICATION OF LEDGER
Ledger accounts can be divided into
Personal account: These are the accounts for debtors and creditors.
Impersonal account: This can further be divided into real and nominal account.
Nominal accounts: These are accounts of income and expenditure such as wages, rent, electricity etc. They cannot be seen or touched.
Real account: These are account relating to property or material objects. E.g land, car, plant etc.
EVALUATION:
What is ledger?
mention two classification of ledger with examples
Draw the format of a ledger.
HOME-WORK: what is typewriting?