SCHEME OF WORK
WEEKS .............TOPICS
1. Revision
2. Production – Meaning of Production, Types of production: industry – Extractive manufacturing and constructive industry. Commerce- Trade, Aids to Trade, Services. Effects of Production on the Environment/Society
3. Factors of production: land, labour, capital, entrepreneur and importance of each.
4. Types of occupation: meaning of occupation, Divisions – industrial, commercial and service occupation, and factors which affect occupations
5. Forms of business organization: Types of business organization - Sole Trade/sole proprietorship, partnership, limited liability companies, cooperative society, advantages and disadvantages of each forms of business organization
6. Mail Handling; Filling
7. Forms of Business Organization: Ownership of Business
8. Partnership in Business: Types of Partners
9. Public Corporation: Public Enterprise
10. Cooperative Society
11. Introduction to bookkeeping: meaning, importance, essential quality of bookkeeping, common bookkeeping practice and bookkeeping ethics; Source Documents and Special Journals: meaning, uses of source document, types of source document, invoice – sales invoice and purchase invoice, receipt for payment made, cash registered tapes, credit note, debit notes, Cheques; Books of original entry.
9. Double entry bookkeeping: meaning of double entry, double entry treatment of asset, double entry treatment of liability, double entry treatment of expenses, meaning of journals, types of journals, meaning of ledgers, classes of ledger, classification of accounts: real, personal and impersonal; Introduction to shorthand: define and explain the meaning of shorthand, historical development of shorthand, importance of shorthand in the business world and major shorthand systems
11, Revision
2ND TERM
WEEK 1
LESSON 1
Topic: PRODUCTION
CONTENT:
1. Meaning and Forms of Production
2. Factors of Production
Meaning and Forms of Production
Production could be defined as any human activity that involves the making of physical goods and provision of services for the satisfaction of human wants. It is also seen as creation of utilities, utility means the ability of goods and services to satisfy human wants.
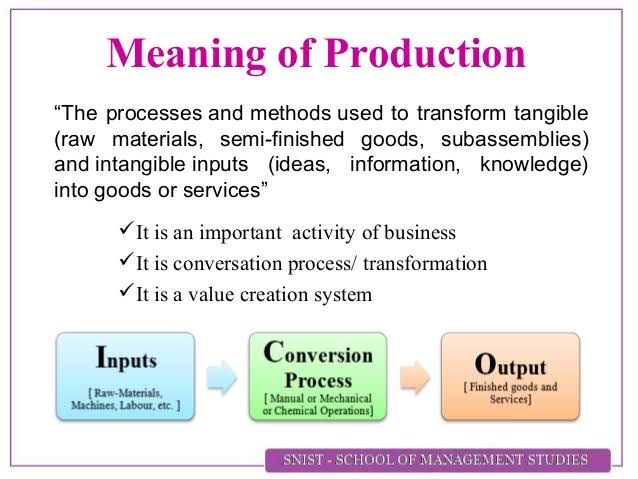
Forms of Production
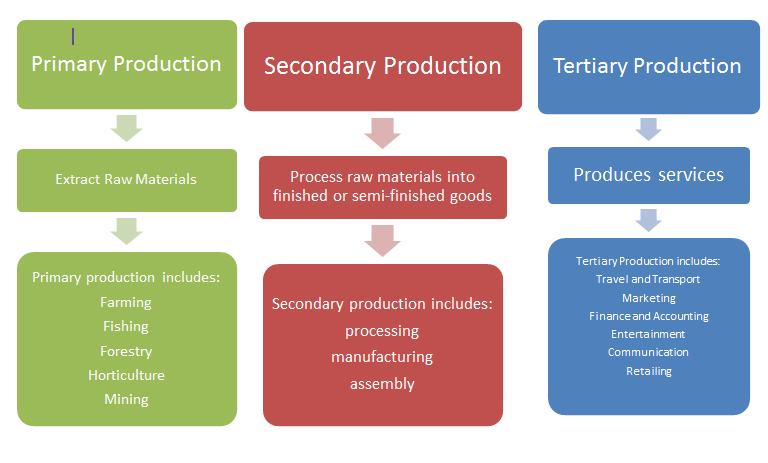
There are three forms of production namely primary (extractive industry), secondary production (manufacturing and constructive industry) and tertiary production (commercial and personal or professional services).
Primary Production (Extractive Industry)
This type of production involves the extraction of raw materials or tapping and harnessing of natural resources from the land, sea and atmosphere. It includes farming, fishing, hunting, mining, quarrying, oil drilling etc. This form of production is referred to as primary production.
Secondary Production (Manufacturing and Constructive Industry)
This is the process of converting of raw materials or primary products from the extractive industry into finished or semi-finished goods. This class of production includes furniture making, road construction, bridges, paper milling, food processing, car production, chemical, textile etc.
Tertiary Production (Commercial and Professional Services)
It is made up of those who render commercial and professional services to satisfy other people. The help commercial services help to bring the raw materials, finished or semi-finished goods to those who need them (the users). Such services include, trading, banking, advertising, warehousing, insurance, transportation and communication. The professional services which are equally known as direct or personal are services provided or rendered directly or indirectly by people to give satisfaction to those who want them. These are services like teaching, catering, tailoring, hair dressing etc.
Evaluation:
1. What is Production?
2. State the three forms of production.
https://www.slideshare.net/harinadhkari ... -function2
LESSON 2
Factors of Production
The term factor of production is defined as all the visible and invisible resources that are combined together for the purpose of production of goods and services. There are four factors of production.
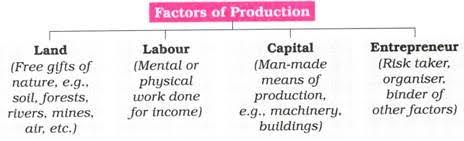
(a) Land: Land refers to gift of nature or all the natural resources available, applied and used for production without the help of a man. It includes the fixed natural land and other natural resources such as water, forest, mineral deposits etc. The reward for land is rent.

(b) Labour: Labour means all human efforts physical or mental, skilled or unskilled directed toward the production of economic goods and services. The reward of labour is wages and salaries.

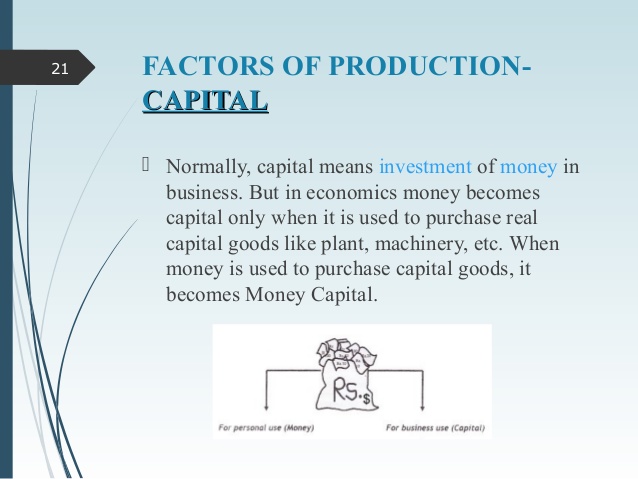
(c) Capital: These are wealth used for the production of further wealth. Capital consists of machinery and equipment, buildings, motor vehicles, tools, raw materials and money. The reward for capital is interest.
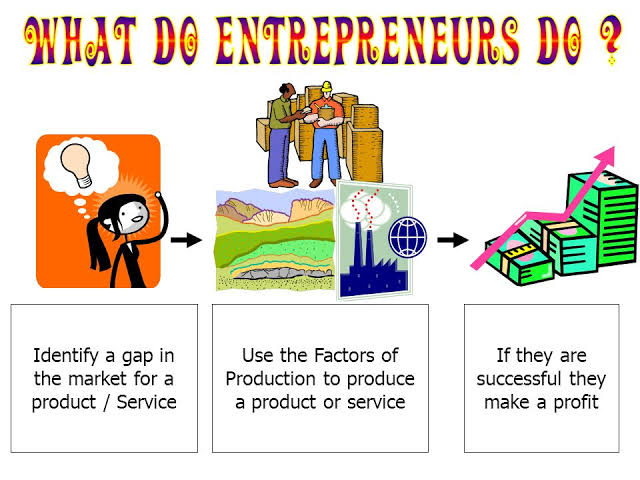
(d) Entrepreneur: This is a factor that organizes and coordinates the human and material resources in the production of goods and services. The entrepreneur is the initiator, innovator, risk-bearer, and decision-maker. These functions distinguish entrepreneurship from routine managerial activities. The entrepreneur gets profit as a reward for his services.
Evaluation:
1. Explain the term factors of production
2. Explain the four factors of production.
Reading Assignment:
Business Studies for Junior Secondary School Book 1 produced by Cross River State Government Chapter 5 pages 26-27
Assignment:
Objectives:
1. The first form of production usually referred to as primary production consists of
(a) manufacturing industry (b) extractive industry (c) commercial services
2. There are ------- forms of production (a) 2 (b) 5 (c) 3
3. ---------- as a factor of production is a free gift of nature.
(a) land (b) capital (c) labour
4. The reward for capital is (a) rent (b) interest (c) profit
5. The factor of production that organizes or coordinates other factors is
(a) Entrepreneur (b) capital (c) labour
Theory:
1. What is production?
2. Explain the factors of production.
LESSON 3
MAIN TOPIC: PRODUCTION
SPECIFIC TOPIC: Effects of production on the environment
REFERENCE BOOKS:
Macmillan JSS1 Business Studies by Awoyokun A.A et al .Pages 34-38
WABP JSS Business Studies 1 by Egbe T. Ehiametalor. Pages 30-33
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVES: At the end of the lesson, students should be able to:
Mention the positive effects of production on the environment
CONTENTS:
POSITIVE EFFECTS OF PRODUCTION ON THE ENVIRONMENT
Production makes goods and services available for the satisfaction of human wants.?
It provides employment opportunity for people
Factories and big offices make our environment look beautiful and admirable.
NEGATIVE EFFECTS OF PRODUCTION ON THE ENVIRONMENT[/b]
Production causes pollution
The excavation practiced in the primary production leaves big holes that can lead to erosion.
Waste materials from secondary production have adverse effect on clean water.
Vehicles used in transporting goods and services in the tertiary production emit gaseous fumes which are dangerous to health.
EVALUATION:
Mention four positive effects of production to the environment.
HOME-WORK: What are the hazards of primary stage of production to the environment
Mention the hazards of each stage of production on the environment.
Mention ten mail room equipment.
https://www.slideshare.net/GabrielKazun ... lideshow=1
Topic: PRODUCTION
CONTENT:
1. Meaning and Forms of Production
2. Factors of Production
Meaning and Forms of Production
Production could be defined as any human activity that involves the making of physical goods and provision of services for the satisfaction of human wants. It is also seen as creation of utilities, utility means the ability of goods and services to satisfy human wants.

Forms of Production
There are three forms of production namely primary (extractive industry), secondary production (manufacturing and constructive industry) and tertiary production (commercial and personal or professional services).
Primary Production (Extractive Industry)
This type of production involves the extraction of raw materials or tapping and harnessing of natural resources from the land, sea and atmosphere. It includes farming, fishing, hunting, mining, quarrying, oil drilling etc. This form of production is referred to as primary production.
Secondary Production (Manufacturing and Constructive Industry)
This is the process of converting of raw materials or primary products from the extractive industry into finished or semi-finished goods. This class of production includes furniture making, road construction, bridges, paper milling, food processing, car production, chemical, textile etc.
Tertiary Production (Commercial and Professional Services)
It is made up of those who render commercial and professional services to satisfy other people. The help commercial services help to bring the raw materials, finished or semi-finished goods to those who need them (the users). Such services include, trading, banking, advertising, warehousing, insurance, transportation and communication. The professional services which are equally known as direct or personal are services provided or rendered directly or indirectly by people to give satisfaction to those who want them. These are services like teaching, catering, tailoring, hair dressing etc.

Evaluation:
1. What is Production?
2. State the three forms of production.
https://www.slideshare.net/harinadhkari ... -function2
LESSON 2
Factors of Production
The term factor of production is defined as all the visible and invisible resources that are combined together for the purpose of production of goods and services. There are four factors of production.

(a) Land: Land refers to gift of nature or all the natural resources available, applied and used for production without the help of a man. It includes the fixed natural land and other natural resources such as water, forest, mineral deposits etc. The reward for land is rent.

(b) Labour: Labour means all human efforts physical or mental, skilled or unskilled directed toward the production of economic goods and services. The reward of labour is wages and salaries.

