MAIN TOPIC : Acid, Bases and Salt
SPECIFIC TOPIC : Acid
REFERENCE BK :Nigerian Basic Science Project, Pupils - Textbook Three
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVE: At the end of the lesson the students should be able to:
(1)define acid
(2)state the features or characteristics of acid
CONTENT
Acid, Base and Salt
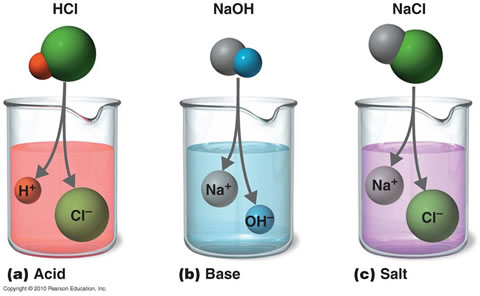
There is a link between acid, base and salt .Acid are generally known to be corrosive but not all acid are corrosive .
Types of acid
Natural acid : example of natural acid are ; amino acid, ascorbic acid,
Citric acid, fatty acid, lactice acid, tartaric acid.
mineral acid : example are HCL,H2SO4ETC
Characteristics of acid
1. Turns blue litmus paper red
2. Acid are corrosive
3. Acid react with substances to produce gases
4. Acid have soar taste

watch video
https://youtu.be/rHRoCyAc4YI
https://youtu.be/K_b6b8huAx8
EVALUATION/CLASSWORK
Describe acid
State the characteristics of acid
further studies
http://www.chem4kids.com/files/react_acidbase.html
http://www.neok12.com/Acids-and-Bases.htm
http://www.ehow.com/list_7241740_charac ... tml#page=0
practice test
http://chemistry.about.com/library/week ... idquiz.htm
http://www.quia.com/quiz/101121.html
http://www.funtrivia.com/playquiz/quiz2 ... 771b8.html
LESSON 25
SPECIFIC TOPIC : Acid
REFERENCE BK :Nigerian Basic Science Project, Pupils - Textbook Three
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVE: At the end of the lesson the students should be able to:
(1) define salt
(2) state the features or characteristics of base and salt.
(3) carry simple experiment on acid and base test
CONTENT
Bases are regarded as the opposites of acid. According to the definition of Arrhenius, a base is any hydroxide that dissolves in water to yield hydroxide (OH) ion as the only negative ion.
CHARACTERISTICS OF BASES
1. Bases have a slippery or soapy feel
2. Bases turn red litmus paper blue.
3. Concentrated solution of bases are corrosive

