TOPIC: HABITAT
OBJECTIVE: At the end of the lesson, the students should be able to:
1. Define habitat.
2. Mention major types of habitat.
3. Enumerate types of terrestrial habitat.
CONTENT:
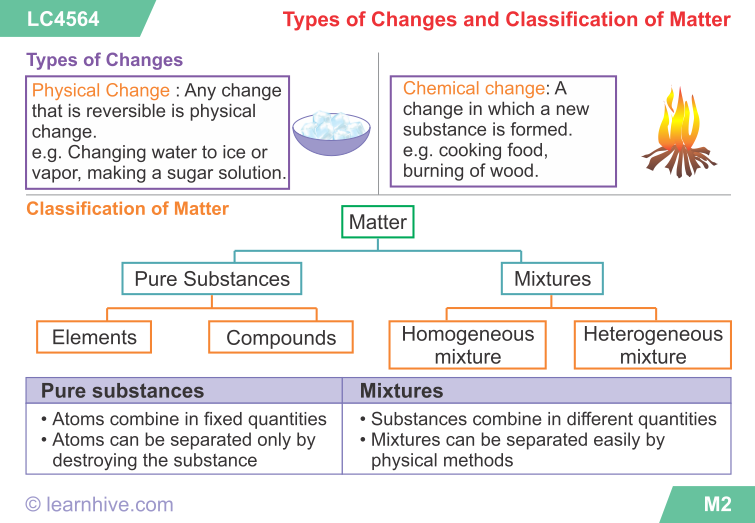
Every living organism has a particular place where it normally lives. The kind of place or environment where an organism normally lives is called HABITAT. It means the home where an organism inhabits. Every organism is able to adjust itself to its habitat in order for it to survive.
There are two major habitats:
(1) TERRESTRIAL HABITATS:
The terrestrial habitat refers to land environment. Living organisms found living in terrestrial habitat include human beings, domestic animals, wild animals and plants.
The terrestrial habitats can be:
a. Arboreal: in or on trees e.g. monkeys, birds and ants.
b. On the ground: e.g. grasscutters.
c. Underground: e.g. earthworm.
Ground habitat may be tropical, rain forest, savannah, grassland, semi desert and desert.

EVALUATION:
What is habitat?
What are the major types of habitat?
What are the types of terrestrial habitat?
ASSIGNMENT:
Name three major kinds of habitats for living things and two kinds of living things that can be found in each of the habitat.
further studies
http://www.preservearticles.com/2011010 ... types.html
practice test
http://www.quibblo.com/quiz/bTuXN_n/Lec ... l-habitats
LESSON 40
TOPIC: AQUATIC HABITAT
OBJECTIVE: At the end of the lesson, the students should be able to:
1. Define aquatic habitat.
2. Define salinity.
3. Mention the three subdivisions of aquatic habitat.
4. Describe brackish water habitat.
CONTENT:
Aquatic habitats include all bodies of water in which organisms live. According to the salinity of the water, that is, salt concentration in the water, aquatic habitat can be subdivided into three:
(1) MARINE OR SALT WATER:
These include the sea, oceans, and salty lakes. Examples of organisms found in the marine water are fish, whale, turtles, crocodiles, water lilies etc.

(2) FRESH WATER:
These include rivers and streams. Also lakes and ponds. Organisms found here include fish, cray fish, crabs, protozoa and large fish.

(3) BRAKISH WATER:
This is found at estuarines, that is river mouths where rivers enter into the sea or where salt and fresh water meet. The water here is neither salty nor fresh. Hermit crab, periwinkles and lobsters are found here. Examples of such areas are bays and lagoons.

ADAPTATION OF LIVING THINGS TO THEIR HABITAT
The suiting of an organism to its habitat is called ADAPTATION. An organism is able to live in a particular habitat because it has certain characteristic features that help it to carry out all the characteristics of living. Such features are called ADAPTIVE FEATURES.