(c) Capital: These are wealth used for the production of further wealth. Capital consists of machinery and equipment, buildings, motor vehicles, tools, raw materials and money. The reward for capital is interest.

(d) Entrepreneur: This is a factor that organizes and coordinates the human and material resources in the production of goods and services. The entrepreneur is the initiator, innovator, risk-bearer, and decision-maker. These functions distinguish entrepreneurship from routine managerial activities. The entrepreneur gets profit as a reward for his services.

Evaluation:
1. Explain the term factors of production
2. Explain the four factors of production.
Reading Assignment:
Business Studies for Junior Secondary School Book 1 produced by Cross River State Government Chapter 5 pages 26-27
Assignment:
Objectives:
1. The first form of production usually referred to as primary production consists of
(a) manufacturing industry (b) extractive industry (c) commercial services
2. There are ------- forms of production (a) 2 (b) 5 (c) 3
3. ---------- as a factor of production is a free gift of nature.
(a) land (b) capital (c) labour
4. The reward for capital is (a) rent (b) interest (c) profit
5. The factor of production that organizes or coordinates other factors is
(a) Entrepreneur (b) capital (c) labour
Theory:
1. What is production?
2. Explain the factors of production.
LESSON 3
MAIN TOPIC: PRODUCTION
SPECIFIC TOPIC: Effects of production on the environment
REFERENCE BOOKS:
Macmillan JSS1 Business Studies by Awoyokun A.A et al .Pages 34-38
WABP JSS Business Studies 1 by Egbe T. Ehiametalor. Pages 30-33
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVES: At the end of the lesson, students should be able to:
Mention the positive effects of production on the environment
CONTENTS:
POSITIVE EFFECTS OF PRODUCTION ON THE ENVIRONMENT
Production makes goods and services available for the satisfaction of human wants.?
It provides employment opportunity for people
Factories and big offices make our environment look beautiful and admirable.
NEGATIVE EFFECTS OF PRODUCTION ON THE ENVIRONMENT[/b]
Production causes pollution
The excavation practiced in the primary production leaves big holes that can lead to erosion.
Waste materials from secondary production have adverse effect on clean water.
Vehicles used in transporting goods and services in the tertiary production emit gaseous fumes which are dangerous to health.
EVALUATION:
Mention four positive effects of production to the environment.
HOME-WORK: What are the hazards of primary stage of production to the environment
Mention the hazards of each stage of production on the environment.
Mention ten mail room equipment.
https://www.slideshare.net/GabrielKazun ... lideshow=1
WEEK 2
LESSON 4
MAIN TOPIC: Factors of production
SPECIFIC TOPIC: Meaning and listing of factors of production.
REFERENCE BOOKS:
Macmillan JSS1 Business Studies by Awoyokun A.A et al .Pages 34-38
WABP JSS Business Studies 1 by Egbe T. Ehiametalor. Pages 30-33
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVES: At the end of the lesson, students should be able to:
state the meaning of factors of production
list factors of production
mention the characteristics and importance of land as one of the factors of production.
State the reward for land.
CONTENTS:
Factors of production are the basic things or resources used for producing goods and services.
They are those things that must be in place before production can be possible.
We have four factors of production and they are:
Land
Labour
Capital
Entrepreneur or organisation.

LAND
This includes all the resources provided by nature such as minerals, forests, rivers and mountains.
They are collectively called the "gift of nature". Examples are farmland, seas and the fishes in the sea, forestry, minerals such as coal, crude oil etc.
FEATURES OF LAND
Land is a gift of nature.
The price of land varies from one place to the other.
Land is fixed. It cannot be moved from one place to the other.

IMPORTANCE OF LAND
It is for the excavation of mineral resources.
It is used for the erection of buildings, offices etc.
The reward for land is rent.
EVALUATION:
What do you understand by factors of production?
List four factors of production.
What is land?
Mention two characteristics and two importance of land.
What is the reward for land?
HOME-WORK: What is labour?
LESSON 5
MAIN TOPIC: Factors of production
SPECIFIC TOPIC: Labour and capital
REFERENCE BOOKS:
Macmillan JSS1 Business Studies by Awoyokun A.A et al .Pages 34-38
WABP JSS Business Studies 1 by Egbe T. Ehiametalor. Pages 30-33
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVES: At the end of the lesson, students should be able to:
state the meaning of labour and capital
mention the features of labour and capital
mention the importance of labour and capital as one of the factors of production.
State the reward for labour and capital.
CONTENTS:
LABOUR
This can be defined as the natural skills of people and what they have thought out and learned from experience.
It is the actual effort both physical and mental made by human beings towards production.
FEATURES OF LABOUR
It is the effort of man in production
Labour costs money
Labour can move from place to place.

IMPORTANCE OF LABOUR
It gives room for mobility
It aids national development
It creates career development
The reward for labour is wages and salary.
CAPITAL
This is anything that helps man to maximize the use of land and labour.
It is wealth which has been made by man to produce more wealth.
FEATURES OF CAPITAL
It is man-made
Capital as money is difficult to get.

IMPORTANCE OF CAPITAL
It helps in the provision of material for production
It helps in the execution of other factors of production
It makes assessment of the business possible.
The reward for capital is interest.
EVALUATION:
What is labour?
What is capital?
Mention two features and two importances each of labour and capital.
What is the reward for capital?
What is the reward for labour?
HOME-WORK: Briefly discuss organization.
LESSON 6
MAIN TOPIC: Factors of production
SPECIFIC TOPIC: Entrepreneur/Organisation
REFERENCE BOOKS:
Macmillan JSS1 Business Studies by Awoyokun A.A et al .Pages 34-38
WABP JSS Business Studies 1 by Egbe T. Ehiametalor. Pages 30-33
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVES: At the end of the lesson, students should be able to:
state the meaning of organisation
mention the features of organisation
mention the major differences between labour and an entrepreneur.
State the reward for organisation.
CONTENTS:
ORGANISATION/ENTREPRENEUR
An entrepreneur is the person who co-ordinates the other factors of production that is land, labour and capital to
Produce goods and services.
FEATURES OF AN ENTREPRENEUR
He is not an employee but an employer.
He co-ordinates all other factors of production.
He takes all the profit if the business succeeds and bears the loss if the business fails.
The reward for an entrepreneur is profit.

EVALUATION:
Who is an entrepreneur?
Mention two features of an entrepreneur.
What is the reward for an entrepreneur?
Distinguish between an entrepreneur and labour.
HOME-WORK: mention ten mail room equipment.
https://www.slideshare.net/AnkitBhanush ... n-69229330
MAIN TOPIC: Factors of production
SPECIFIC TOPIC: Meaning and listing of factors of production.
REFERENCE BOOKS:
Macmillan JSS1 Business Studies by Awoyokun A.A et al .Pages 34-38
WABP JSS Business Studies 1 by Egbe T. Ehiametalor. Pages 30-33
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVES: At the end of the lesson, students should be able to:
state the meaning of factors of production
list factors of production
mention the characteristics and importance of land as one of the factors of production.
State the reward for land.
CONTENTS:
Factors of production are the basic things or resources used for producing goods and services.
They are those things that must be in place before production can be possible.
We have four factors of production and they are:
Land
Labour
Capital
Entrepreneur or organisation.

LAND
This includes all the resources provided by nature such as minerals, forests, rivers and mountains.
They are collectively called the "gift of nature". Examples are farmland, seas and the fishes in the sea, forestry, minerals such as coal, crude oil etc.
FEATURES OF LAND
Land is a gift of nature.
The price of land varies from one place to the other.
Land is fixed. It cannot be moved from one place to the other.

IMPORTANCE OF LAND
It is for the excavation of mineral resources.
It is used for the erection of buildings, offices etc.
The reward for land is rent.
EVALUATION:
What do you understand by factors of production?
List four factors of production.
What is land?
Mention two characteristics and two importance of land.
What is the reward for land?
HOME-WORK: What is labour?
LESSON 5
MAIN TOPIC: Factors of production
SPECIFIC TOPIC: Labour and capital
REFERENCE BOOKS:
Macmillan JSS1 Business Studies by Awoyokun A.A et al .Pages 34-38
WABP JSS Business Studies 1 by Egbe T. Ehiametalor. Pages 30-33
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVES: At the end of the lesson, students should be able to:
state the meaning of labour and capital
mention the features of labour and capital
mention the importance of labour and capital as one of the factors of production.
State the reward for labour and capital.
CONTENTS:
LABOUR
This can be defined as the natural skills of people and what they have thought out and learned from experience.
It is the actual effort both physical and mental made by human beings towards production.
FEATURES OF LABOUR
It is the effort of man in production
Labour costs money
Labour can move from place to place.

IMPORTANCE OF LABOUR
It gives room for mobility
It aids national development
It creates career development
The reward for labour is wages and salary.
CAPITAL
This is anything that helps man to maximize the use of land and labour.
It is wealth which has been made by man to produce more wealth.
FEATURES OF CAPITAL
It is man-made
Capital as money is difficult to get.

IMPORTANCE OF CAPITAL
It helps in the provision of material for production
It helps in the execution of other factors of production
It makes assessment of the business possible.
The reward for capital is interest.
EVALUATION:
What is labour?
What is capital?
Mention two features and two importances each of labour and capital.
What is the reward for capital?
What is the reward for labour?
HOME-WORK: Briefly discuss organization.
LESSON 6
MAIN TOPIC: Factors of production
SPECIFIC TOPIC: Entrepreneur/Organisation
REFERENCE BOOKS:
Macmillan JSS1 Business Studies by Awoyokun A.A et al .Pages 34-38
WABP JSS Business Studies 1 by Egbe T. Ehiametalor. Pages 30-33
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVES: At the end of the lesson, students should be able to:
state the meaning of organisation
mention the features of organisation
mention the major differences between labour and an entrepreneur.
State the reward for organisation.
CONTENTS:
ORGANISATION/ENTREPRENEUR
An entrepreneur is the person who co-ordinates the other factors of production that is land, labour and capital to
Produce goods and services.
FEATURES OF AN ENTREPRENEUR
He is not an employee but an employer.
He co-ordinates all other factors of production.
He takes all the profit if the business succeeds and bears the loss if the business fails.
The reward for an entrepreneur is profit.

EVALUATION:
Who is an entrepreneur?
Mention two features of an entrepreneur.
What is the reward for an entrepreneur?
Distinguish between an entrepreneur and labour.
HOME-WORK: mention ten mail room equipment.
https://www.slideshare.net/AnkitBhanush ... n-69229330
WEEK 3
LESSON 7
Topic: TYPES OF OCCUPATION: – MEANING AND CLASSIFICATION OF OCCUPATION
CONTENT
- MEANING AND FACTORS THAT DETERMINE THE CHOICE OF OCCUPATION
- CLASSIFICATION OF OCCUPATION
MEANING OF OCCUPATION
Occupation is any legitimate activity one engages in order to earn a living. For example some people work in industries that extract raw materials from land or sea, some work in manufacturing industries which change the extracted raw materials into finished goods or semi-finished goods. Some others provide services for others such as Nursing, Teaching, Hairdressing, carpentry etc. Also others provide commercial services by helping to sell the finished goods to those that need them, as well as engaged some of those auxiliary services that help commerce to function properly such as banking, insurance, advertising etc.