SALT
Salt is defined as a compound which consists of positive metallic ion and a negative, non-metallic ion. A salt is composed of the sodium ion, Na+ . Salt is as a result of neutralization.
https://youtu.be/rkaZoKUR0oY
PRACTICAL WORK ON TEST FOR ACID, BASE AND THEIR CHARACTERISTICS
http://www.funsci.com/fun3_en/acids/acids.htm
https://youtu.be/4cL1kmjASbY
EVALUATION/CLASSWORK
Describe salt
State the characteristics of salt
Carry simple experiment on acid ,base and salt
https://youtu.be/qIQWGTV50yE
ASSIGNMENT:
State the uses of acid, base and salt
further studies
http://www.syvum.com/cgi/online/serve.c ... salts.html
http://www.chem4kids.com/files/react_acidbase.html
http://www.excellup.com/classten/scienc ... esalt.aspx
practice test
http://www.visionlearning.com/library/q ... d=58&mcid=
http://excellup.com/seven_science/seven ... _base.aspx
http://www.syvum.com/cgi/online/mult.cg ... alts.tdf?0
LESSON 26
SPECIFIC TOPIC : Kinetic theory of matter
REFERENCE BK : Basic Science for JSS by Evans
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVE : At the end of the lesson the students should be able to:
(1) Define kinetic theory
(2) State the kinetic theories of matter
(3) Explain terms related to kinetic theory of matter
Content
Kinetic theory of matter (energy).
- Simple qualitative aspects of the kinetic theory.
- Its assumption and its uses in explaining some phenomenon (boiling point, melting point and freezing point).
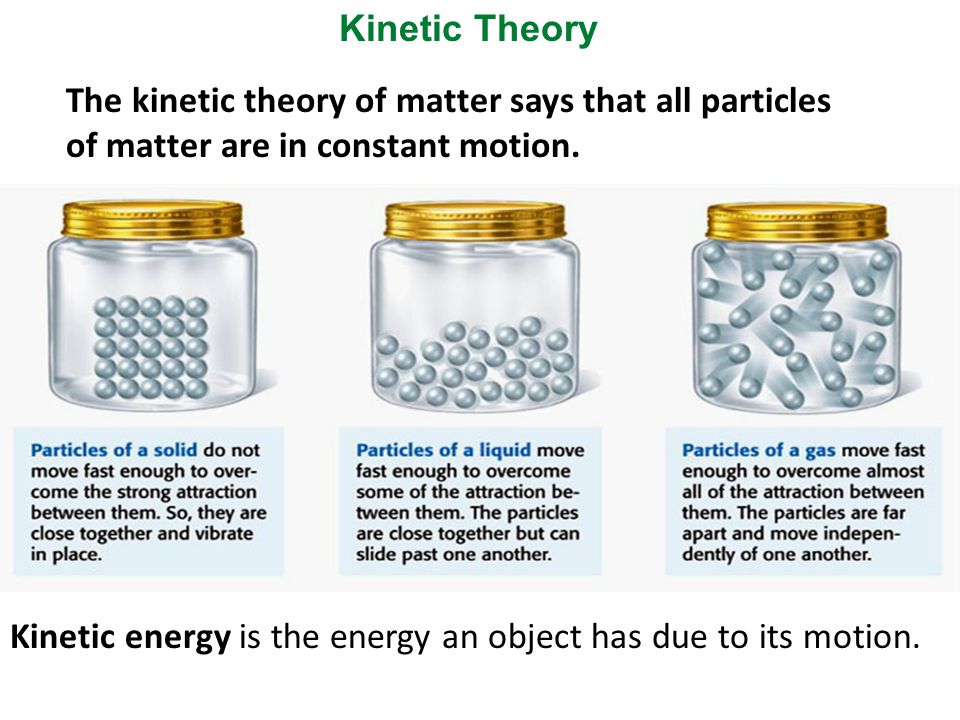
The Kinetic Molecular Theory of Matter is a concept that basically states that atoms and molecules possess an energy of motion (kinetic energy) that we perceive as temperature. In other words, atoms and molecules are constantly in motion , and we measure the energy of these movements as the temperature of that substance. This means if there is an increase in temperature, the atoms and molecules will gain more energy (kinetic energy) and move even faster.
This kinetic-molecular theory states (postulates) that:
All matter (solid, liquid, and gas) is made up of tiny particles called atoms, or atoms that are joined to form molecules.

These particles are in constant motion.
Molecular motion is random.
Particles in motion possess kinetic energy.
Their motion increase as they gain energy.
There is an exchange (transfer) of energy between particles (atoms and molecules) during a collision between them.
Particles (molecules) in gases do not exert large forces on each other, unless they are in collision with each other.
Collisions between these particles are perfectly elastic.
Molecular motion is greatest in gases, less in liquids, and least in solids.
Solids retain a fixed volume and shape - particles are tightly packed, usually in a regular pattern.
Liquids assume the shape of the container which it occupies but maintain their volume - particles close together with no regular arrangement.
Gases assumes the shape and volume of its container and will expand to fill a container of any size - particles are very well far apart with no regular arrangement.

https://youtu.be/R1l1Cww88XQ
The kinetic molecular theory is very useful in explaining or describing the forces between molecules and the energy that they possess, as well as, the effects of thermal energy, temperature and pressure on matter.
https://youtu.be/LQKhYVbfgMs
Evaluation
Define Kinetic theory
State the kinetic theories of matter
Explain the terms - Melting Point, Freezing Point & Boiling Point
further studies
http://www.hometrainingtools.com/kineti ... ip/a/1216/
practice test
http://www.docbrown.info/page03/3_52sta ... tatesQ.htm