EVALUATION:
What is aquatic habitat?
What is salinity?
What are the three subdivisions of aquatic habitat?
What is brackish water habitat?
ASSIGNMENT:
In a tabular form state four adaptive features of a fish and the uses of these features.
Visit a pond and write a report of what they observed.
further studies
http://www.sciencekids.co.nz/sciencefac ... ceans.html
http://kidsresearchexpress-8.blogspot.c ... itats.html
http://www.kidzworld.com/article/1951-b ... ld-aquatic
practice test
http://www.quizplz.com/science/biology/ ... e-quiz.htm
LESSON 41
TOPIC: ADAPTATION OF PLANTS
OBJECTIVE: At the end of the lesson, the students should be able to:
1. Mention the adaptation of plants in desert areas in relation to water.
2. Mention adaptations of plants that live on water.
CONTENT:
In desert areas in relation to water:
Plants that live in areas with limited rainfall, such as the desert have extensive root system with a long taproot that is able to penetrate deep into the ground to tap available water. Some have adventitious roots that spread widely to cover large areas. Some have developed water storage tissues in their leaves and stems.
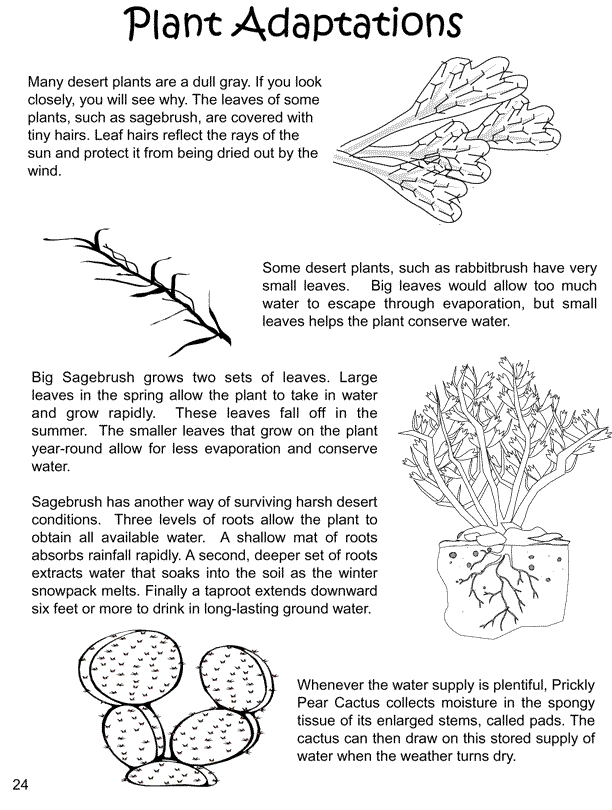
Plants that live on water
They have pearly developed root system. They have their leaves an stem covered with thin layer of cubicle that is permeable so that water, oxygen, mineral salt, carbon (IV) oxide are easily absorbed into the whole surface of the plant. Generally, leaves of aquatic plants have large air spaces. The air spaces keep the plants buoyant and help them to absorb oxygen.

EVALUATION:
What are the adaptations of plants in the desert areas in relation to water?
What are the adaptations of plants that live on water?
ASSIGNMENT:
Write a comprehensive note on the adaptive features identified in the school environment.
further studies
http://www.slideshare.net/ciellauren/pl ... elementary
practice test
http://www.nhptv.org/natureworks/quiz.htm
LESSON 42
TOPIC: ADAPTATION OF AQUATIC ANIMALS
OBJECTIVE: At the end of the lesson, the students should be able to:
1. Mention the adaptations of fish.
2. Enumerate the adaptations of amphibians.
3. Identify the adaptations of terrestrial animals.
CONTENT:
Fishes have tail and fins for swimming and balancing in water. They have a streamlined body shape which allows them to move through water without being pushed back by water current. They also have swim bladder for adjusting to changes in water pressure at different depths of water.
ADAPTATION OF AMPHIBIANS
Amphibians live in both water and land. They live in water because of their streamline body shape. Webs between their toes for swimming.
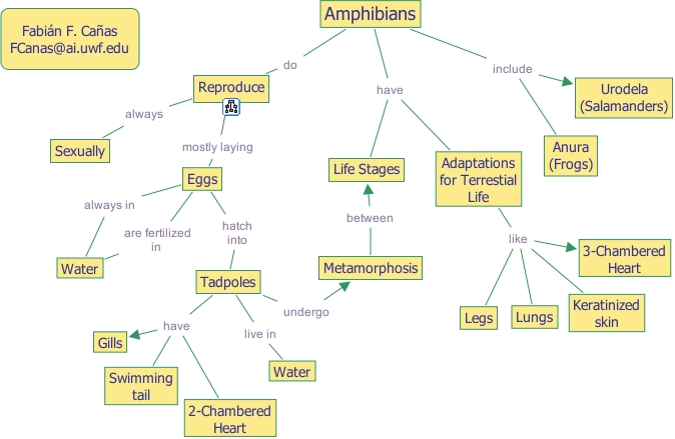
ADAPTATION OF TERRESTRIAL ANIMALS
Lungs for breathing on land, scales on the body to reduce loss of water through the skin.

watch video
https://youtu.be/h87ri4qzqVA
EVALUATION:
What are the adaptations of fish?
What are the adaptations of amphibians?
What are the adaptations of terrestrial animals?
ASSIGNMENT:
Name two major kinds of habitats for living things.
Write down four kinds of living things that can be found in the habitat.
http://www.slideshare.net/secor1sm/adap ... powerpoint
further studies
http://marinelife.about.com/od/marineli ... neLife.htm
http://www.kmuska.com/ocean/adaptations.html
http://www.softschools.com/quizzes/biol ... iz521.html
practice test
http://www.animalcorner.co.uk/animalqui ... equiz.html
http://animals.howstuffworks.com/mammal ... -quiz1.htm