FACTORS THAT DETERMINE OCCUPATION
1 Climatic and Weather Condition: Because of climate and weather differences from place to place, people engage themselves in one form of occupation or the other to earn a living.
2. Natural Resources: Natural resources endowment is also a determinant of one’s occupation. The presence of mineral resources in a particular place will attract the presence of miners and also determines the location of different types of industries. The availability of seaports and large bodies of water like ocean which are part of natural resources has accounted for people’s engagement in different activities and occupation.
3. Health Factor: There are some occupations which people who are not physically fit cannot engage themselves e.g. Nursing, Teaching etc.
4. Skill and Training: People engaged themselves in occupation in which they have acquired skill and training.
5. Interest and Aptitude: People engaged in occupation they have interest in.
6. Salary and Wages: The salary and wages attached to a particular occupation determines the number of people that will be interested in such occupation

EVALUATION
1. Define Occupation
2. State 3 factors that could determine occupation.
LESSON 8
CLASSIFICATION OF OCCUPATION
CONTENT
The different occupation in which people engage themselves can be classified into three main division namely; Industrial Occupation, Commercial Occupation and Service Workers.
Industrial Occupation: This form of occupation involves obtaining raw materials and free gifts of nature, changing them into finished products and assembling the finished products into different forms usable by man. This industrial work includes extraction, manufacturing and construction.
(a) Extraction: This occupation is concerned with the removal of raw materials from air, land or sea for the purpose of being worked upon by the manufacturing and construction industries. For example Agriculture, Mining and Quarrying, Fishing and Forestry etc.
(b) Manufacturing: This form of Industrial occupation involves the process of changing raw materials obtained by workers in the extractive industry into finished goods. Some of the manufacturing industries are:
(i) Plastics-making industries which produce plastic plates, spoons, cups etc.
(ii) Food industries which produce various types of items like flour. Sugar, beverages etc.
(iii) Textile industries that produce various types of clothing for man.
(iv) Mechanical engineering industries that produce all types and sizes of machinery such as equipment, industrial engines, mechanical tools etc.
(v) Hardware industries that produce metal, major items of military equipment electronic and electrical devices, etc.
(vi) Cosmetic industries that produce various body creams, pomades, soap, detergent etc.
(c) Construction: Construction industry is concerned with the process of putting together or assembling of manufactured products into usable forms. Those engaged in construction industries are building contractors, architects, surveyors, bricklayers, plumbers, decorators, civil engineers, water engineers etc.
Commercial Industries
The raw materials extracted by the extractive industry are worked upon by way of manufacturing to change their original form so as to make them usable. For these products to be usable implies that they are now finished goods. In order to complete the process of production, the services of commercial workers are necessary. People who are engaged in commercial industries are responsible for getting the finished products to the consumers who want them, when they want them. It is commercial occupation that links up the producer with the supplier of the raw materials. It in turn links up the various processes of manufacture; and finally distributes the finished products to consumers through ancillary services that facilitate trading activities such as advertising, insurance, banking, transporting, warehousing and communication.
Service Workers
In occupational engagements, there are those who are not employed to work in industry and commerce, yet they still earn a living. Those in this category are known as service workers. They are referred to as service workers because they render personal and direct services to people who need their services on payment directly or indirectly. Services may be direct or indirect.
EVALUATION
1. The form of occupation that involves extraction, manufacturing and construction industry is termed _________________
2. Give five examples of Manufacturing Industry
READING ASSIGNMENT
Business Studies for Junior Secondary School Book 1 produced by Cross River State Government Chapter 6 pages 42-43
ASSIGNMENT
1. One of this is not a factor that could determine occupation.
(a) Salary and Wages (b) Skill and Training (c) Friend’s choice
2. Mining, Agriculture, Fishing are examples of --------form of occupation
(a) Extractive (b) Service (c) Construction
3. Assemblying of manufactured products into usable forms are the responsibility of ------- industry. (a) Extractive (b) Manufacturing (c) Construction
4. Those who render personal or direct services to people who need their services and they are paid directly or indirectly are called ------ (a) Commercial occupation (b) Service workers (b) Industrial worker
5. The removal of the raw material from the air, land and sea is the responsibility of -------- industry. (a) Industrial worker (b) Extraction (c) Services
THEORY
1. What do you understand by the term occupation?
2. Name three classes of occupation
Topic: TYPES OF OCCUPATION: – MEANING AND CLASSIFICATION OF OCCUPATION
CONTENT
- MEANING AND FACTORS THAT DETERMINE THE CHOICE OF OCCUPATION
- CLASSIFICATION OF OCCUPATION
MEANING OF OCCUPATION
Occupation is any legitimate activity one engages in order to earn a living. For example some people work in industries that extract raw materials from land or sea, some work in manufacturing industries which change the extracted raw materials into finished goods or semi-finished goods. Some others provide services for others such as Nursing, Teaching, Hairdressing, carpentry etc. Also others provide commercial services by helping to sell the finished goods to those that need them, as well as engaged some of those auxiliary services that help commerce to function properly such as banking, insurance, advertising etc.

FACTORS THAT DETERMINE OCCUPATION
1 Climatic and Weather Condition: Because of climate and weather differences from place to place, people engage themselves in one form of occupation or the other to earn a living.
2. Natural Resources: Natural resources endowment is also a determinant of one’s occupation. The presence of mineral resources in a particular place will attract the presence of miners and also determines the location of different types of industries. The availability of seaports and large bodies of water like ocean which are part of natural resources has accounted for people’s engagement in different activities and occupation.
3. Health Factor: There are some occupations which people who are not physically fit cannot engage themselves e.g. Nursing, Teaching etc.
4. Skill and Training: People engaged themselves in occupation in which they have acquired skill and training.
5. Interest and Aptitude: People engaged in occupation they have interest in.
6. Salary and Wages: The salary and wages attached to a particular occupation determines the number of people that will be interested in such occupation

EVALUATION
1. Define Occupation
2. State 3 factors that could determine occupation.
LESSON 8
CLASSIFICATION OF OCCUPATION
CONTENT
The different occupation in which people engage themselves can be classified into three main division namely; Industrial Occupation, Commercial Occupation and Service Workers.
Industrial Occupation: This form of occupation involves obtaining raw materials and free gifts of nature, changing them into finished products and assembling the finished products into different forms usable by man. This industrial work includes extraction, manufacturing and construction.
(a) Extraction: This occupation is concerned with the removal of raw materials from air, land or sea for the purpose of being worked upon by the manufacturing and construction industries. For example Agriculture, Mining and Quarrying, Fishing and Forestry etc.
(b) Manufacturing: This form of Industrial occupation involves the process of changing raw materials obtained by workers in the extractive industry into finished goods. Some of the manufacturing industries are:
(i) Plastics-making industries which produce plastic plates, spoons, cups etc.
(ii) Food industries which produce various types of items like flour. Sugar, beverages etc.
(iii) Textile industries that produce various types of clothing for man.
(iv) Mechanical engineering industries that produce all types and sizes of machinery such as equipment, industrial engines, mechanical tools etc.
(v) Hardware industries that produce metal, major items of military equipment electronic and electrical devices, etc.
(vi) Cosmetic industries that produce various body creams, pomades, soap, detergent etc.
(c) Construction: Construction industry is concerned with the process of putting together or assembling of manufactured products into usable forms. Those engaged in construction industries are building contractors, architects, surveyors, bricklayers, plumbers, decorators, civil engineers, water engineers etc.
Commercial Industries
The raw materials extracted by the extractive industry are worked upon by way of manufacturing to change their original form so as to make them usable. For these products to be usable implies that they are now finished goods. In order to complete the process of production, the services of commercial workers are necessary. People who are engaged in commercial industries are responsible for getting the finished products to the consumers who want them, when they want them. It is commercial occupation that links up the producer with the supplier of the raw materials. It in turn links up the various processes of manufacture; and finally distributes the finished products to consumers through ancillary services that facilitate trading activities such as advertising, insurance, banking, transporting, warehousing and communication.
Service Workers
In occupational engagements, there are those who are not employed to work in industry and commerce, yet they still earn a living. Those in this category are known as service workers. They are referred to as service workers because they render personal and direct services to people who need their services on payment directly or indirectly. Services may be direct or indirect.

EVALUATION
1. The form of occupation that involves extraction, manufacturing and construction industry is termed _________________
2. Give five examples of Manufacturing Industry
READING ASSIGNMENT
Business Studies for Junior Secondary School Book 1 produced by Cross River State Government Chapter 6 pages 42-43
ASSIGNMENT
1. One of this is not a factor that could determine occupation.
(a) Salary and Wages (b) Skill and Training (c) Friend’s choice
2. Mining, Agriculture, Fishing are examples of --------form of occupation
(a) Extractive (b) Service (c) Construction
3. Assemblying of manufactured products into usable forms are the responsibility of ------- industry. (a) Extractive (b) Manufacturing (c) Construction
4. Those who render personal or direct services to people who need their services and they are paid directly or indirectly are called ------ (a) Commercial occupation (b) Service workers (b) Industrial worker
5. The removal of the raw material from the air, land and sea is the responsibility of -------- industry. (a) Industrial worker (b) Extraction (c) Services
THEORY
1. What do you understand by the term occupation?
2. Name three classes of occupation
WEEK 4
LESSON 9
FORMS OF BUSINESS ORGANIZATION
CONTENT: 1. Types of Business Organisations
2. Advantages and Disadvantages of each of the Business Organisation
Meaning of Sole Trade
Meaning: Sole Trade is a business owned by one person. The size of the business may be large or small but it is important to note that it is owned by one man. Examples are restaurants supermarkets, Filing Station, Schools etc. The owner of the business is called a sole trader or a sole proprietor. Another name for sole trade is sole proprietorship.

Advantages of Sole Trade:
1. It is easy to start.
2. The sole proprietor has a close contact with his customers and attends to them personally.
3. He takes all decisions affecting his business alone.

Disadvantages of Sole Trade:
1. The provision of capital and ability is limited.
2. The business ends when a sole trader dies.
3. He suffers and bears risks alone
4. If business fails, he may have to sell his personal property to pay the debt.

Evaluation:
1. State at least three advantages of Sole Trade
2. Identify at least three disadvantages of Sole Trade.
Reading Assignment:
Business Studies for Junior Secondary School Book 1 produced by Cross River State Chapter 7 pages 38-39
LESSON 10
Partnership
CONTENT: 1. Meaning of Partnership
2. Advantages and Disadvantage of Partnership
Meaning of Partnership
Meaning of Partnership: A Partnership is a business owned and managed by two or more persons who become partners by written agreement. The partnership act of 1890 and the companies Act of 1958 state that the maximum number of people who can form a Partnership is restricted to 20 persons while the minimum should be 2 persons. These partners share the profit or losses and the responsibilities of their business.

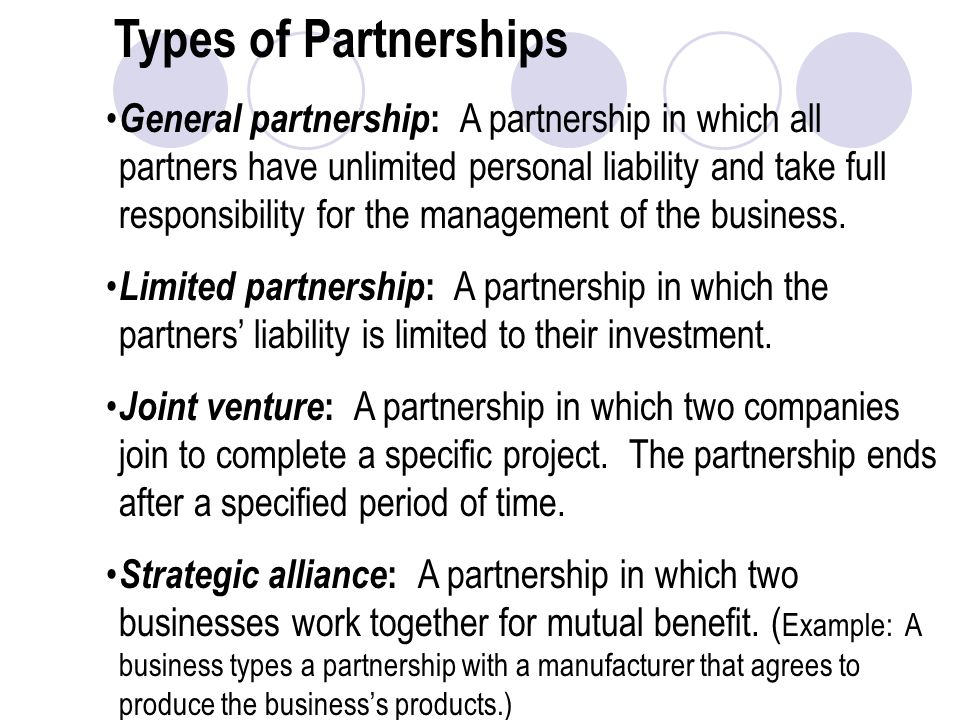
Types of Partnership: There are various types of partnerships as stated below:
(a) Ordinary Partnership: This is a partnership in which all members are held liable for the debts of the business. Partnership may be dissolved if one partner dies.
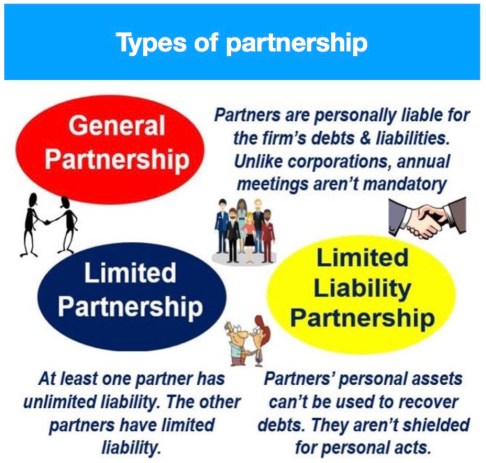
(b) Limited Partnership: This is a partnership with limited liability in that members will not be asked to contribute more money that the one used to start the business in case the business fails. For Partnership to become limited, it must be registered with the Registrar of Companies otherwise it will be treated as ordinary partnership.
(c) Active and Sleeping Partners: Partners who take part in running the business are active partners while those who do not take part in the running of the business are sleeping partners.
(d) Quasi or Nominal Partners: A quasi partner is not really a partner but may conduct himself in such a way as to make himself liable for the debts of the firm, even though he does not take part in sharing the profit of the business.
Advantages of Partnership:
(i) It has more capital than sole trading
ii Partners have different ability and talents therefore, each partner specializes in an aspect of business which he is best suited.
(iii) Partners meet to discuss matters relating to the firm

Disadvantages of Partnership:
(i0 Partners have unlimited liability for debts in case of business failure.
(ii) If one partner takes a wrong decision, it affects other partners.
(iii) Disagreement among partners causes confusion in the business.
(iv) Partnership comes to an end with the death or resignation of a partner.

Evaluation
Objectives:
1. Another name for Sole Trade is -------- (a) Sole Proprietorship (b) Partnership (c) Restaurant
2. Sole Trade is the business of ---------- (a) two people (b) two men (c) one person
3. The simplest and most common form of business organization is (a) Partnership (b) Sole trade (c) Filing station
4. One of the disadvantages of Sole trade is ---------- (a) He takes all decisions affecting his business (b) He bears and suffers risk alone (c) he enjoys his profits alone
5. One of the source of capital to a sole trader is (a) easy to start (b) personal savings (c) members’ contribution
6. The minimum number of Partners in Partnership is (a) 5 (b) 2 (c) 4
7. The type of partnership in which all the members are held liable for debts of the business is ------ (a) quasi partnership (b) Ordinary partnership (c) limited partnership
8. One of the sources of capital for partnership is ------ (a) contribution of capital by members (b) personal saving (c) limited partners
9. The disadvantage of partnership is ---------- (a) Wrong decision of one partners affect others (b) Losses are shared among partners (c) it has more capital than sole trading
10. All are advantages of Partnership except (a) Death of one partner may end the business (b) Responsibilities are shared among partners (c) It has more capital than sole trading.
Essay
1. What is Sole Proprietorship?
2. Mention all the sources of capital of sole trade.
3. What is Partnership?
4. Outline two advantages and two disadvantages of Partnership
5. Define Partnership.
6. Explain the following types of partnership: (a) ordinary Partnership (b) Quasi Partnership
Reading Assignment:
Business Studies for Junior Secondary School Book 1 produced by Cross River State Government Chapter 7 pages 39-41
https://drive.google.com/file/d/1EDOUlp ... sp=sharing
LESSON 11
Cooperative Societies
Meaning of Cooperative Societies
A cooperative Society exists when groups of workers, individuals, organizations, farmers or
Communities pull their resources together towards a common goal. The main purpose of the cooperative society is to:
(i) Sell goods and services to members at a cheap rate.
(ii) to do business together for profit purpose and share the profits among the members.

Types of Cooperative Society:
The common types of cooperative societies are:
(a) Producers Cooperative
(b) Consumers Cooperative

(a) Producers Cooperative:
Producers form a common association in order to sell their products in a uniform price instead of selling individually, e.g. producers of yam, garri, cocoa etc may form a cooperative society for the selling of their products.
(b) Consumers Cooperative:
In consumers’ cooperative, the members are consumers who contribute funds and buy goods in large quantities from the producers and sell in retail prices to members at a reduced and cheaper rate.
Advantages of Cooperative Society:
1. Members have equal rights and votes.
2. Prices are lower as they buy in bulk.
3. Benefits of repayment of capital to any member who withdraws.
Disadvantages of Cooperative Society:
1. Election of committee members may not lead to efficient business.
2. Calculation of dividends to members is always a problem.
3. Non-members may be reluctant to engage in marketing activities with the cooperative.
https://www.slideshare.net/miemslou/adv ... operatives
Evaluation:
1. What do you understand by the term Cooperative Society?
2. Mention three advantages of Cooperative society.
Reading Assignment:
Business Studies for Junior Secondary School Book 1 produced by Cross River State Chapter 7 pages 42-43.
Assignment:
Objectives:
1. What is the maximum of number of persons that can be admitted into the society? (a) No maximum (b) 20 (c) 30
2. Cooperative Society is managed by (a) Board of Directors (b) Committee of management (c) shareholders
3. The common types of cooperative societies are
(a) Sole Proprietorship and partnership (b) Young and old cooperative (c) Producer and Consumer Cooperative
4. In cooperative Society every members have equal rights and votes. True/False
5. The main purpose of cooperative society is to (a)buy goods for everybody (b) provide essentials services at cheaper rate (c) sell goods and services to members at a cheap rate
LESSON 12
Limited Liability Company (Public Limited Liability Company)
Limited Liability Company:
A Limited Liability Company is a company in which the responsibility or liability of members for debts of the company is limited to the capital they have contributed or agreed to contribute. The private property of members are excluded, and all that members lose if the company fails is the money they have contributed. It is formed and registered under the law known as the Company Act. When a company is formed and registered with the Registrar of Companies, it is said to be incorporated.
There are two types of Limited Liability Company namely, Private and Public Companies.
Public Limited Liability Company:
A Public Limited Liability Company is a business unit that carries on business to make profit
for its owners. Examples are Nigerian bottling company Ltd., Total Nigeria Limited, First Bank of
Nigeria Plc. It is owned by Shareholders and managed and control by Board of management.
https://www.slideshare.net/ry_moore/lim ... o-29828149
Advantages of Public Limited Liability Company
1. It can raise money from the public through issuing of shares and debentures. This
enhances the company expansion.
2. It is a legal entity because it can sue and can be sued.
3. The company’s properties are different from that of its owners.
4. It enjoys continuity because it has perpetual life. The company can only be wounded voluntarily or on the order of a law court.
5. Share holders cannot lose more than the value of their shares. This is because the company enjoys limited liability.

Disadvantages of Public Limited Liability Company:
1. Shareholders have little say in the running of the company
2. It does not enjoy privacy. It annual account must be published in the Newspaper for the public to see.
3. It suffers from double taxation. The net profit of the company is taxed and the dividends of the shareholders are also taxed.
Limited Liability Company (Private Limited Liability Company)
CONTENT
1. Private Limited Liability Company (Meaning)
2. Advantages, Disadvantages and Comparison between Public and Private companies
Meaning of Private Limited Liability Company:
A private limited liability company is a profitable making business with few shareholders and no open market for its shares. Examples of private limited liability company are Newswatch Communication Ltd., Ekene Dili Chukwu Transport service Ltd., JIMBAZ Construction Company Ltd. etc.
Advantages of Private Limited Liability Company
(i) They enjoy privacy.
(ii) Their annual report and accounts are not required by law to be published, except for
Taxation.
(iii) Management and control is less complex than in public limited company. Its
management structure is simple.
Disadvantages of Private Limited Liability Company
(i) Shares cannot be issued to the public.
(ii) Capacity to raise external finance to expand business is limited.
(iii) Transfer of shares to others is made difficult.

1. Comparison between the Private and Public Limited Liability Companies.
S/N PUBLIC LIMITED COMPANY -------------------------PRIVATE LIMITED COMPANY
1. Minimum number of members is seven and has no maximum------------ Minimum number of members is two while the maximum is fifty.
2. Shares are offered to the public. -----------------------Shares may not be offered to the public.
3. Shares are easily transferable.------------------ Shares are not transferable.
4. Account is publish to the public----------------------- Account is publish for the information of Registrar of companies.
https://www.slideshare.net/krishnakhata ... ed-company
EVALUATION
1. What is a limited liability company?
2. State 3 advantages of public limited liability company
READING ASSIGNMENT
Business studies for junior secondary schools, new edition book 1 by O. A. Lawal Chapter 5 pages 23-25
1. Define Private Limited Liability Company
2. State the comparison between the public and private companies.
3. Outline the 4 advantages and the 4 disadvantages of Private companies.
ASSIGNMENT
1. The maximum number of members in a private limited liability company (a) 50 (b) 100 (c) 10
2. Private liability company enjoys. (a ) enough capital (b) privacy (c) non-Payment of tax (d) transfer of shares to others.
3. The following are disadvantages of private limited liability company except (a) not listed in the stock exchange (b) cannot sell shares (c) management structure is simple.
4. The minimum number of owners needed to form a public limited company
Is (a) seven ( b)two (c) fifty (d) eight
5. Which of this can sell shares to the public (a) Sole proprietor (b) Private
Limited company (c) Public limited company
6. The maximum number of owners a public Limited liability company is (a) twenty (b) two (c) no maximum.
7. Public Limited Liability Company is owned by ------------------ (a) government (b) politicians (c) Shareholders
8. The major source of capital for Public Limited Liability Company is
(a) selling of shares (b) personal savings (c) partnership contribution
THEORY
1. State 3 advantages of private limited liability company
2. Enumerate 3 disadvantages of private limited liability company
FORMS OF BUSINESS ORGANIZATION
CONTENT: 1. Types of Business Organisations
2. Advantages and Disadvantages of each of the Business Organisation
Meaning of Sole Trade
Meaning: Sole Trade is a business owned by one person. The size of the business may be large or small but it is important to note that it is owned by one man. Examples are restaurants supermarkets, Filing Station, Schools etc. The owner of the business is called a sole trader or a sole proprietor. Another name for sole trade is sole proprietorship.

Advantages of Sole Trade:
1. It is easy to start.
2. The sole proprietor has a close contact with his customers and attends to them personally.
3. He takes all decisions affecting his business alone.

Disadvantages of Sole Trade:
1. The provision of capital and ability is limited.
2. The business ends when a sole trader dies.
3. He suffers and bears risks alone
4. If business fails, he may have to sell his personal property to pay the debt.

Evaluation:
1. State at least three advantages of Sole Trade
2. Identify at least three disadvantages of Sole Trade.
Reading Assignment:
Business Studies for Junior Secondary School Book 1 produced by Cross River State Chapter 7 pages 38-39
LESSON 10
Partnership
CONTENT: 1. Meaning of Partnership
2. Advantages and Disadvantage of Partnership
Meaning of Partnership
Meaning of Partnership: A Partnership is a business owned and managed by two or more persons who become partners by written agreement. The partnership act of 1890 and the companies Act of 1958 state that the maximum number of people who can form a Partnership is restricted to 20 persons while the minimum should be 2 persons. These partners share the profit or losses and the responsibilities of their business.

Types of Partnership: There are various types of partnerships as stated below:
(a) Ordinary Partnership: This is a partnership in which all members are held liable for the debts of the business. Partnership may be dissolved if one partner dies.

(b) Limited Partnership: This is a partnership with limited liability in that members will not be asked to contribute more money that the one used to start the business in case the business fails. For Partnership to become limited, it must be registered with the Registrar of Companies otherwise it will be treated as ordinary partnership.
(c) Active and Sleeping Partners: Partners who take part in running the business are active partners while those who do not take part in the running of the business are sleeping partners.
(d) Quasi or Nominal Partners: A quasi partner is not really a partner but may conduct himself in such a way as to make himself liable for the debts of the firm, even though he does not take part in sharing the profit of the business.

Advantages of Partnership:
(i) It has more capital than sole trading
ii Partners have different ability and talents therefore, each partner specializes in an aspect of business which he is best suited.
(iii) Partners meet to discuss matters relating to the firm

Disadvantages of Partnership:
(i0 Partners have unlimited liability for debts in case of business failure.
(ii) If one partner takes a wrong decision, it affects other partners.
(iii) Disagreement among partners causes confusion in the business.
(iv) Partnership comes to an end with the death or resignation of a partner.

Evaluation
Objectives:
1. Another name for Sole Trade is -------- (a) Sole Proprietorship (b) Partnership (c) Restaurant
2. Sole Trade is the business of ---------- (a) two people (b) two men (c) one person
3. The simplest and most common form of business organization is (a) Partnership (b) Sole trade (c) Filing station
4. One of the disadvantages of Sole trade is ---------- (a) He takes all decisions affecting his business (b) He bears and suffers risk alone (c) he enjoys his profits alone
5. One of the source of capital to a sole trader is (a) easy to start (b) personal savings (c) members’ contribution
6. The minimum number of Partners in Partnership is (a) 5 (b) 2 (c) 4
7. The type of partnership in which all the members are held liable for debts of the business is ------ (a) quasi partnership (b) Ordinary partnership (c) limited partnership
8. One of the sources of capital for partnership is ------ (a) contribution of capital by members (b) personal saving (c) limited partners
9. The disadvantage of partnership is ---------- (a) Wrong decision of one partners affect others (b) Losses are shared among partners (c) it has more capital than sole trading
10. All are advantages of Partnership except (a) Death of one partner may end the business (b) Responsibilities are shared among partners (c) It has more capital than sole trading.
Essay
1. What is Sole Proprietorship?
2. Mention all the sources of capital of sole trade.
3. What is Partnership?
4. Outline two advantages and two disadvantages of Partnership
5. Define Partnership.
6. Explain the following types of partnership: (a) ordinary Partnership (b) Quasi Partnership
Reading Assignment:
Business Studies for Junior Secondary School Book 1 produced by Cross River State Government Chapter 7 pages 39-41
https://drive.google.com/file/d/1EDOUlp ... sp=sharing
LESSON 11
Cooperative Societies
Meaning of Cooperative Societies
A cooperative Society exists when groups of workers, individuals, organizations, farmers or
Communities pull their resources together towards a common goal. The main purpose of the cooperative society is to:
(i) Sell goods and services to members at a cheap rate.
(ii) to do business together for profit purpose and share the profits among the members.

Types of Cooperative Society:
The common types of cooperative societies are:
(a) Producers Cooperative
(b) Consumers Cooperative

(a) Producers Cooperative:
Producers form a common association in order to sell their products in a uniform price instead of selling individually, e.g. producers of yam, garri, cocoa etc may form a cooperative society for the selling of their products.
(b) Consumers Cooperative:
In consumers’ cooperative, the members are consumers who contribute funds and buy goods in large quantities from the producers and sell in retail prices to members at a reduced and cheaper rate.
Advantages of Cooperative Society:
1. Members have equal rights and votes.
2. Prices are lower as they buy in bulk.
3. Benefits of repayment of capital to any member who withdraws.
Disadvantages of Cooperative Society:
1. Election of committee members may not lead to efficient business.
2. Calculation of dividends to members is always a problem.
3. Non-members may be reluctant to engage in marketing activities with the cooperative.
https://www.slideshare.net/miemslou/adv ... operatives
Evaluation:
1. What do you understand by the term Cooperative Society?
2. Mention three advantages of Cooperative society.
Reading Assignment:
Business Studies for Junior Secondary School Book 1 produced by Cross River State Chapter 7 pages 42-43.
Assignment:
Objectives:
1. What is the maximum of number of persons that can be admitted into the society? (a) No maximum (b) 20 (c) 30
2. Cooperative Society is managed by (a) Board of Directors (b) Committee of management (c) shareholders
3. The common types of cooperative societies are
(a) Sole Proprietorship and partnership (b) Young and old cooperative (c) Producer and Consumer Cooperative
4. In cooperative Society every members have equal rights and votes. True/False
5. The main purpose of cooperative society is to (a)buy goods for everybody (b) provide essentials services at cheaper rate (c) sell goods and services to members at a cheap rate
LESSON 12
Limited Liability Company (Public Limited Liability Company)
Limited Liability Company:
A Limited Liability Company is a company in which the responsibility or liability of members for debts of the company is limited to the capital they have contributed or agreed to contribute. The private property of members are excluded, and all that members lose if the company fails is the money they have contributed. It is formed and registered under the law known as the Company Act. When a company is formed and registered with the Registrar of Companies, it is said to be incorporated.
There are two types of Limited Liability Company namely, Private and Public Companies.
Public Limited Liability Company:
A Public Limited Liability Company is a business unit that carries on business to make profit
for its owners. Examples are Nigerian bottling company Ltd., Total Nigeria Limited, First Bank of
Nigeria Plc. It is owned by Shareholders and managed and control by Board of management.
https://www.slideshare.net/ry_moore/lim ... o-29828149
Advantages of Public Limited Liability Company
1. It can raise money from the public through issuing of shares and debentures. This
enhances the company expansion.
2. It is a legal entity because it can sue and can be sued.
3. The company’s properties are different from that of its owners.
4. It enjoys continuity because it has perpetual life. The company can only be wounded voluntarily or on the order of a law court.
5. Share holders cannot lose more than the value of their shares. This is because the company enjoys limited liability.

Disadvantages of Public Limited Liability Company:
1. Shareholders have little say in the running of the company
2. It does not enjoy privacy. It annual account must be published in the Newspaper for the public to see.
3. It suffers from double taxation. The net profit of the company is taxed and the dividends of the shareholders are also taxed.

Limited Liability Company (Private Limited Liability Company)
CONTENT
1. Private Limited Liability Company (Meaning)
2. Advantages, Disadvantages and Comparison between Public and Private companies
Meaning of Private Limited Liability Company:
A private limited liability company is a profitable making business with few shareholders and no open market for its shares. Examples of private limited liability company are Newswatch Communication Ltd., Ekene Dili Chukwu Transport service Ltd., JIMBAZ Construction Company Ltd. etc.
Advantages of Private Limited Liability Company
(i) They enjoy privacy.
(ii) Their annual report and accounts are not required by law to be published, except for
Taxation.
(iii) Management and control is less complex than in public limited company. Its
management structure is simple.

Disadvantages of Private Limited Liability Company
(i) Shares cannot be issued to the public.
(ii) Capacity to raise external finance to expand business is limited.
(iii) Transfer of shares to others is made difficult.

1. Comparison between the Private and Public Limited Liability Companies.
S/N PUBLIC LIMITED COMPANY -------------------------PRIVATE LIMITED COMPANY
1. Minimum number of members is seven and has no maximum------------ Minimum number of members is two while the maximum is fifty.
2. Shares are offered to the public. -----------------------Shares may not be offered to the public.
3. Shares are easily transferable.------------------ Shares are not transferable.
4. Account is publish to the public----------------------- Account is publish for the information of Registrar of companies.
https://www.slideshare.net/krishnakhata ... ed-company
EVALUATION
1. What is a limited liability company?
2. State 3 advantages of public limited liability company
READING ASSIGNMENT
Business studies for junior secondary schools, new edition book 1 by O. A. Lawal Chapter 5 pages 23-25
1. Define Private Limited Liability Company
2. State the comparison between the public and private companies.
3. Outline the 4 advantages and the 4 disadvantages of Private companies.
ASSIGNMENT
1. The maximum number of members in a private limited liability company (a) 50 (b) 100 (c) 10
2. Private liability company enjoys. (a ) enough capital (b) privacy (c) non-Payment of tax (d) transfer of shares to others.
3. The following are disadvantages of private limited liability company except (a) not listed in the stock exchange (b) cannot sell shares (c) management structure is simple.
4. The minimum number of owners needed to form a public limited company
Is (a) seven ( b)two (c) fifty (d) eight
5. Which of this can sell shares to the public (a) Sole proprietor (b) Private
Limited company (c) Public limited company
6. The maximum number of owners a public Limited liability company is (a) twenty (b) two (c) no maximum.
7. Public Limited Liability Company is owned by ------------------ (a) government (b) politicians (c) Shareholders
8. The major source of capital for Public Limited Liability Company is
(a) selling of shares (b) personal savings (c) partnership contribution
THEORY
1. State 3 advantages of private limited liability company
2. Enumerate 3 disadvantages of private limited liability company
WEEK 5
LESSON 13
MAIN TOPIC: Mail Handling
SPECIFIC TOPIC: Meaning and procedure for handling mails.
REFERENCE BOOKS:
Macmillan JSS2 Business Studies by Awoyokun A.A et al .Pages 6-10
WABP JSS Business Studies 2by Egbe T. Ehiametalor. Pages 9-15
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVES: At the end of the lesson, students should be able to:
state the meaning of mail
State the procedures for handling the following types of mails:
Business letters
Private letters
Confidential letters
CONTENTS:
Every organisation receives and sends out letters.
Mails(letters) that come into the organisation are called incoming mails while those that are sent out of the organisation are called out-going mails.
Any mail that comes into an organisation whether by hand or by post is usually sorted out into three main categories and they are:
Business letters
Private letters
Confidential letters
Envelopes which contain business letters are opened and the letters passed on to the officer who will take the necessary action while envelopes which contain private and confidential letters are usually unopened and are passed intact to the persons concerned.

EVALUATION:
What do you understand by mail?
How should the following letters be handled?
Business letters
Private letters
Confidential letters
HOME-WORK: What are correspondence records?
LESSON 14
MAIN TOPIC: Mail Handling
SPECIFIC TOPIC: Correspondence records
REFERENCE BOOKS:
Macmillan JSS1 Business Studies by Awoyokun A.A et al .Pages 6-10
WABP JSS Business Studies 1 by Egbe T. Ehiametalor. Pages 9-15
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVES: At the end of the lesson, students should be able to:
state the meaning of correspondence records
list the different correspondence records used in organisation
mention the uses of the various correspondence records.
CONTENTS:
Correspondence records are books which record mails which come into an organisation and mails which go out of the organisation.
TYPES OF CORRESPONDENCE RECORDS
MAIL INWARDS BOOK: This is used to record all mails coming into an organisation
MAIL OUTWARDS BOOK: This is used for recording letters that are prepared for postage by an organisation.
POSTAGE BOOK: This is also used to record letters going out the organisation and that will be posted . It serves as a check on the amount spent on postage stamp and the number of letters dispatched in each day.
DESPATCH BOOK: This is used to record letters that are delivered by hand.

EVALUATION:
What are correspondence records?
Mention four correspondence records.
What is the purpose of a dispatch book.
HOME-WORK: mention five mail room equipment.
LESSON 15
MAIN TOPIC: Mail Handling
SPECIFIC TOPIC: Mail room equipment
REFERENCE BOOKS:
Macmillan JSS1 Business Studies by Awoyokun A.A et al .Pages 6-10
WABP JSS Business Studies 1 by Egbe T. Ehiametalor. Pages 9-15
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVES: At the end of the lesson, students should be able to:
state the meaning of mail room equipment
list equipment used in mail room
mention the uses of equipment used in the mail room
CONTENTS:
Mail room equipment are equipment used in the mail room to allow smooth running of the job.
Examples of such equipment are mail bag, fax machine, mail opening machine etc.

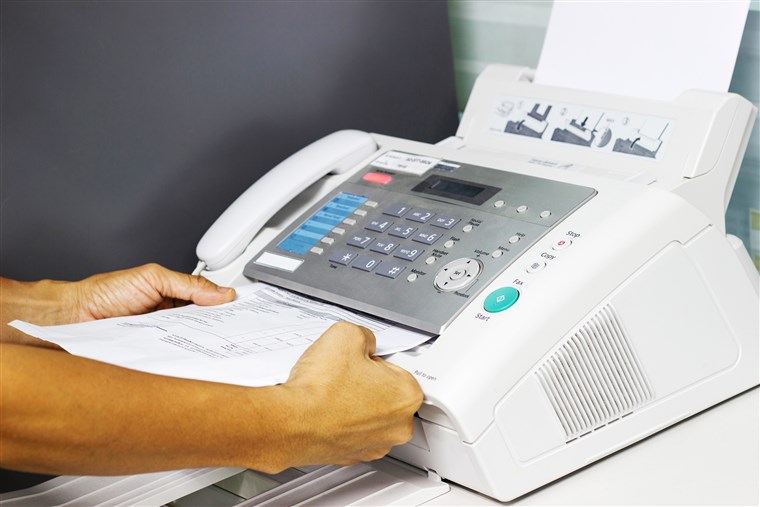
FAX MACHINE: This is a device used in passing information through electronic means to another person.
The receiver must have a fax machine to be able to print the message.

MACHINE SCALE: This is a device used to measure the weight of the mail to be sent.

LETTER OPENING MACHINE: This equipment is used to open large number of letters. It is used in such a way that the contents of the letter are not destroyed.

FRANKING MACHINE: This is a printing machine that has meter fitted to it. The machine prints the amount of postage on an envelope. It is also called postage meter.

STAMP AFFIXING MACHINE: This is a machine used to affix stamps on letters. It is usually used in an office with very large outgoing mails.
The stamps are bought and put in the machine. It is a faster and neater way of fixing stamps on an envelope.

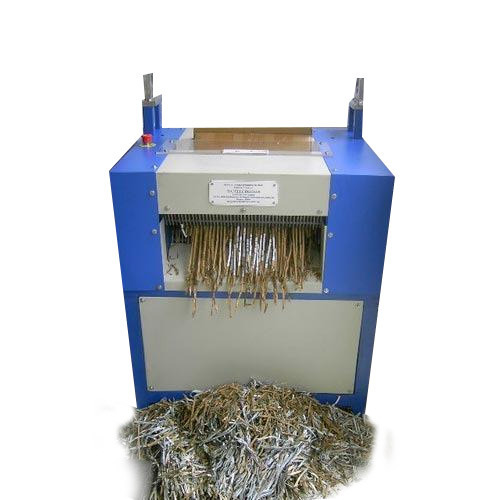
SHREDDING MACHINE: This machine is used to destroy documents that are no longer needed or confidential mails that have been treated. This machine shreds them into pieces.

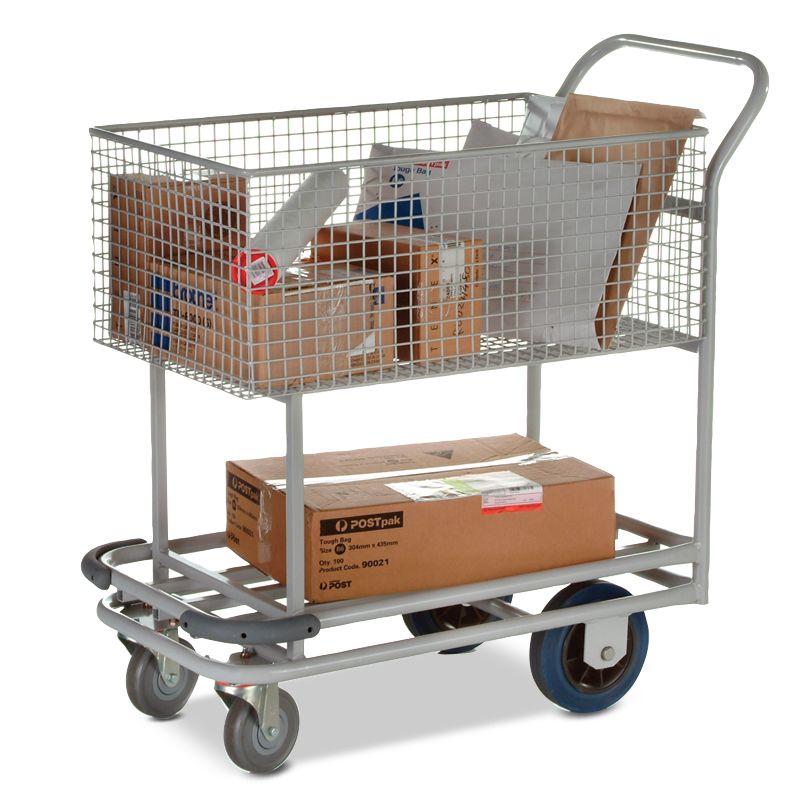
TROLLEY AND BASKETS: These are used for keeping and distributing mails and also for keeping unclaimed mails.

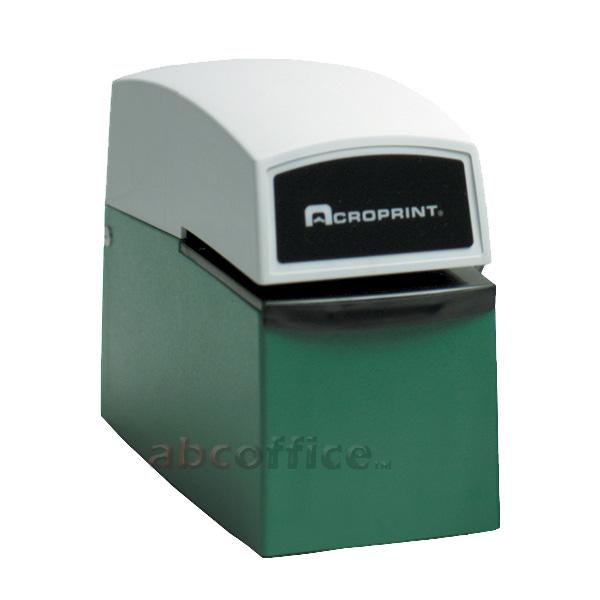
DATE STAMPING MACHINE: This is a tool used to stamp date and time of arrival of letters on an envelope

GUILLOTINE MACHINE: This is a sharp edged tool with a long blade for cutting or trimming paper into any required size and shape.
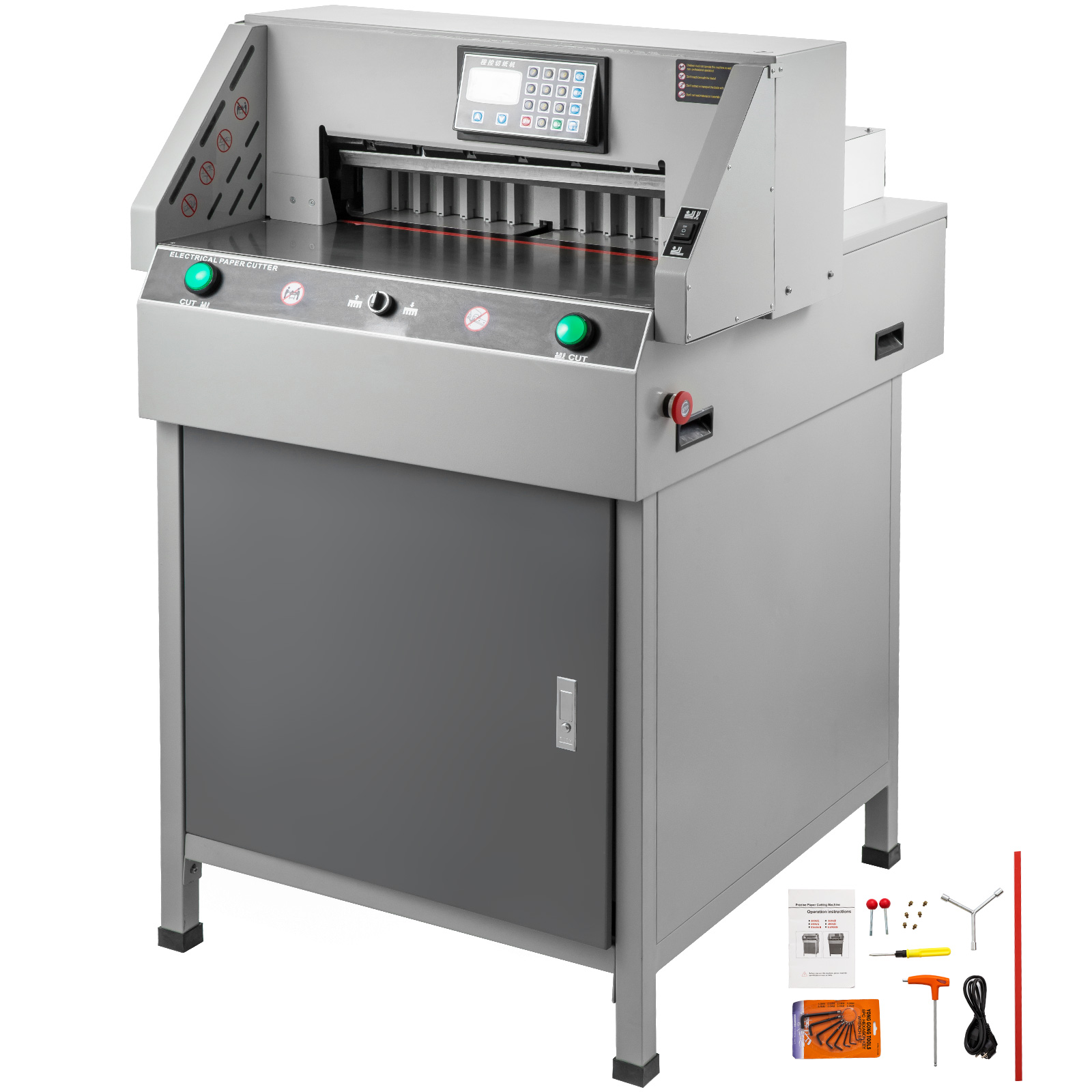

EVALUATION:
What are mail room equipment?
Mention five mail room equipment
What are the uses of the mailroom equipment that you mentioned.
HOME-WORK: Who is a sole proprietor.
LESSON 16
MAIN TOPIC: Filing
SPECIFIC TOPIC: Meaning and filing systems
REFERENCE BOOKS:
Macmillan JSS2 Business Studies by Awoyokun A.A et al .Pages 7
WABP JSS Business Studies 2 by Egbe T. Ehiametalor. Page 13-14
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVES: At the end of the lesson, students should be able to:
define filing
mention reasons for filing
list the two filing systems
CONTENTS:
Filing is the systematic storing of letters and other types of documents.
Filing is important for two main reasons:
preservation of correspondence and other documents
availability of information for ease of reference.


FILING SYSTEMS
Filing systems vary and the type of system adapted depends on how large the organisation is.
A filing system can be:
CENTRALISED FILING: This means that all the files are kept and controlled together in one room under the care of one or more clerks.
DEPARTMENTAL FILING: This simply means that each department does its own filing rather than using a centralised system.
CHARACTERISTICS OF AN EFFICIENT FILING SYSTEM
An efficient filing system must be:
simple to understand and operate even by those who are not formally trained in filing
must not occupy too much space
must be accessible
must guarantee security of documents and letters
https://www.slideshare.net/PhilJohannCo ... ing-system
FILING CLASSIFICATION METHODS
Electronic filing method
Alphabetical filing method
Numerical filing method
Geographical filing method
Chronological filing method
subject filing method
https://drive.google.com/file/d/1uIwsFq ... sp=sharing
EVALUATION:
MAIN TOPIC: Mail Handling
SPECIFIC TOPIC: Meaning and procedure for handling mails.
REFERENCE BOOKS:
Macmillan JSS2 Business Studies by Awoyokun A.A et al .Pages 6-10
WABP JSS Business Studies 2by Egbe T. Ehiametalor. Pages 9-15
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVES: At the end of the lesson, students should be able to:
state the meaning of mail
State the procedures for handling the following types of mails:
Business letters
Private letters
Confidential letters
CONTENTS:
Every organisation receives and sends out letters.
Mails(letters) that come into the organisation are called incoming mails while those that are sent out of the organisation are called out-going mails.
Any mail that comes into an organisation whether by hand or by post is usually sorted out into three main categories and they are:
Business letters
Private letters
Confidential letters
Envelopes which contain business letters are opened and the letters passed on to the officer who will take the necessary action while envelopes which contain private and confidential letters are usually unopened and are passed intact to the persons concerned.

EVALUATION:
What do you understand by mail?
How should the following letters be handled?
Business letters
Private letters
Confidential letters
HOME-WORK: What are correspondence records?
LESSON 14
MAIN TOPIC: Mail Handling
SPECIFIC TOPIC: Correspondence records
REFERENCE BOOKS:
Macmillan JSS1 Business Studies by Awoyokun A.A et al .Pages 6-10
WABP JSS Business Studies 1 by Egbe T. Ehiametalor. Pages 9-15
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVES: At the end of the lesson, students should be able to:
state the meaning of correspondence records
list the different correspondence records used in organisation
mention the uses of the various correspondence records.
CONTENTS:
Correspondence records are books which record mails which come into an organisation and mails which go out of the organisation.
TYPES OF CORRESPONDENCE RECORDS
MAIL INWARDS BOOK: This is used to record all mails coming into an organisation
MAIL OUTWARDS BOOK: This is used for recording letters that are prepared for postage by an organisation.
POSTAGE BOOK: This is also used to record letters going out the organisation and that will be posted . It serves as a check on the amount spent on postage stamp and the number of letters dispatched in each day.

DESPATCH BOOK: This is used to record letters that are delivered by hand.

EVALUATION:
What are correspondence records?
Mention four correspondence records.
What is the purpose of a dispatch book.
HOME-WORK: mention five mail room equipment.
LESSON 15
MAIN TOPIC: Mail Handling
SPECIFIC TOPIC: Mail room equipment
REFERENCE BOOKS:
Macmillan JSS1 Business Studies by Awoyokun A.A et al .Pages 6-10
WABP JSS Business Studies 1 by Egbe T. Ehiametalor. Pages 9-15
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVES: At the end of the lesson, students should be able to:
state the meaning of mail room equipment
list equipment used in mail room
mention the uses of equipment used in the mail room
CONTENTS:
Mail room equipment are equipment used in the mail room to allow smooth running of the job.
Examples of such equipment are mail bag, fax machine, mail opening machine etc.

FAX MACHINE: This is a device used in passing information through electronic means to another person.
The receiver must have a fax machine to be able to print the message.

MACHINE SCALE: This is a device used to measure the weight of the mail to be sent.

LETTER OPENING MACHINE: This equipment is used to open large number of letters. It is used in such a way that the contents of the letter are not destroyed.

FRANKING MACHINE: This is a printing machine that has meter fitted to it. The machine prints the amount of postage on an envelope. It is also called postage meter.

STAMP AFFIXING MACHINE: This is a machine used to affix stamps on letters. It is usually used in an office with very large outgoing mails.
The stamps are bought and put in the machine. It is a faster and neater way of fixing stamps on an envelope.

SHREDDING MACHINE: This machine is used to destroy documents that are no longer needed or confidential mails that have been treated. This machine shreds them into pieces.

TROLLEY AND BASKETS: These are used for keeping and distributing mails and also for keeping unclaimed mails.

DATE STAMPING MACHINE: This is a tool used to stamp date and time of arrival of letters on an envelope

GUILLOTINE MACHINE: This is a sharp edged tool with a long blade for cutting or trimming paper into any required size and shape.

EVALUATION:
What are mail room equipment?
Mention five mail room equipment
What are the uses of the mailroom equipment that you mentioned.
HOME-WORK: Who is a sole proprietor.
LESSON 16
MAIN TOPIC: Filing
SPECIFIC TOPIC: Meaning and filing systems
REFERENCE BOOKS:
Macmillan JSS2 Business Studies by Awoyokun A.A et al .Pages 7
WABP JSS Business Studies 2 by Egbe T. Ehiametalor. Page 13-14
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVES: At the end of the lesson, students should be able to:
define filing
mention reasons for filing
list the two filing systems
CONTENTS:
Filing is the systematic storing of letters and other types of documents.
Filing is important for two main reasons:
preservation of correspondence and other documents
availability of information for ease of reference.


FILING SYSTEMS
Filing systems vary and the type of system adapted depends on how large the organisation is.
A filing system can be:
CENTRALISED FILING: This means that all the files are kept and controlled together in one room under the care of one or more clerks.
DEPARTMENTAL FILING: This simply means that each department does its own filing rather than using a centralised system.
CHARACTERISTICS OF AN EFFICIENT FILING SYSTEM
An efficient filing system must be:
simple to understand and operate even by those who are not formally trained in filing
must not occupy too much space
must be accessible
must guarantee security of documents and letters
https://www.slideshare.net/PhilJohannCo ... ing-system
FILING CLASSIFICATION METHODS
Electronic filing method
Alphabetical filing method
Numerical filing method
Geographical filing method
Chronological filing method
subject filing method
https://drive.google.com/file/d/1uIwsFq ... sp=sharing
EVALUATION:
- What is filing
- What are the importance of filing
- Mention and explain the two filing system that you know.
- Mention five characteristics of an efficient filing system.
- Mention three characteristics of an efficient filing system
- Mention three filing classification methods.
- Explain the following filing methods:
Electronic filing method
Alphabetical filing method
Numerical filing method - What is the minimum number that can start a public limited liability company?
WEEK 6
LESSON 17
MAIN TOPIC: OWNERSHIP OF BUSINESS
SPECIFIC TOPIC: Sole proprietorship
REFERENCE BOOKS:
Macmillan JSS2 Business Studies by Awoyokun A.A et al .Pages 44-45
WABP JSS Business Studies 2 by Egbe T. Ehiametalor. Pages 39-40
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVES: At the end of the lesson, students should be able to:
Identify the various forms of business ownership
define a sole proprietorship business
mention the basic features of a sole proprietorship business.
CONTENTS: OWNERSHIP OF BUSINESS
SOLE PROPRIETORSHIP
Shoemaker

Kiosk owner

Supermarket

Consultancy

CO-OPERATIVE
Thrift society

Consumer Co-op.

https://www.slideshare.net/shruthyajith ... -societies
PARTNERSHIP
Manufacturing

Farming

LIMITED LIABILITY COMPANY
Private ----- Public
WABP ltd ----- Cadbury plc
HEMMA ltd ----- Unilever Plc


Sole proprietorship is defined as a business organisation established, owned, financed and controlled by one person with the aim of making profit.
EVALUATION: mention the various forms of business ownership that exist
What is sole proprietorship business?
What are the features of a sole proprietorship business?
HOME-WORK: What are the sources of capital for a sole proprietorship business?
LESSON 18
MAIN TOPIC: SOLE PROPRIETORSHIP
SPECIFIC TOPIC: Sources of capital
REFERENCE BOOKS:
Macmillan JSS1 Business Studies by Awoyokun A.A et al .Pages 44-45
WABP JSS Business Studies 1 by Egbe T. Ehiametalor. Pages 39-40
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVES: At the end of the lesson, students should be able to:
Mention the sources of capital for a one-man business.
CONTENTS:
SOURCES OF CAPITAL FOR ONE_MAN BUSINESS
Money from his personal savings
Loan from relations or friends
Loans from banks
Credit facilities from wholesalers or other distributors
ADVANTAGES
A small amount of capital is needed to commence the business
The owner enjoys privacy
The owner can give personal attention to the business
The owner enjoys al all the profit at the end of the business year.
Complete control: A sole proprietor has complete control and decision-making power over the business. He or she doesn’t need to check with a board of directors or shareholders before making a pricey purchase or sealing a big deal.
Time is on your side: Because there are fewer legal restrictions on this form of business, sole proprietorships can get started quickly. Plus, a sole proprietor can own the business for any length of time and sell it whenever and for whatever price he or she wants. As owner, a sole proprietor can even pass a business down to his or her heirs.
Taxes: In a sole proprietorship, the company does not pay business taxes. Instead, the owner pays taxes on income from the business as part of his or her personal income tax payments.
Less paperwork: Although sole proprietors do need to comply with licensing requirements in the states in which they’re doing business, as well as local regulations and zoning ordinances, the paperwork and other formalities are substantially less than those that affect corporations.
Lower cost: There are minimal legal costs involved in forming a sole proprietorship and fewer government filing fees.
DISADVANTAGES
A sole trader runs his business with little capital
The death of the owner may lead to the end of the business
If the business fails, he bears all the losses
He may have to work for long hours in other to survive.
Personal liability: Without the protection of a corporation or LLC structure, a sole proprietor of a business can be held personally liable for the debts and obligations of the business. Additionally, this risk extends to any liabilities incurred as a result of acts committed by employees of the company. Even if the business files all the applicable forms under the fictitious name or under doing business as (DBA), it does not mean that the business is a separate entity from a legal standpoint.
Decisions-Making: All responsibilities and business decisions fall on the shoulders of the sole proprietor. Sometimes it’s hard to trust your instincts when your whole business is on the line. Sole proprietors usually find solace in joining networking groups or working with a mentor so they can get some feedback and guidance.
Attracting investors: Because sole proprietorships are seen as a riskier investment, it may be harder to convince venture capitalists and other investors (or even bankers) to take a chance on your business.
EVALUATION:
Mention five sources of capital available to a one-man business.
HOME-WORK:
MAIN TOPIC: OWNERSHIP OF BUSINESS
SPECIFIC TOPIC: Sole proprietorship
REFERENCE BOOKS:
Macmillan JSS2 Business Studies by Awoyokun A.A et al .Pages 44-45
WABP JSS Business Studies 2 by Egbe T. Ehiametalor. Pages 39-40
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVES: At the end of the lesson, students should be able to:
Identify the various forms of business ownership
define a sole proprietorship business
mention the basic features of a sole proprietorship business.
CONTENTS: OWNERSHIP OF BUSINESS
SOLE PROPRIETORSHIP
Shoemaker

Kiosk owner

Supermarket

Consultancy

CO-OPERATIVE
Thrift society

Consumer Co-op.

https://www.slideshare.net/shruthyajith ... -societies
PARTNERSHIP
Manufacturing

Farming

LIMITED LIABILITY COMPANY
Private ----- Public
WABP ltd ----- Cadbury plc
HEMMA ltd ----- Unilever Plc


Sole proprietorship is defined as a business organisation established, owned, financed and controlled by one person with the aim of making profit.
EVALUATION: mention the various forms of business ownership that exist
What is sole proprietorship business?
What are the features of a sole proprietorship business?
HOME-WORK: What are the sources of capital for a sole proprietorship business?
LESSON 18
MAIN TOPIC: SOLE PROPRIETORSHIP
SPECIFIC TOPIC: Sources of capital
REFERENCE BOOKS:
Macmillan JSS1 Business Studies by Awoyokun A.A et al .Pages 44-45
WABP JSS Business Studies 1 by Egbe T. Ehiametalor. Pages 39-40
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVES: At the end of the lesson, students should be able to:
Mention the sources of capital for a one-man business.
CONTENTS:
SOURCES OF CAPITAL FOR ONE_MAN BUSINESS
Money from his personal savings
Loan from relations or friends
Loans from banks
Credit facilities from wholesalers or other distributors
ADVANTAGES
A small amount of capital is needed to commence the business
The owner enjoys privacy
The owner can give personal attention to the business
The owner enjoys al all the profit at the end of the business year.
Complete control: A sole proprietor has complete control and decision-making power over the business. He or she doesn’t need to check with a board of directors or shareholders before making a pricey purchase or sealing a big deal.
Time is on your side: Because there are fewer legal restrictions on this form of business, sole proprietorships can get started quickly. Plus, a sole proprietor can own the business for any length of time and sell it whenever and for whatever price he or she wants. As owner, a sole proprietor can even pass a business down to his or her heirs.
Taxes: In a sole proprietorship, the company does not pay business taxes. Instead, the owner pays taxes on income from the business as part of his or her personal income tax payments.
Less paperwork: Although sole proprietors do need to comply with licensing requirements in the states in which they’re doing business, as well as local regulations and zoning ordinances, the paperwork and other formalities are substantially less than those that affect corporations.
Lower cost: There are minimal legal costs involved in forming a sole proprietorship and fewer government filing fees.
DISADVANTAGES
A sole trader runs his business with little capital
The death of the owner may lead to the end of the business
If the business fails, he bears all the losses
He may have to work for long hours in other to survive.
Personal liability: Without the protection of a corporation or LLC structure, a sole proprietor of a business can be held personally liable for the debts and obligations of the business. Additionally, this risk extends to any liabilities incurred as a result of acts committed by employees of the company. Even if the business files all the applicable forms under the fictitious name or under doing business as (DBA), it does not mean that the business is a separate entity from a legal standpoint.
Decisions-Making: All responsibilities and business decisions fall on the shoulders of the sole proprietor. Sometimes it’s hard to trust your instincts when your whole business is on the line. Sole proprietors usually find solace in joining networking groups or working with a mentor so they can get some feedback and guidance.
Attracting investors: Because sole proprietorships are seen as a riskier investment, it may be harder to convince venture capitalists and other investors (or even bankers) to take a chance on your business.
EVALUATION:
Mention five sources of capital available to a one-man business.
HOME-WORK:
- Mention three advantages and two disadvantages of sole proprietorship.
- Mention three advantages of one-man business
- Mention three disadvantages of one-man business
- What is a partnership business?
WEEK 7
LESSON 19
MAIN TOPIC: Partnership business
SPECIFIC TOPIC: Meaning and Formation
REFERENCE BOOKS:
Macmillan JSS1 Business Studies by Awoyokun A.A et al .Pages 45-47
WABP JSS Business Studies 1by Egbe T. Ehiametalor. Page 41
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVES: At the end of the lesson, students should be able to:
define a partnership business
mention the number of people that can form a partnership business
mention types of partnership
mention sources of capital for a partnership business
CONTENTS:
Partnership business can be defined as what exists when two or more persons contribute their skills, money or money's worth in order to establish, own and manage a business organization.
Partnership business is formed between two and twenty people.
Profit and loss are shared equally among the partners unless there is a contrary agreement in the partnership deed.

TYPES OF PARTNERS
Ordinary partnership
Limited partnership
Sleeping partners
SOURCES OF CAPITAL
Members individual contribution
Loans and overdraft from the bank
Loans from known private individuals
Credit purchases from companies or individuals
EVALUATION:
Define partnership business
How many people can form a partnership business
What are the sources of capital available to partnership business
Discuss the different types of partners.
HOME-WORK: Mention three advantages of partnership business.
https://www.slideshare.net/MRshakin/par ... p-43053101
LESSON 20
MAIN TOPIC: Partnership
SPECIFIC TOPIC: Advantages and disadvantages of Partnership business
REFERENCE BOOKS:
Macmillan JSS1 Business Studies by Awoyokun A.A et al .Pages 45-47
WABP JSS Business Studies 1by Egbe T. Ehiametalor. Page 41
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVES: At the end of the lesson, students should be able to:
mention advantages of partnership business
mention the disadvantages of partnership business
CONTENTS:
ADVANTAGES OF PARTNERSHIP
There is more capital available for partnership business than for one-man business
The individual member's talents and ideas will make for better management of the business.
Partnership allows for division of labour and specialization
The risks of the business are shared by the partners.
DISADVANTAGES OF PARTNERSHIP
The liability of individual member is unlimited, that is, each member may have to sell his personal property to pay the debt of the business.
Disagreement or quarrel among the partners may lead to the end of the partnership.
Death or withdrawal of a partner may lead to the end of the partnership.
PARTNERSHIP DEED
Partnership deed is a legal document that contains the agreement of the partners.
It contains the following information:
The nature, type and location of the business
The contribution of each partner
How to admit new partners
How to share profit and losses of the business
The duties of each partner
DISSOLUTION OF PARTNERSHIP
The following are the conditions for the dissolution of partnership business:
When any of the partners request for its dissolution
When the time fixed in the partnership deed expires
When there is a disagreement or quarrel among members
EVALUATION:
mention four advantages of partnership business
mention four disadvantages of partnership business
what is a partnership deed
what are the contents of a partnership deed
mention five conditions under which a partnership business can be dissolved.
HOME-WORK:
What is partnership deed.
what are public corporations
https://www.slideshare.net/MRshakin/par ... p-43053101
MAIN TOPIC: Partnership business
SPECIFIC TOPIC: Meaning and Formation
REFERENCE BOOKS:
Macmillan JSS1 Business Studies by Awoyokun A.A et al .Pages 45-47
WABP JSS Business Studies 1by Egbe T. Ehiametalor. Page 41
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVES: At the end of the lesson, students should be able to:
define a partnership business
mention the number of people that can form a partnership business
mention types of partnership
mention sources of capital for a partnership business
CONTENTS:
Partnership business can be defined as what exists when two or more persons contribute their skills, money or money's worth in order to establish, own and manage a business organization.
Partnership business is formed between two and twenty people.
Profit and loss are shared equally among the partners unless there is a contrary agreement in the partnership deed.

TYPES OF PARTNERS
Ordinary partnership
Limited partnership
Sleeping partners
SOURCES OF CAPITAL
Members individual contribution
Loans and overdraft from the bank
Loans from known private individuals
Credit purchases from companies or individuals
EVALUATION:
Define partnership business
How many people can form a partnership business
What are the sources of capital available to partnership business
Discuss the different types of partners.
HOME-WORK: Mention three advantages of partnership business.
https://www.slideshare.net/MRshakin/par ... p-43053101
LESSON 20
MAIN TOPIC: Partnership
SPECIFIC TOPIC: Advantages and disadvantages of Partnership business
REFERENCE BOOKS:
Macmillan JSS1 Business Studies by Awoyokun A.A et al .Pages 45-47
WABP JSS Business Studies 1by Egbe T. Ehiametalor. Page 41
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVES: At the end of the lesson, students should be able to:
mention advantages of partnership business
mention the disadvantages of partnership business
CONTENTS:
ADVANTAGES OF PARTNERSHIP
There is more capital available for partnership business than for one-man business
The individual member's talents and ideas will make for better management of the business.
Partnership allows for division of labour and specialization
The risks of the business are shared by the partners.
DISADVANTAGES OF PARTNERSHIP
The liability of individual member is unlimited, that is, each member may have to sell his personal property to pay the debt of the business.
Disagreement or quarrel among the partners may lead to the end of the partnership.
Death or withdrawal of a partner may lead to the end of the partnership.
PARTNERSHIP DEED
Partnership deed is a legal document that contains the agreement of the partners.
It contains the following information:
The nature, type and location of the business
The contribution of each partner
How to admit new partners
How to share profit and losses of the business
The duties of each partner
DISSOLUTION OF PARTNERSHIP
The following are the conditions for the dissolution of partnership business:
When any of the partners request for its dissolution
When the time fixed in the partnership deed expires
When there is a disagreement or quarrel among members
EVALUATION:
mention four advantages of partnership business
mention four disadvantages of partnership business
what is a partnership deed
what are the contents of a partnership deed
mention five conditions under which a partnership business can be dissolved.
HOME-WORK:
What is partnership deed.
what are public corporations
https://www.slideshare.net/MRshakin/par ... p-43053101
WEEK 8
LESSON 21
MAIN TOPIC: Public Corporation
SPECIFIC TOPIC: Meaning and Formation
REFERENCE BOOKS:
Macmillan JSS1 Business Studies by Awoyokun A.A et al .Pages 51-52
WABP JSS Business Studies 1by Egbe T. Ehiametalor. Page 44-45
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVES: At the end of the lesson, students should be able to:
define public enterprise
mention the aim of public enterprise
mention examples of public corporations
CONTENTS:
Public Corporations/ enterprises are business organisation set up and financed by the government not necessarily to make profit but to provide essential services to the people.
They may be set up by the Federal, State or local government.
Examples are Nigeria Railway Corporation, Water corporations, Public schools and Government hospitals etc.


SOURCES OF CAPITAL
Government grant from tax payers money
loans and overdrafts from banks
credit facilities from their suppliers
grants or loans from foreign organizations e.g. world bank, UNICEF.
REASONS FOR GOVERNMENT PARTICIPATION IN BUSINESS ENTERPRISES.
To provide essential services which due to heavy cost of establishment an individual or a business organisation might be unable to provide e.g. the construction of roads.
To ensure fair and even distribution of essential services to all citizens irrespective of their religion or political beliefs.
To facilitate and quicken the pace of economic development
To prevent the emergence of private monopoly which will be detrimental to the interest of the citizens.
Advantages of public corporation
Public corporations provide essential services efficiently without profit motive
Capital is made available to corporations by the government at little or no interest rate
They are a means of controlling monopoly.
By providing essential services at low prices they tend to raise the standard of living of the people.
Disadvantages of public corporation
Public corporations are inefficient due to lack of competition
Public enterprises are in some cases a breeding place for fraud, corruption, nepotism etc.
The management of public corporation is usually inexperienced and inefficient because of the civil service system of management usually adopted.
EVALUATION:
What is public corporation?
Give five examples of public corporation
what is the main aim of public corporation
HOME-WORK:
Mention three reasons for government participation in business enterprise.
Mention four sources of capital for public enterprises.
Mention three reasons why government participate in public enterprises
Mention three advantages of public enterprise
Mention five advantages of public enterprises
Mention five disadvantages of public enterprises
MAIN TOPIC: Public Corporation
SPECIFIC TOPIC: Meaning and Formation
REFERENCE BOOKS:
Macmillan JSS1 Business Studies by Awoyokun A.A et al .Pages 51-52
WABP JSS Business Studies 1by Egbe T. Ehiametalor. Page 44-45
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVES: At the end of the lesson, students should be able to:
define public enterprise
mention the aim of public enterprise
mention examples of public corporations
CONTENTS:
Public Corporations/ enterprises are business organisation set up and financed by the government not necessarily to make profit but to provide essential services to the people.
They may be set up by the Federal, State or local government.
Examples are Nigeria Railway Corporation, Water corporations, Public schools and Government hospitals etc.


SOURCES OF CAPITAL
Government grant from tax payers money
loans and overdrafts from banks
credit facilities from their suppliers
grants or loans from foreign organizations e.g. world bank, UNICEF.
REASONS FOR GOVERNMENT PARTICIPATION IN BUSINESS ENTERPRISES.
To provide essential services which due to heavy cost of establishment an individual or a business organisation might be unable to provide e.g. the construction of roads.
To ensure fair and even distribution of essential services to all citizens irrespective of their religion or political beliefs.
To facilitate and quicken the pace of economic development
To prevent the emergence of private monopoly which will be detrimental to the interest of the citizens.
Advantages of public corporation
Public corporations provide essential services efficiently without profit motive
Capital is made available to corporations by the government at little or no interest rate
They are a means of controlling monopoly.
By providing essential services at low prices they tend to raise the standard of living of the people.
Disadvantages of public corporation
Public corporations are inefficient due to lack of competition
Public enterprises are in some cases a breeding place for fraud, corruption, nepotism etc.
The management of public corporation is usually inexperienced and inefficient because of the civil service system of management usually adopted.
EVALUATION:
What is public corporation?
Give five examples of public corporation
what is the main aim of public corporation
HOME-WORK:
Mention three reasons for government participation in business enterprise.
Mention four sources of capital for public enterprises.
Mention three reasons why government participate in public enterprises
Mention three advantages of public enterprise
Mention five advantages of public enterprises
Mention five disadvantages of public enterprises
WEEK 9
LESSON 22
MAIN TOPIC: Co-operative Society
SPECIFIC TOPIC: Meaning and types
REFERENCE BOOKS:
Macmillan JSS1 Business Studies by Awoyokun A.A et al .Pages 50
WABP JSS Business Studies 1by Egbe T. Ehiametalor. Page 41-43
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVES: At the end of the lesson, students should be able to:
define Co-operative society
mention types of co-operative society
CONTENTS:
A co-operative society is a type of business organisation formed by people who have common interests in owning and running a business for the benefit of its owners.
It can also be defined as an association of individuals with common interests who agree to come together to promote the welfare of members.
The aim of the business is not to make profit for itself but for members.

TYPES OF CO-OPERATIVE SOCIETY
Producer co-operative society
Consumers co-operative society
Multi-purpose co-operative society
Credit and thrift co-operative society
CHARACTERISTICS OF CO-OPERATIVE SOCIETY
Membership of co-operative society is open to anybody who shares common interest with others.
A member can own only one share in the society.
Management of the society is by the elected members of the society.
Profits are shared on the basis of sales, purchases or loans taken by each member from the society.
watch video
http://www.slideshare.net/prabhat1111/c ... esentation
Advantages of co-operative society
The society encourages members to form saving habit
Co-operative society gives loan to members at very low interest rate.
There is democracy in the control and management of co-operative society
They provide and sell consumer goods to members at low prices.
Disadvantages of co-operative society
Co-operative societies do not always have adequate capital to run their business.
The members elected to manage the society may have little or no experience about managing a business.
Any misunderstanding between the members and the management committee may affect the smooth running of the business.
EVALUATION:
What is co-operative society
Mention three advantages of co-operative society
Mention four types of co-operative society
Mention five characteristics of co-operative society.
Mention five disadvantages of co-operative society
What are limited liability company
MAIN TOPIC: Co-operative Society
SPECIFIC TOPIC: Meaning and types
REFERENCE BOOKS:
Macmillan JSS1 Business Studies by Awoyokun A.A et al .Pages 50
WABP JSS Business Studies 1by Egbe T. Ehiametalor. Page 41-43
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVES: At the end of the lesson, students should be able to:
define Co-operative society
mention types of co-operative society
CONTENTS:
A co-operative society is a type of business organisation formed by people who have common interests in owning and running a business for the benefit of its owners.
It can also be defined as an association of individuals with common interests who agree to come together to promote the welfare of members.
The aim of the business is not to make profit for itself but for members.

TYPES OF CO-OPERATIVE SOCIETY
Producer co-operative society
Consumers co-operative society
Multi-purpose co-operative society
Credit and thrift co-operative society
CHARACTERISTICS OF CO-OPERATIVE SOCIETY
Membership of co-operative society is open to anybody who shares common interest with others.
A member can own only one share in the society.
Management of the society is by the elected members of the society.
Profits are shared on the basis of sales, purchases or loans taken by each member from the society.
watch video
http://www.slideshare.net/prabhat1111/c ... esentation
Advantages of co-operative society
The society encourages members to form saving habit
Co-operative society gives loan to members at very low interest rate.
There is democracy in the control and management of co-operative society
They provide and sell consumer goods to members at low prices.
Disadvantages of co-operative society
Co-operative societies do not always have adequate capital to run their business.
The members elected to manage the society may have little or no experience about managing a business.
Any misunderstanding between the members and the management committee may affect the smooth running of the business.
EVALUATION:
What is co-operative society
Mention three advantages of co-operative society
Mention four types of co-operative society
Mention five characteristics of co-operative society.
Mention five disadvantages of co-operative society
What are limited liability company